
235023.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5161
Introduction
Welcome, fellow moss enthusiasts! Today, we’re going to delve into the fascinating world of

989225.jpg from: https://www.bio-forum.pl/messages/3280/989219.html
Pseudoleskeella catenulata (Brid. ex Schrad.) Kindb., a captivating moss species from the Pseudoleskeellaceae family, commonly known as Pseudoleskeella. Prepare to be amazed by the intricate beauty and resilience of this tiny, yet mighty, bryophyte.
Background
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty details, let’s set the stage. Bryophytes, or non-vascular plants, are a diverse group that includes mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. These ancient organisms have been around for millions of years, predating even the dinosaurs! Despite their diminutive size, they play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
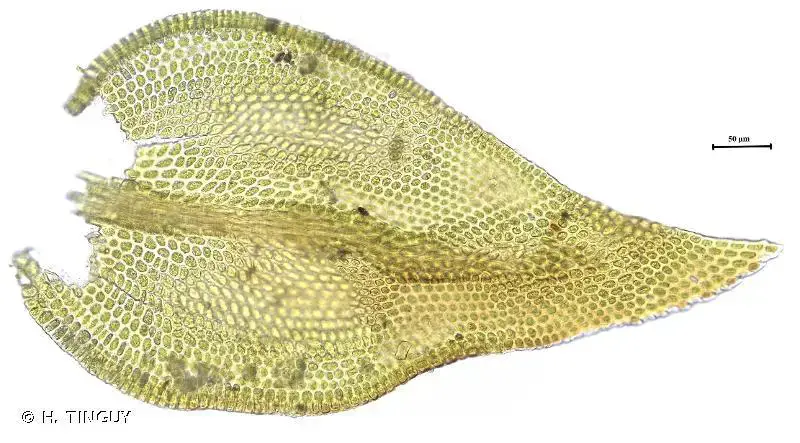
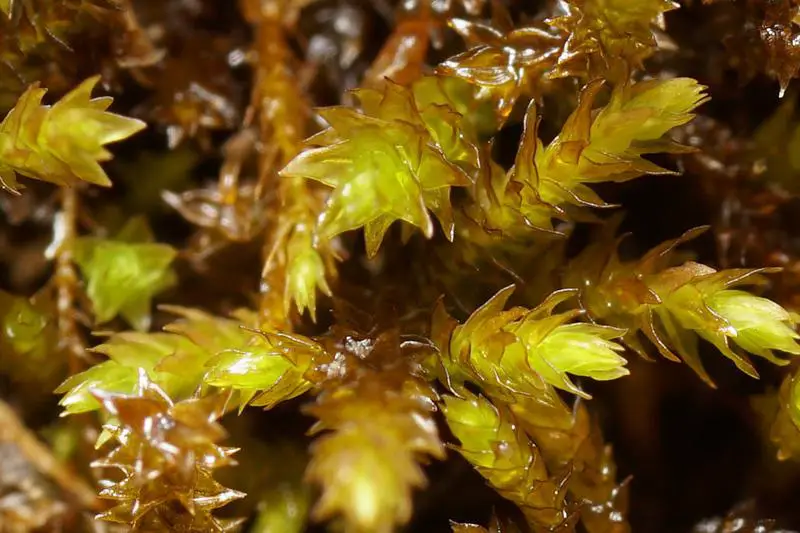
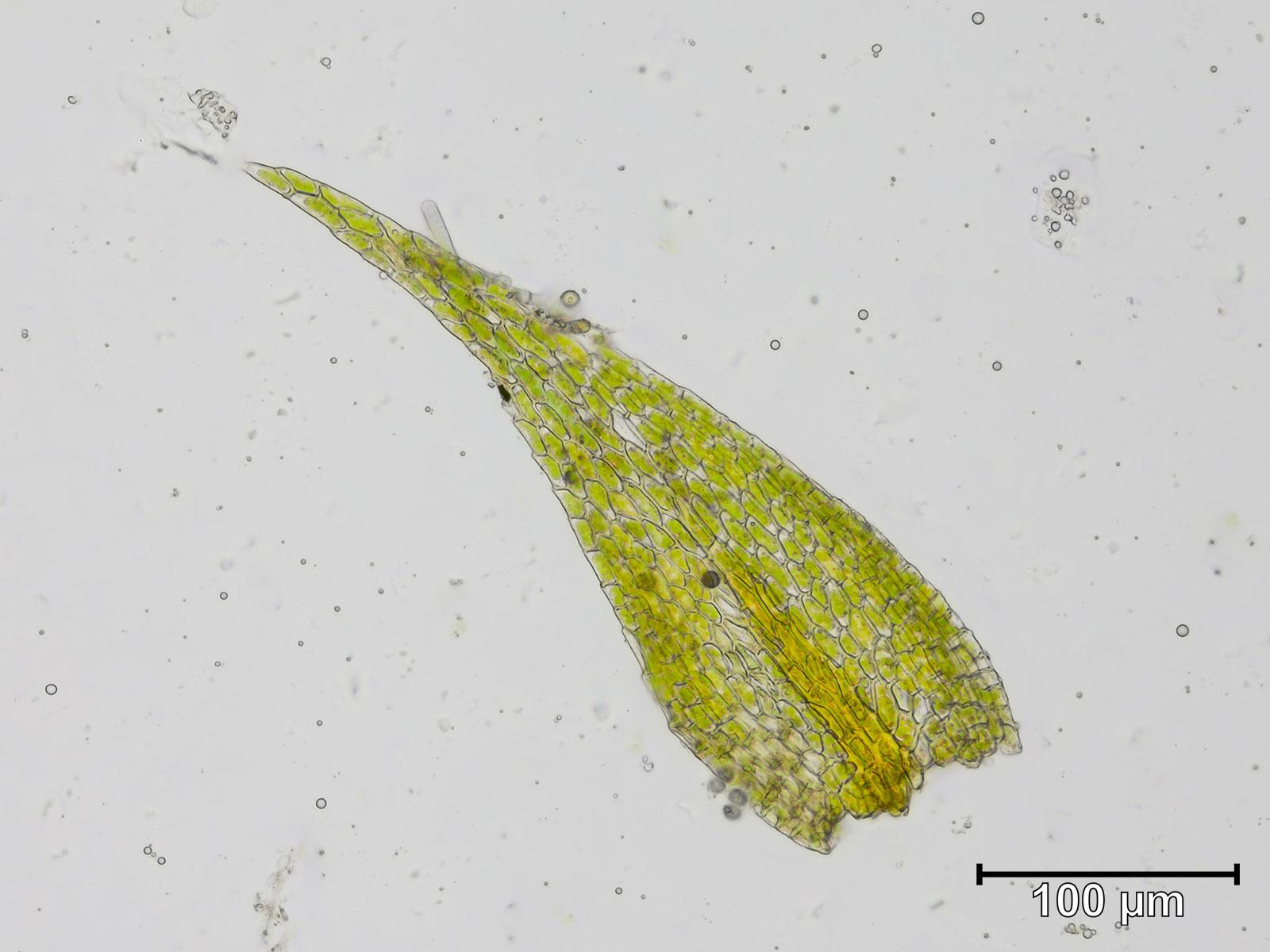
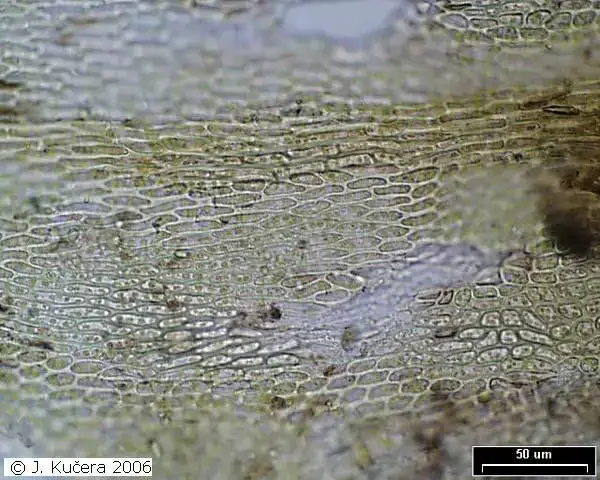
Pseudoleskeella catenulata is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems and branches grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, creeping stems are adorned with delicate, overlapping leaves that form a feathery appearance. The leaves themselves are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and acuminate (tapering to a slender point), with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends nearly to the leaf tip.
One of the most striking features of this moss is its catenulate (chain-like) branching pattern, which gives it a unique and easily recognizable appearance. This characteristic is reflected in its specific epithet,

original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/4279191
catenulata

pseudoleskeella_catenulata_blatt_2.jpeg from: https://www.korseby.net/outer/flora/bryophyta/leskeaceae/index.html
, derived from the Latin word “catena,” meaning chain.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Pseudoleskeella catenulata is a cosmopolitan species, meaning it can be found on multiple continents around the world. It thrives in various habitats, including moist and shaded areas such as forests, rock crevices, and even urban environments like old walls and tree bases.

fels-kettenmoos-deu–pseudoleskeella-catenulata.jpg from: https://www.plantsnap.com/plant-encyclopedia/bryophytes/Leskeaceae/pseudoleskeella-papillosa/
This moss is particularly well-adapted to survive in dry conditions, thanks to its ability to undergo desiccation tolerance. When the environment becomes too dry, Pseudoleskeella catenulata can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves and slowing down its metabolic processes until more favorable conditions return.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Pseudoleskeella catenulata plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and water retention, creating microhabitats for other organisms to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a food source for various invertebrates and provides nesting material for some bird species.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Pseudoleskeella catenulata is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. During favorable conditions, it produces sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) that release spores for sexual reproduction. However, when conditions are less favorable, it can propagate through gemmae (specialized asexual reproductive bodies) or fragmentation, ensuring its survival and dispersal.
Case Study: Urban Moss Gardens
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in creating urban moss gardens, where species like Pseudoleskeella catenulata are cultivated and showcased. These miniature landscapes not only bring a touch of nature into urban settings but also serve as educational tools, raising awareness about the importance of bryophytes and their role in the environment.
Technical Table

94-A09%2B1516211162.JPG from: https://v3.boldsystems.org/index.php/Taxbrowser_Taxonpage?taxid=803618

Pse_rup_cells.jpg from: https://botanika.prf.jcu.cz/bryoweb/klic/genera/pseudoleskeella.html
203914.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/436308
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Pseudoleskeellaceae |
| Genus | Pseudoleskeella
 203947.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5162 |
| Species | catenulata |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, acuminate |
| Branching Pattern | Catenulate (chain-like) |
| Reproduction | Sexual (sporophytes) and asexual (gemmae, fragmentation) |
Conclusion
Pseudoleskeella catenulata is a true marvel of nature, showcasing the incredible diversity and resilience of the bryophyte world. From its intricate morphology to its remarkable adaptations, this moss species continues to captivate and inspire moss enthusiasts worldwide.
As we bid farewell to our mossy friend, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: In a world where urbanization and habitat loss threaten many species, how can we better appreciate and protect these often-overlooked, yet vital, components of our ecosystems?