
300378.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/434237
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its resilience and adaptability – the Syntrichia norvegica F.Weber. Belonging to the Pottiaceae family, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the fascinating realm of this Syntrichia moss and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the intricacies of Syntrichia norvegica F.Weber, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have evolved remarkable survival strategies.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
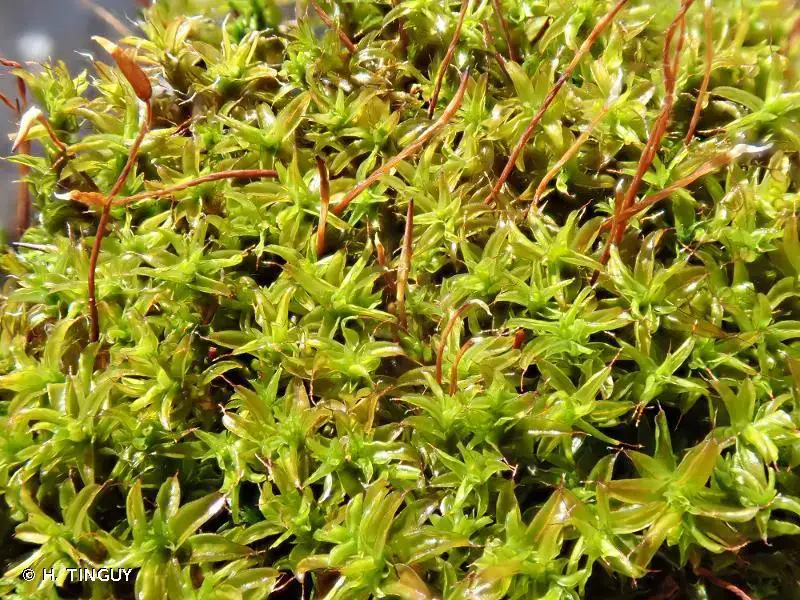
Syntrichia norvegica F.Weber is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a hyaline hair point

s_norvegica3.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/syntrichia_norvegica.html
. This characteristic feature is a key identifier for this species. The capsules, which contain the spores, are cylindrical and erect, often with a twisted peristome (tooth-like structures) that aids in spore dispersal.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Syntrichia norvegica F.Weber is a cosmopolitan species, meaning it can be found on various continents and in diverse habitats. It thrives in temperate and arctic regions, often colonizing exposed rocks, soil, and tree bark. This moss is particularly well-adapted to dry and nutrient-poor environments, making it a true survivor in harsh conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
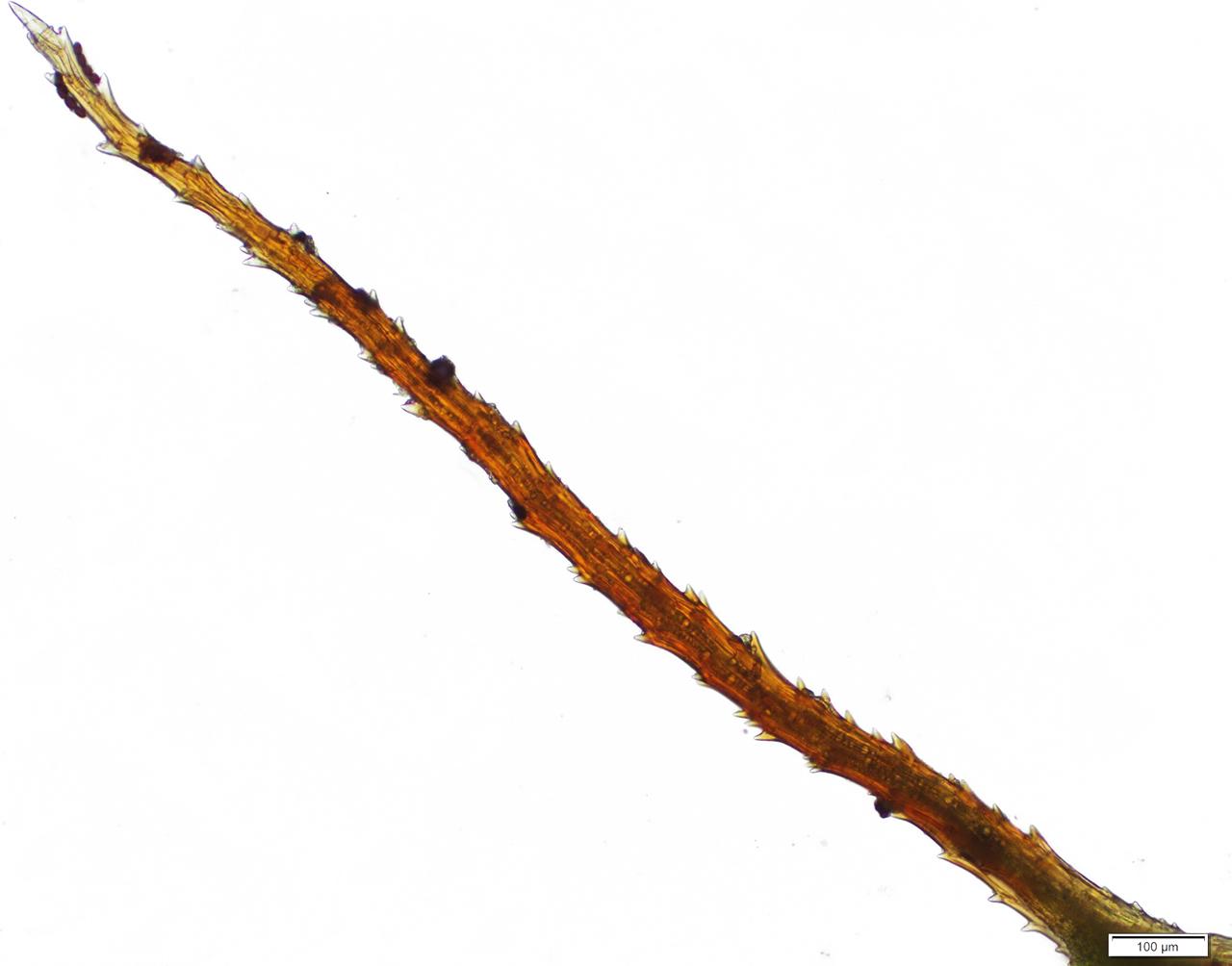
Despite its diminutive size,

s_norvegica9.jpg from: https://admissions.wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/syntrichia_norvegica.html
Syntrichia norvegica F.Weber plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It contributes to soil formation and stabilization, acting as a pioneer species in disturbed areas. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates and provides a nesting material for some bird species.
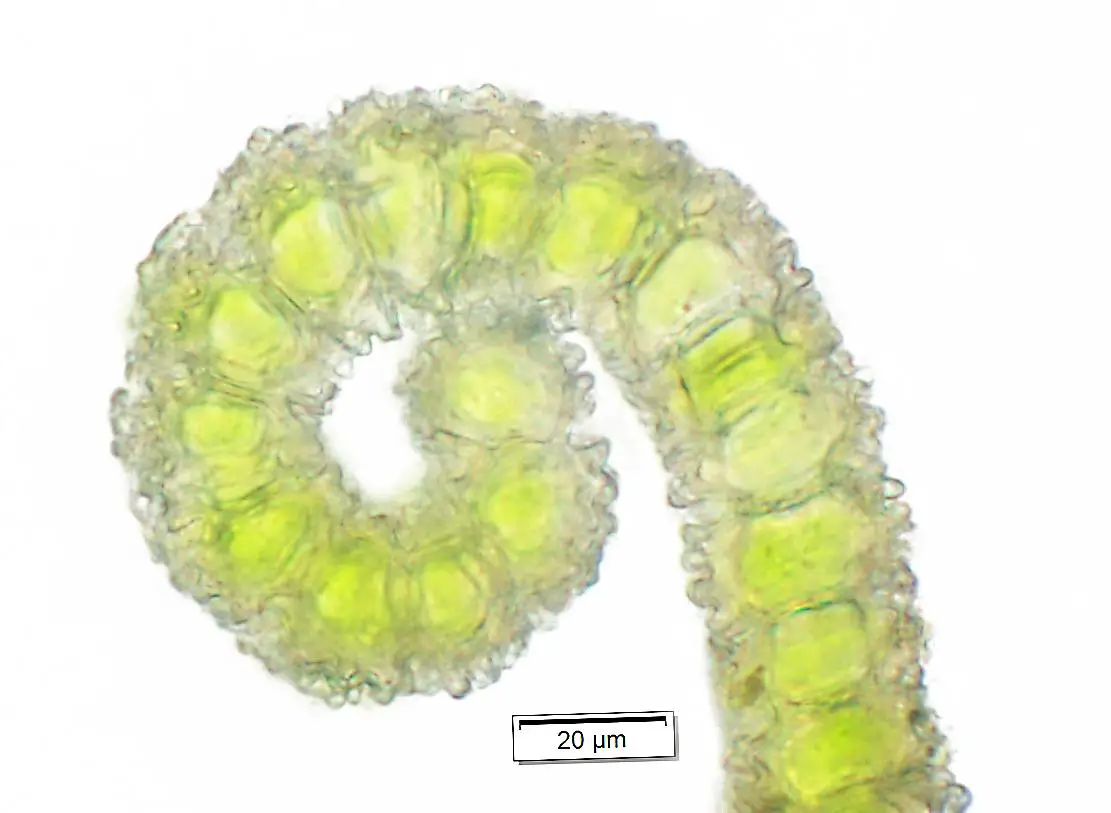
One of the remarkable adaptations of Syntrichia norvegica F.Weber is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. When moisture returns, it quickly revives, demonstrating its incredible resilience.
Case Studies/Examples
In the Arctic tundra
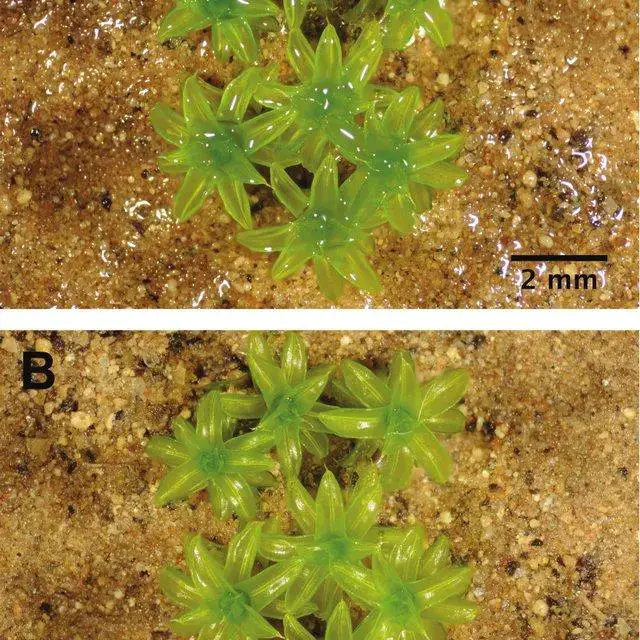
Appearance-of-cultured-shoots-of-Syntrichia-norvegica-exhibiting-A-the-suprasaturated_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Appearance-of-cultured-shoots-of-Syntrichia-norvegica-exhibiting-A-the-suprasaturated_fig1_311484266
, Syntrichia norvegica F.Weber plays a crucial role in stabilizing the fragile soil and preventing erosion. Its dense mats help retain moisture and provide a suitable microhabitat for other plant species to establish themselves.

35187195674_8d9602d171_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/100809177@N03/35187195674/
In urban environments, this moss has been observed growing on concrete surfaces, demonstrating its ability to thrive in human-made habitats. Its tolerance to air pollution and ability to colonize various substrates make it a valuable indicator species for monitoring environmental conditions.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pottiaceae
 6.jpg from: https://nathistoc.bio.uci.edu/Mosses/Syntrichia/index.html  39974066703_391430f3ba_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/29979480@N03/39974066703/ |
| Genus | Syntrichia |
| Species | Syntrichia norvegica F.Weber |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Apex | Hyaline hair point |
| Capsule | Cylindrical, erect |
| Peristome | Twisted |
Conclusion
Syntrichia norvegica F.Weber is a true marvel of the bryophyte world, showcasing remarkable adaptations and ecological significance. From its ability to withstand harsh conditions to its role in soil stabilization and providing microhabitats, this moss species deserves our admiration and respect. As we continue to explore the intricate tapestry of nature, let us ponder: What other wonders lie hidden within the realm of bryophytes, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?