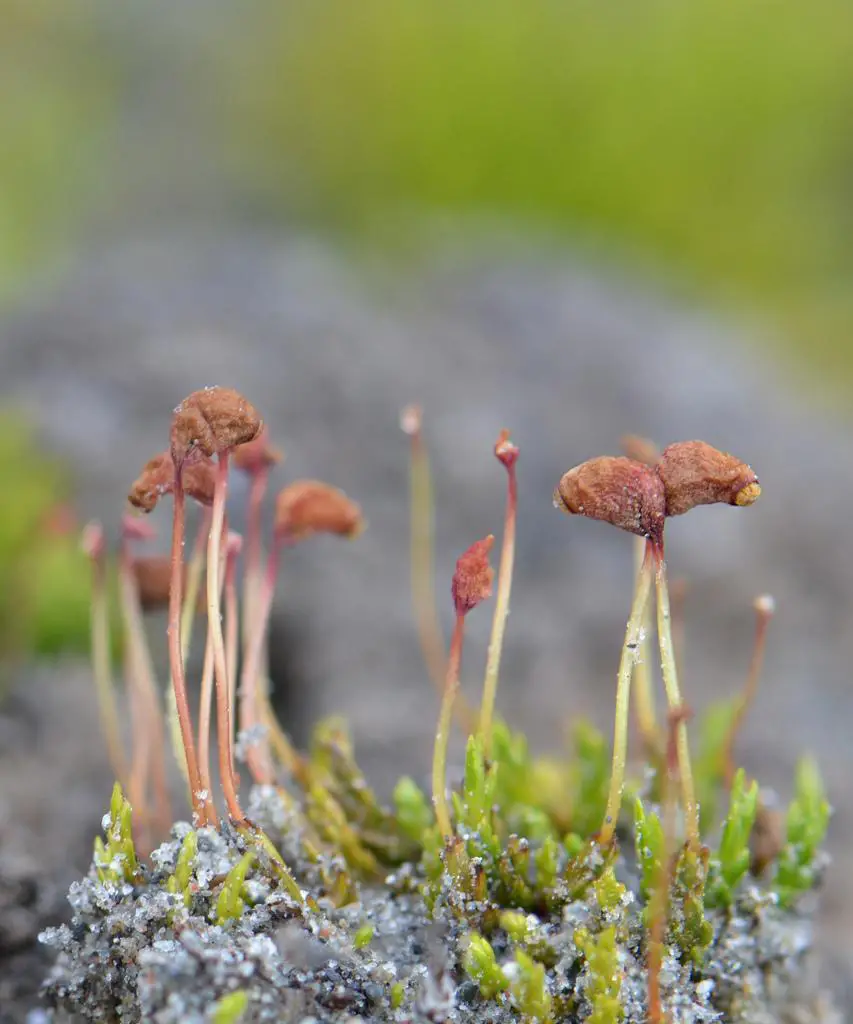

psilopilumlaevigatum.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/bryophytes/polytrichaceae/psilopilum-laevigatum/en/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the Psilopilum laevigatum (Wahlenb.) Lindb. moss, commonly known as Psilopilum. This unassuming yet remarkable plant belongs to the Polytrichaceae family and is a true testament to nature’s resilience and adaptability.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this fascinating moss, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. Bryophytes, a group that includes mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest and most primitive land plants on Earth. These diminutive yet mighty organisms have played a crucial role in the colonization of terrestrial environments, paving the way for the evolution of more complex plant life.

95-B10%2B1516322170.JPG from: https://v3.boldsystems.org/index.php/Taxbrowser_Taxonpage?taxid=411175
Main Content
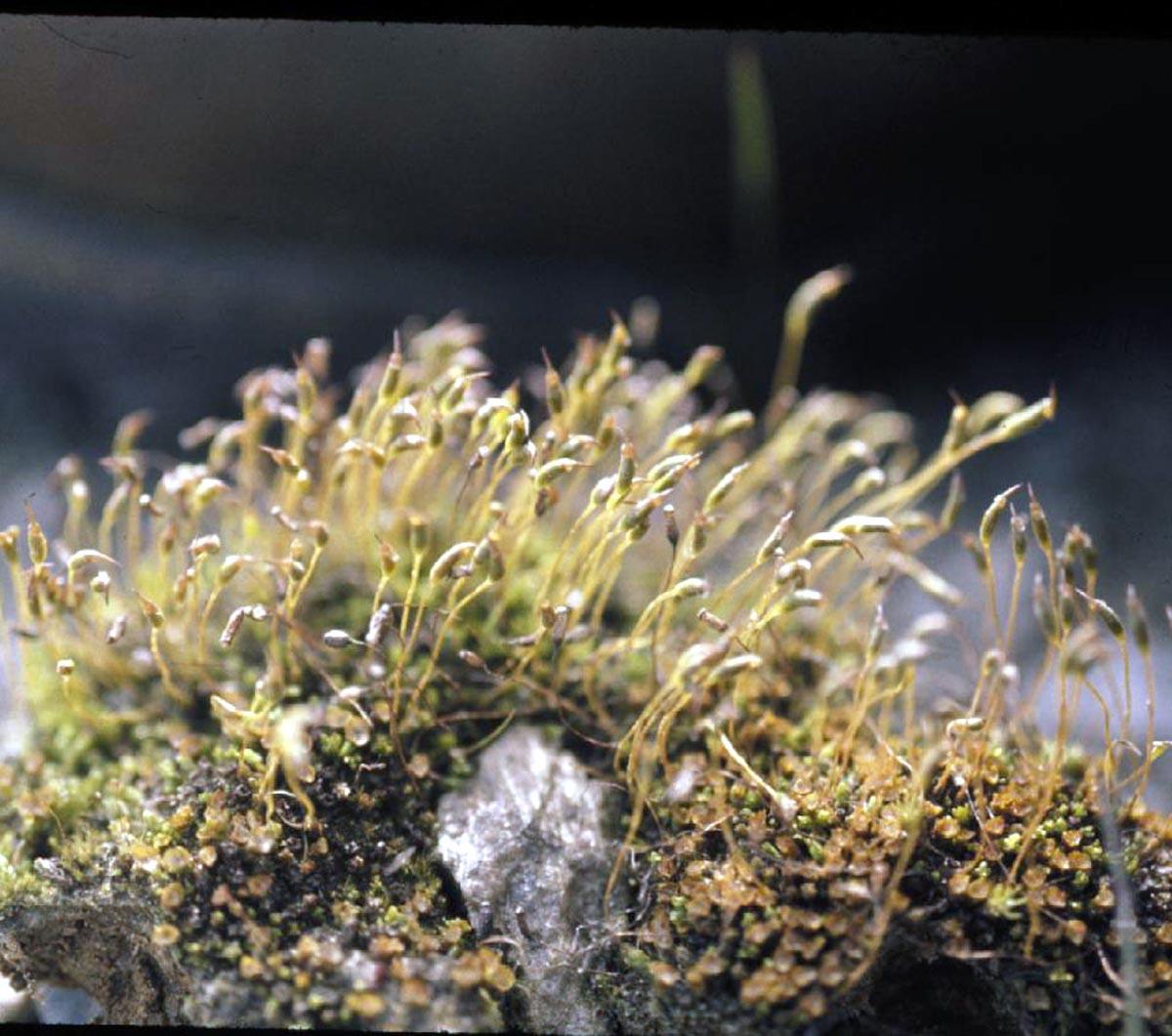

psilopilum_cavifolium.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Polytrichaceae/psilopilum-cavifolium/en/
Morphology and Identification

Equisetumlaevigatum.jpg from: https://en-academic.com/dic.nsf/enwiki/8627787
The Psilopilum laevigatum moss is a true marvel of nature, with its intricate structure and unique features. This acrocarpous moss forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats, often adorned with a striking reddish-brown hue. Its slender stems, typically reaching heights of 2-5 centimeters, are adorned with delicate, lance-shaped leaves that spiral around the stem in a distinctive pattern.
One of the most remarkable characteristics of this moss is its calyptra, a protective cap that covers the developing sporophyte (spore-bearing structure). The calyptra of Psilopilum laevigatum is hairy, a trait that sets it apart from many other moss species and aids in its identification.
Global Distribution and Habitat
The Psilopilum laevigatum moss is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, thriving in a diverse range of habitats. From the cool, moist forests of Europe and North America to the rugged tundra regions of the Arctic, this resilient moss has adapted to a variety of environmental conditions.
17248Lobes.JPG from: https://lichens.twinferntech.net/pnw/species/Nephroma_laevigatum.shtml
While it prefers acidic soils and damp, shaded environments, Psilopilum laevigatum can also be found growing on decaying logs, rocks, and even tree bark, showcasing its remarkable ability to colonize various substrates.

1200px-Taraxacum_laevigatum_Closeup_DehesaBoyaldePuertollano.jpg from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taraxacum_laevigatum
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, the Psilopilum laevigatum moss plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and stabilization, creating a suitable environment for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide a microhabitat for a diverse array of microscopic organisms, including tardigrades (water bears) and rotifers.
One of the most fascinating adaptations of this moss is its ability to withstand desiccation (extreme drying). During periods of drought, Psilopilum laevigatum can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, the moss quickly revives, resuming its growth and photosynthetic activities.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the boreal forests of Canada, researchers found that Psilopilum laevigatum played a crucial role in maintaining soil moisture and nutrient cycling. The dense mats of this moss acted as a sponge, absorbing and retaining water, while also providing a suitable environment for decomposers to break down organic matter.
Another fascinating example comes from the Arctic tundra, where Psilopilum laevigatum has been observed growing in close association with certain lichen species. This symbiotic relationship, known as a bryolichen, allows the moss and lichen to share resources and thrive in harsh, nutrient-poor environments.
Technical Table

593335_1837cff4.jpg from: https://www.plantarium.ru/page/image/id/593335.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Scientific Name
 Limnobium-laevigatum-2.jpg from: https://pflanzenbestimmung.info/limnobium-laevigatum/ |
Psilopilum laevigatum (Wahlenb.) Lindb. |
| Family | Polytrichaceae |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss, forming dense tufts or mats |
Stem Height
 1641.jpeg from: https://www.calflora.org//cgi-bin/species_query.cgi?where-calrecnum=3024 |
2-5 centimeters |
| Leaf Shape | Lance-shaped, spirally arranged around the stem |
| Calyptra | Hairy, covering the developing sporophyte |
| Habitat | Acidic soils, damp and shaded environments, decaying logs, rocks, tree bark |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere (Europe, North America, Arctic regions) |
| Ecological Roles | Soil formation, stabilization, microhabitat provision, moisture retention |
| Adaptations | Desiccation tolerance, dormancy during drought |
Conclusion
The Psilopilum laevigatum moss, a true marvel of the bryophyte world, serves as a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of nature’s smallest inhabitants. From its intricate morphology and unique adaptations to its vital ecological roles, this unassuming plant has captivated the hearts and minds of moss enthusiasts worldwide.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, the Psilopilum laevigatum moss reminds us of the importance of preserving and protecting even the most inconspicuous species, for they play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystems.

50273777573_2dc424f061_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/134511766@N03/50273777573/
Ponder this: In a world where we often overlook the smallest wonders, what other remarkable organisms might we be missing, and what valuable lessons can they teach us about the intricate web of life?