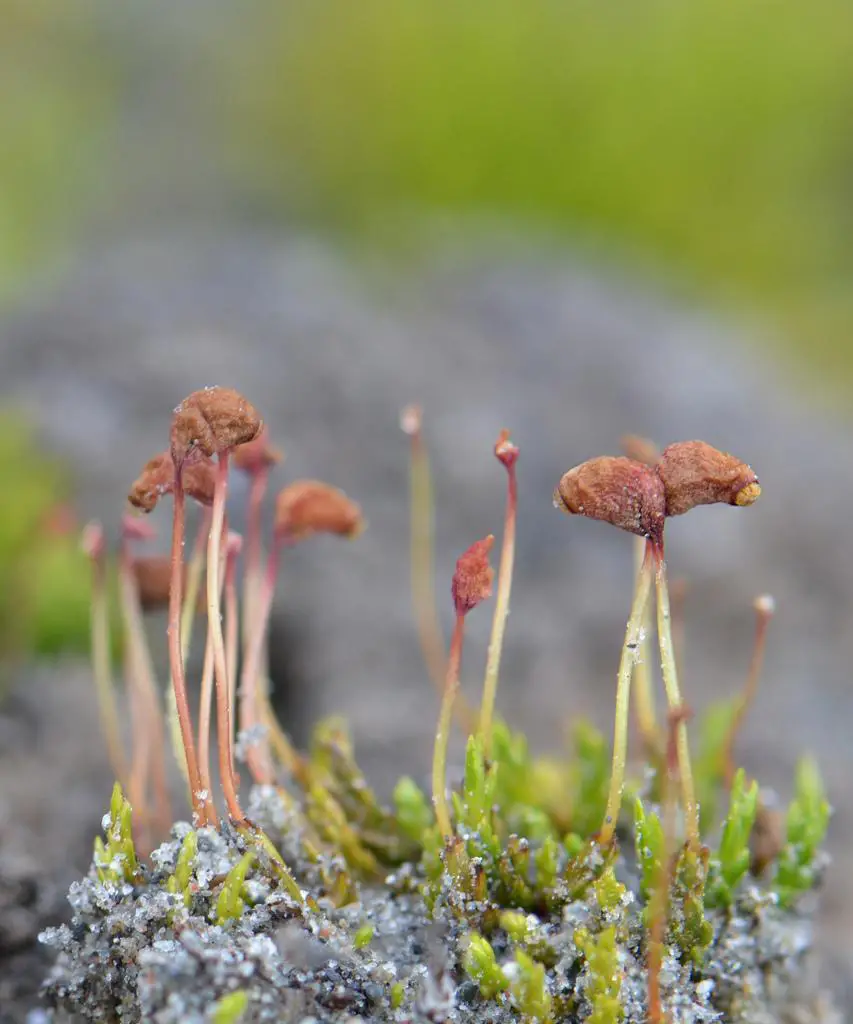

psilopilumlaevigatum.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/bryophytes/polytrichaceae/psilopilum-laevigatum/en/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out as a true marvel of nature – the Psilopilum laevigatum var. aloma I.Hagen. Belonging to the Polytrichaceae family, this unassuming yet extraordinary plant has captured the hearts and minds of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of this fascinating organism, commonly referred to as Psilopilum.

95-B10%2B1516322170.JPG from: https://v3.boldsystems.org/index.php/Taxbrowser_Taxonpage?taxid=411175
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Psilopilum laevigatum var. aloma I.Hagen, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Psilopilum laevigatum var. aloma I.Hagen is a striking moss species characterized by its vibrant green hue and delicate, feathery appearance. Its slender stems, adorned with tiny, overlapping leaves, create a mesmerizing tapestry that captivates the eye. One of the most distinctive features of this moss is its
RtBzvoH23N8Ty1TYvnijiQRe8Zzkc4CKUJxleMVtXT1A from: http://www.nrk.no/video/PS*169146
calyptra, a protective cap that covers the developing sporophyte (spore-bearing structure). The calyptra of Psilopilum is hairy, adding to its unique charm.
Global Distribution and Habitat
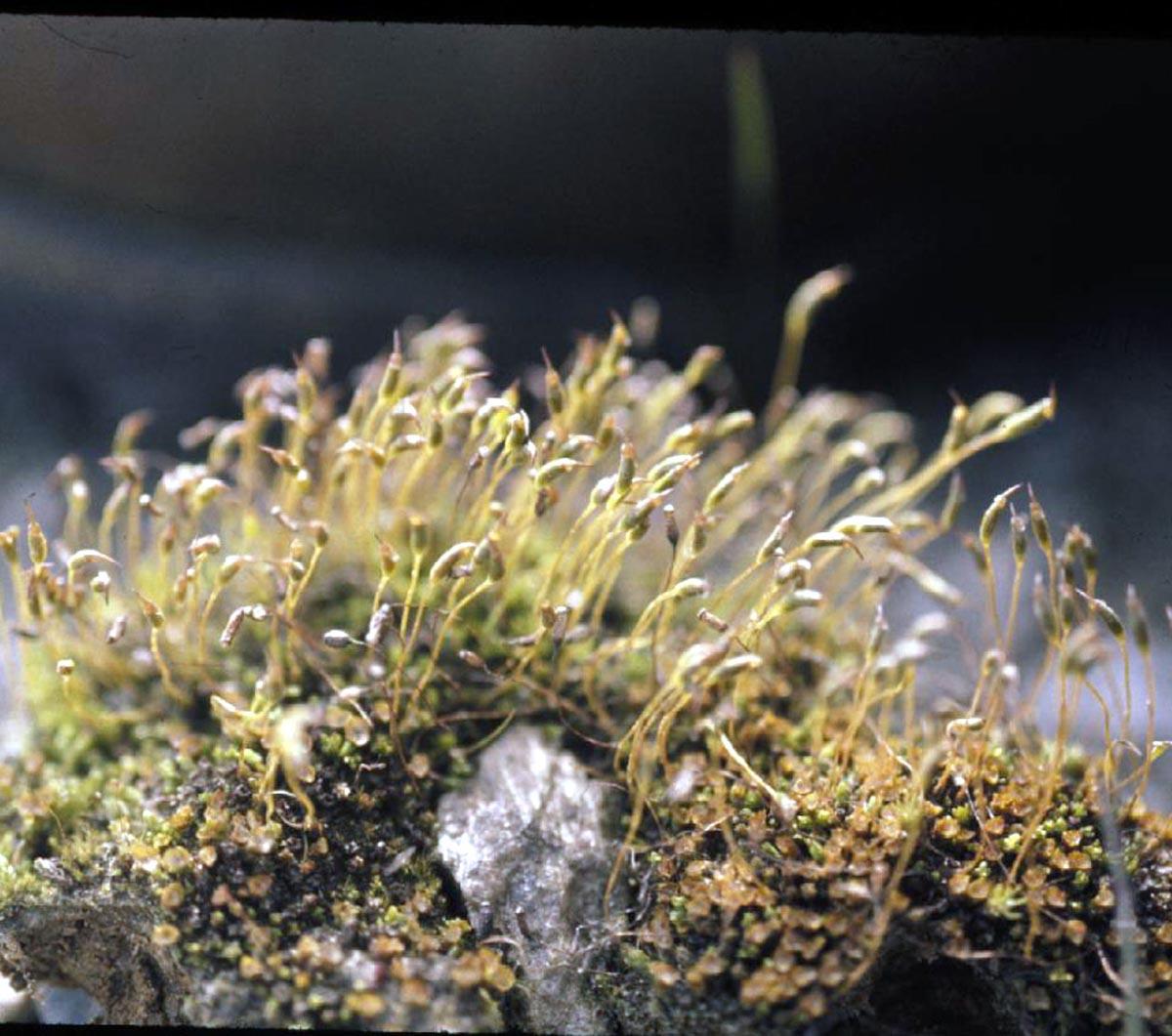

psilopilum_cavifolium.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Polytrichaceae/psilopilum-cavifolium/en/

NF3007_12.jpg from: https://www.orchids.com/Paph-philippinense-var-laevigatum-fma-album-P7550.aspx
This remarkable moss species is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, and Asia. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often found growing on decaying logs, rocks, and soil in forests and woodlands. Psilopilum laevigatum var. aloma I.Hagen is particularly fond of areas with high humidity and moderate temperatures, making it a common sight in temperate and boreal regions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Psilopilum plays a vital role in its ecosystem. These mosses act as pioneers, colonizing bare or disturbed areas and paving the way for other plant species to establish themselves. They also contribute to soil formation and moisture retention, creating favorable conditions for other organisms to thrive.

DSC_0475.jpg from: https://margretheshobbyblogg.blogspot.com/2015/03/var-i-hagen.html
One of the remarkable adaptations of Psilopilum laevigatum var. aloma I.Hagen is its ability to survive periods of desiccation. When conditions become dry, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, only to revive and resume growth once moisture returns. This resilience allows it to persist in challenging environments and ensures its long-term survival.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered a thriving population of

445b25c1b3f7aa280a70f54753b60d87.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/836262224529219464/
Psilopilum laevigatum var. aloma I.Hagen in an old-growth forest. The moss was found to play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of the ecosystem, providing a suitable microhabitat for various invertebrates and serving as a nursery for seedlings of other plant species.
Technical Table
17248Lobes.JPG from: https://lichens.twinferntech.net/pnw/species/Nephroma_laevigatum.shtml

8656983256_e95ed2360c_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/paphioman/8656983256/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Scientific Name
 2014+04+21+blogg+hvit.jpg from: https://utivaarhage22.blogspot.com/2014/04/var-i-hagen.html |
Psilopilum laevigatum var. aloma I.Hagen |
| Family | Polytrichaceae |
| Division | Bryophyta |
| Class | Polytrichopsida |
| Growth Habit | Acrocarpous (upright) |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spirally arranged |
| Calyptra | Hairy |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments (forests, woodlands) |
| Distribution | North America, Europe, Asia |
Conclusion
The Psilopilum laevigatum var. aloma I.Hagen moss is a true testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. Its intricate beauty, ecological significance, and remarkable adaptations make it a fascinating subject of study for moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other hidden gems lie waiting to be discovered in the realm of bryophytes, and what invaluable lessons can they teach us about the intricate web of life?