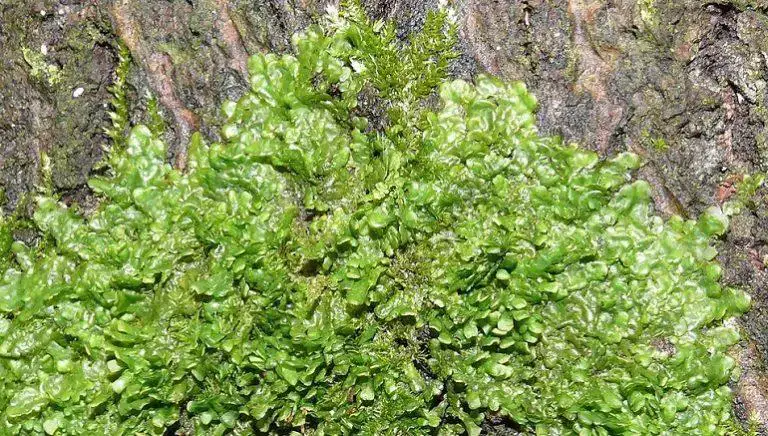

muschio-cannabis-768×436.jpg from: https://www.blitzquotidiano.it/salute/radula-perrottetii-muschio-cannabis-2947552/
Exploring the Fascinating World of Radula perrottetii Gottsche ex Steph. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play crucial roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Radula perrottetii Gottsche ex Steph., commonly known as Radula moss. This small but mighty plant is part of the Radulaceae family and has some unique characteristics. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at Radula perrottetii and explore what makes it so special.
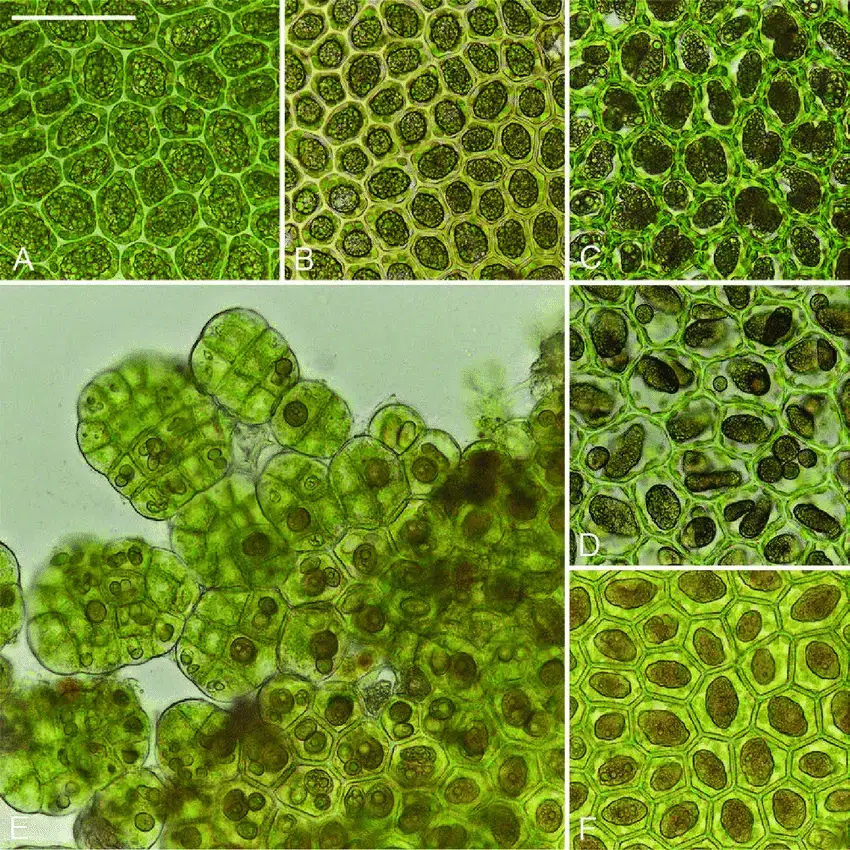
Oil-bodies-photographs-A-Radula-auriculata-Steph-P-34-21-14-VBGI-B-R-japonica.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Oil-bodies-photographs-A-Radula-auriculata-Steph-P-34-21-14-VBGI-B-R-japonica_fig1_342043028
Background
Radula perrottetii is a species of liverwort, which are non-vascular plants in the division Marchantiophyta. Liverworts are similar to mosses but have a few key differences. Radula perrottetii belongs to the class Jungermanniopsida, which contains most liverworts. The genus Radula contains around 200 species found worldwide.
Morphology and Identification
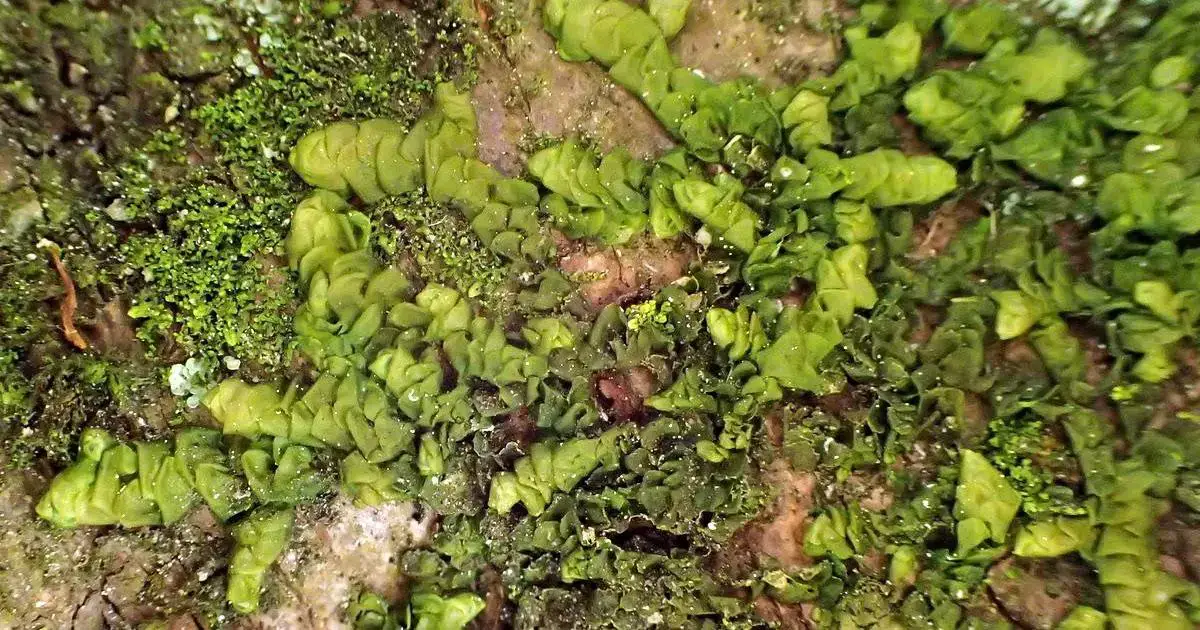
Radula perrottetii forms small, light green mats on tree bark, rocks, and soil. The shoots are irregularly branched and only
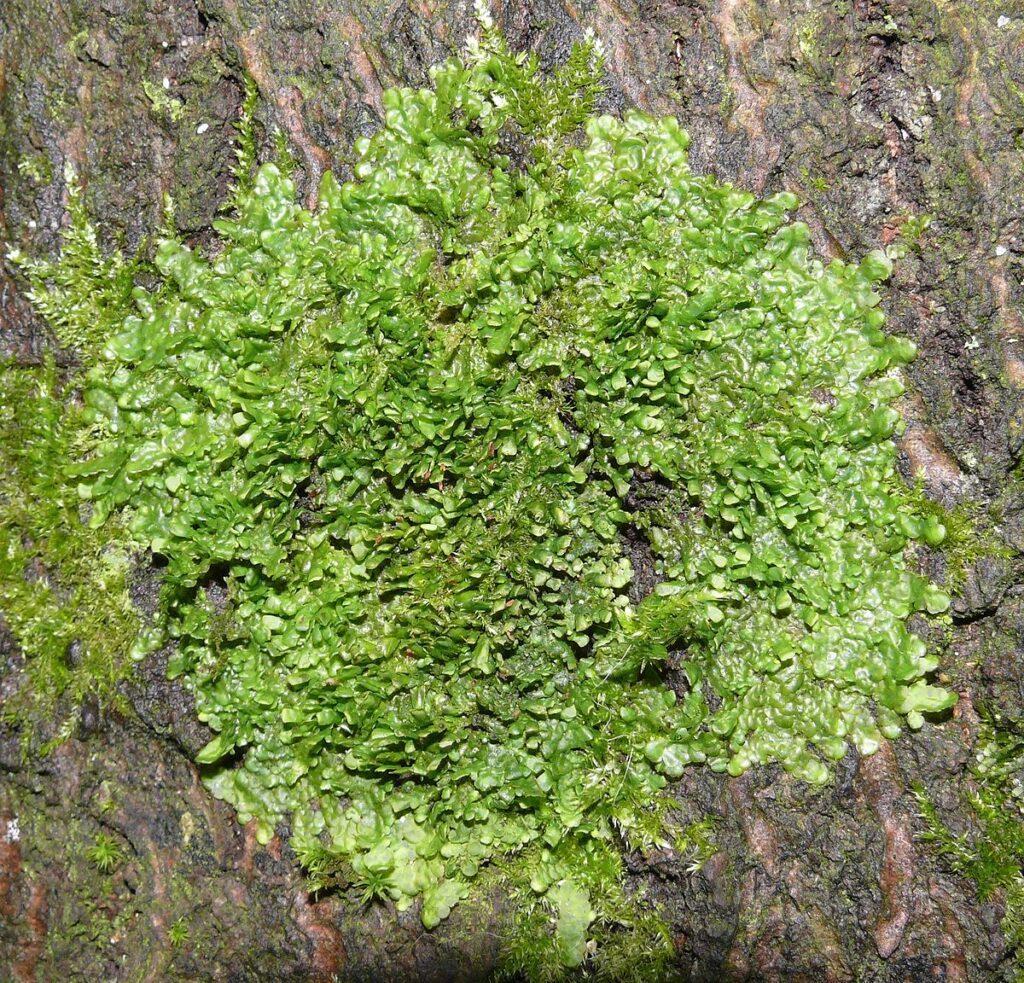

Radula-perrottetii-1024×983.jpg from: https://www.naturalalchemy.com.au/product/liverwort-extract-20-1-radula-perrottetii/
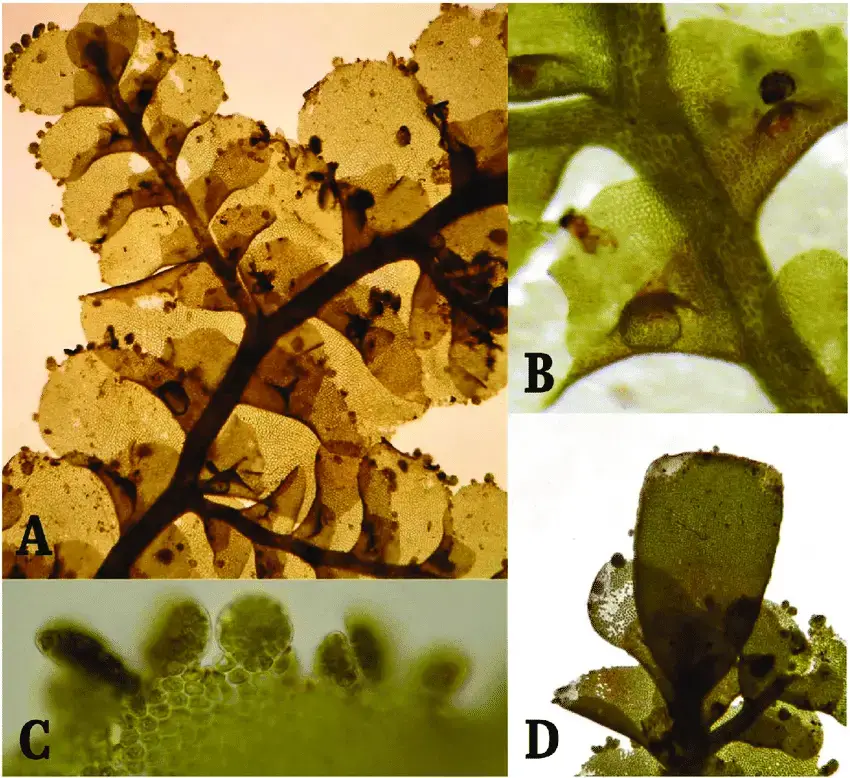
1-2 cm long. The leaves are arranged in two rows and have a unique “pocket” shape formed by a small, helmet-like lobe. This distinct leaf morphology helps with identification. Radula mosses reproduce via spores produced in capsules on short stalks.
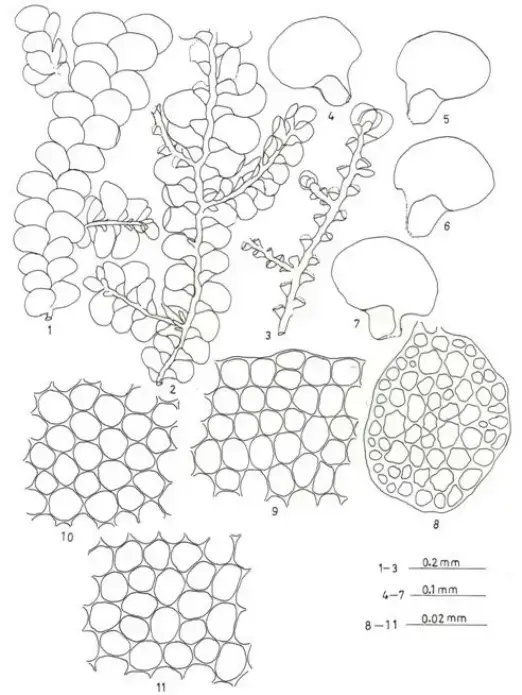
Radula-madagascariensis-Gottsche-Figures-1-11-Figures-1-3-Plant-showing-habit-1.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Radula-madagascariensis-Gottsche-Figures-1-11-Figures-1-3-Plant-showing-habit-1_fig1_258926968

supernahrung-beitrag-lebermoos-768×512.jpg from: https://supernahrung.com/lebermoos/

LEJEUNEACEAE%2BCololejeunea%2Bsp.%2B%2528.%2529%255B2021%252CCasa%252Cpomar_Arv.3-Prunus%2Bdomestica%255D_P4040728.JPG from: https://naturetheplacewhereyoulive.blogspot.com/2022/01/radulaceae-radula-lindbergiana.html
Global Distribution and Habitat
Radula perrottetii has a wide distribution and can be found in tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including parts of Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Americas. It typically grows at low to middle elevations in moist, shaded habitats like rainforests. Radula moss often grows as an epiphyte on tree trunks and branches.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses and liverworts, Radula perrottetii plays important roles in its ecosystem:

original.jpg from: https://www.laborpraxis.vogel.de/cannabis-alternative-besser-als-thc-und-aus-moos-a-769520/
- Helps retain moisture and prevent erosion
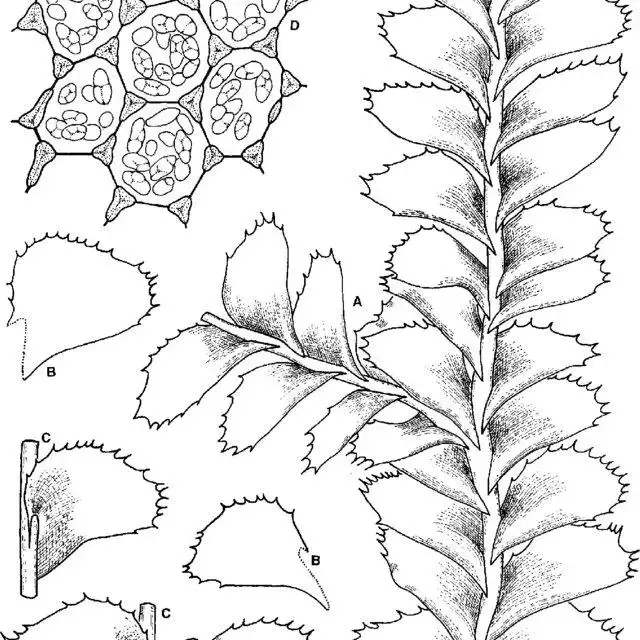
Plagiochila-maderensis-Gottsche-ex-Steph-A-Top-of-shoot-with-terminal-branch-dorsal_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plagiochila-maderensis-Gottsche-ex-Steph-A-Top-of-shoot-with-terminal-branch-dorsal_fig2_29813448
- Provides shelter and habitat for small invertebrates

Radula-tectiloba-Steph-A-Habito-de-crecimiento-de-la-planta-en-vista-ventral-40-B.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Radula-tectiloba-Steph-A-Habito-de-crecimiento-de-la-planta-en-vista-ventral-40-B_fig3_348311027
- Contributes to nutrient cycling as it decomposes
- Serves as a bioindicator of air and water quality
Radula moss has adaptations that allow it to thrive in its environment, such as:
- Rapid water uptake and drought tolerance
- Protective pigments to prevent UV damage
- Asexual reproduction via fragmentation
Conclusion
Radula perrottetii may be small, but this fascinating liverwort has an important place in the world’s ecosystems. Its unique morphology, wide distribution, and ecological roles make it a compelling species to study and appreciate. Next time you’re in a tropical forest, keep an eye out for this tiny but remarkable moss. What other secrets of the natural world are waiting to be discovered?

352413.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/786439