
original.jpg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2682901
Exploring the Fascinating World of Polytrichadelphus abriaquiae Moss
Introduction
Mosses are some of the most ancient and resilient plants on Earth. Among the thousands of moss species, one particularly interesting and lesser-known variety is Polytrichadelphus abriaquiae (Müll.Hal.) A.Jaeger
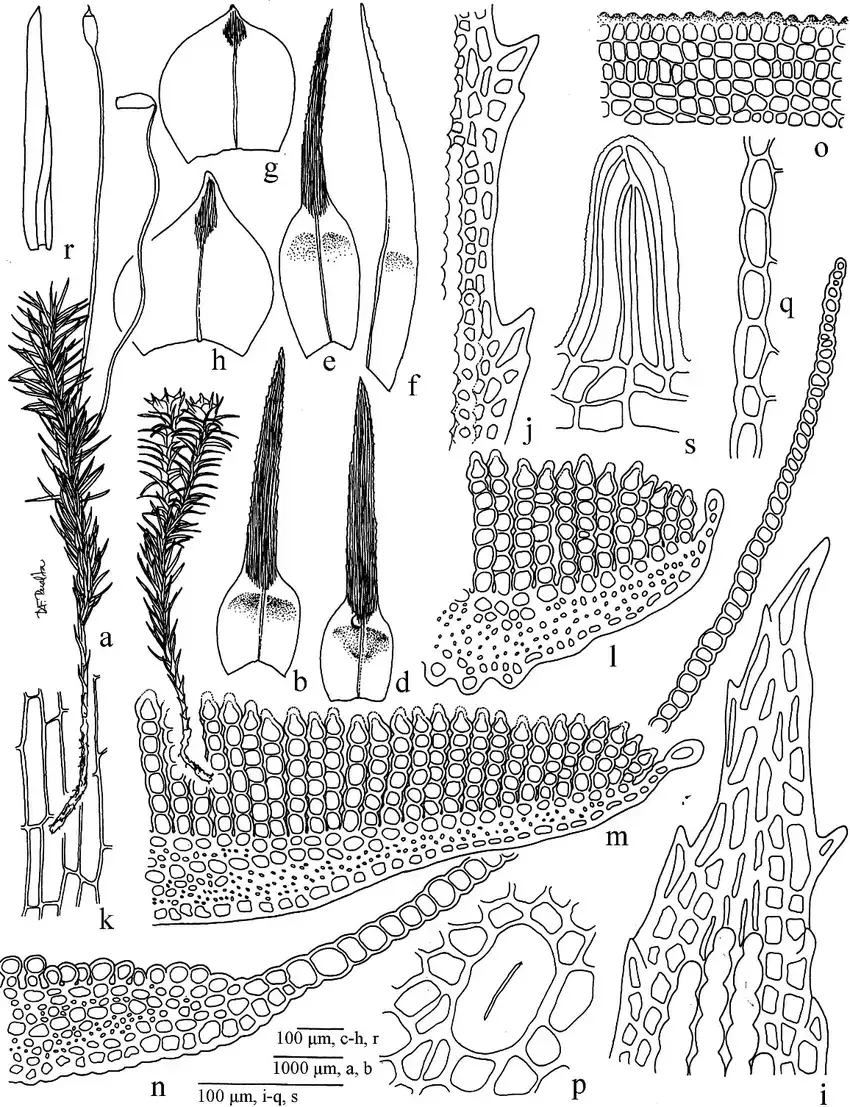

Polytrichadelphus-pseudopolytrichum-a-Female-gametophyte-b-Male-gametophyte-c-d.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Polytrichadelphus-pseudopolytrichum-a-Female-gametophyte-b-Male-gametophyte-c-d_fig10_232670414
, a member of the

5856d54f21c593d9017a4c708465902e.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/944be5363af1050246cc941b5ca41998
Polytrichaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the unique characteristics and ecology of this fascinating moss.
Background on Polytrichadelphus Mosses
The genus Polytrichadelphus belongs to the Polytrichaceae family within the
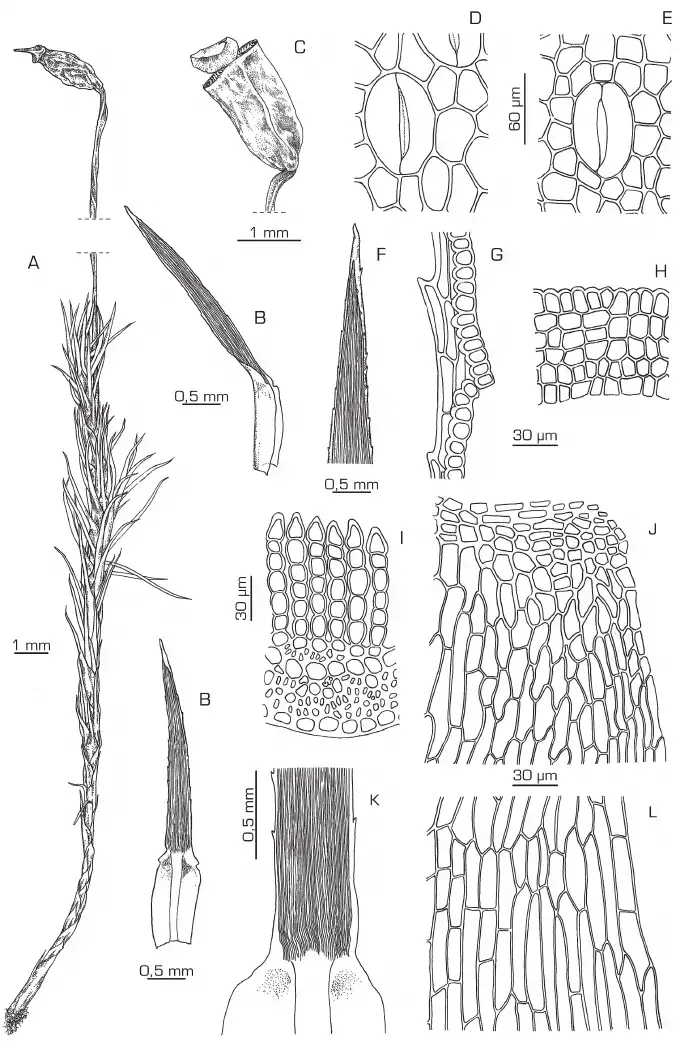
Polytrichadelphus-bolivianus-A-Habito-de-la-planta-al-estado-seco-B-Hojas-caulina.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Polytrichadelphus-bolivianus-A-Habito-de-la-planta-al-estado-seco-B-Hojas-caulina_fig1_264117612
Bryophyta division and Polytrichopsida class. Polytrichadelphus mosses are known for their relatively large size compared to other mosses. They often have stiff, wiry stems and leaves arranged in distinct ranks or rows.
Morphology and Identification of P. abriaquiae
Polytrichadelphus abriaquiae is characterized by its tall, unbranched stems that can reach up to 10 cm in height. The leaves are long and narrow, with toothed margins, and are spirally arranged around the stem. Capsules are borne on long stalks called setae and have a distinctive four-angled shape. The calyptra (cap) that covers the young capsule is densely hairy.
Global Distribution and Habitat
P. abriaquiae has a neotropical distribution, found in Central and South America, including countries like Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia. It typically grows at high elevations between 1500-3000 meters

239257.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/786477
, in cool and humid montane forests. This moss is often found growing on soil, rocks, or as an epiphyte on tree trunks and branches.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, P. abriaquiae plays important ecological roles:
- Helps retain moisture and prevent soil erosion
- Provides habitat for micro-organisms and small invertebrates
- Participates in nutrient cycling
- Acts as a bioindicator of air and water quality
P. abriaquiae has several adaptations that allow it to thrive in its montane habitat:
- Thick, waxy cuticle on leaves to prevent water loss
- Rhizoids (root-like structures) to anchor it to substrates
- Ability to absorb water and nutrients over its entire surface
- Tolerance to freezing temperatures and high UV radiation
Conclusion
Polytrichadelphus abriaquiae is a prime example of the incredible diversity and resilience of mosses. From its unique morphology to its specialized habitat, this moss has much to teach us about survival and adaptation in challenging environments. Next time you’re hiking in the neotropical mountains, keep an eye out for this intriguing plant! What other secrets might the miniature world of mosses hold?