
tormentil-potentilla-erecta-growing-amongst-moss-on-moorland-may-B422AW.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-tormentil-potentilla-erecta-growing-amongst-moss-on-moorland-may-19714769.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Pottia recta (With.) Mitt. moss stands out as a remarkable species within the Pottiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Pottia, this unassuming yet resilient moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Pottia recta, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes
Pottia3.jpg from: http://blogs.ubc.ca/biology321/?page_id=7074
. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing barren areas and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Pottia recta is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense tufts or cushions. Its leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive recurved margin and a reddish-brown color when dry. The
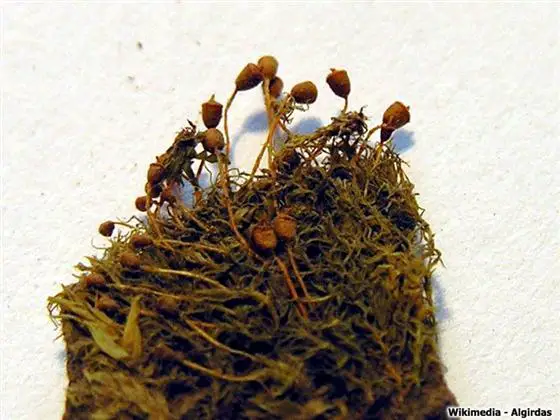

Pottia_truncata.jpg from: https://azoresbioportal.uac.pt/azorean-species/tortula-truncata-12087/
capsules, which are borne on short setae, are erect and cylindrical, often with a reddish-brown hue. One of the key identifying features of this moss is its twisted and contorted peristome teeth, which aid in spore dispersal.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Pottia recta is a cosmopolitan species, found on every continent except Antarctica. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, including disturbed areas, arable fields, roadsides, and urban environments. This moss is particularly well-adapted to dry and nutrient-poor conditions, making it a pioneer species in colonizing bare or disturbed soils.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Pottia recta plays a vital role in various ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, paving the way for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for numerous invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Pottia recta is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to thrive in harsh environments where other plants might struggle.
Case Studies/Examples
In urban areas, Pottia recta has been observed colonizing cracks in sidewalks, walls, and other man-made structures. Its ability to establish itself in these seemingly inhospitable environments showcases its remarkable adaptability and highlights the importance of preserving even the smallest green spaces in cities.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Pottia |
| Species | Pottia recta (With.) Mitt. |
| Growth Form | Dense tufts or cushions |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Color | Reddish-brown when dry |
| Capsule | Erect, cylindrical, reddish-brown |
| Peristome | Twisted and contorted teeth |
Conclusion
The Pottia recta (With.) Mitt. moss, a member of the Pottiaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its ability to thrive in harsh environments, its ecological significance, and its unique morphological features make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, let us ponder: What other hidden wonders await discovery in the intricate tapestry of life that surrounds us?