
3d0b95809d86349f8bcd66ff55cdb6f6–fungi-flora.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/sphagnum-falcatulum–205476801721501101/
Rhaphidorrhynchium falcatulum: The Fascinating Falcate Moss
Introduction
Have you ever noticed the tiny, delicate mosses growing on trees and rocks in tropical forests? One particularly interesting species is Rhaphidorrhynchium falcatulum (Besch.) Broth.

Sphagnum-2.jpg from: https://www.jardineriaon.com/zh-CN/泥炭藓.html
, a moss in the Sematophyllaceae
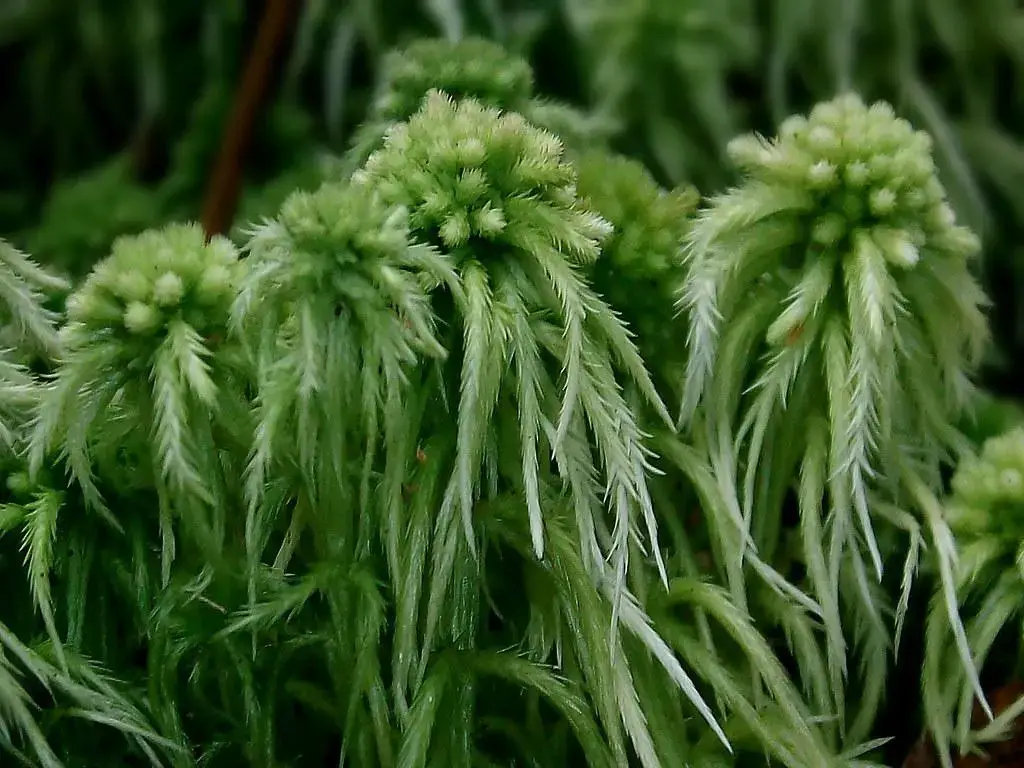

4535531875_59e47b9803_b.jpg from: https://flickr.com/photos/43304457@N03/4535531875
family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of this unique moss, exploring its morphology, global distribution, ecological roles, and adaptations. Get ready to be amazed by the miniature world of Rhaphidorrhynchium!
Background
Rhaphidorrhynchium falcatulum
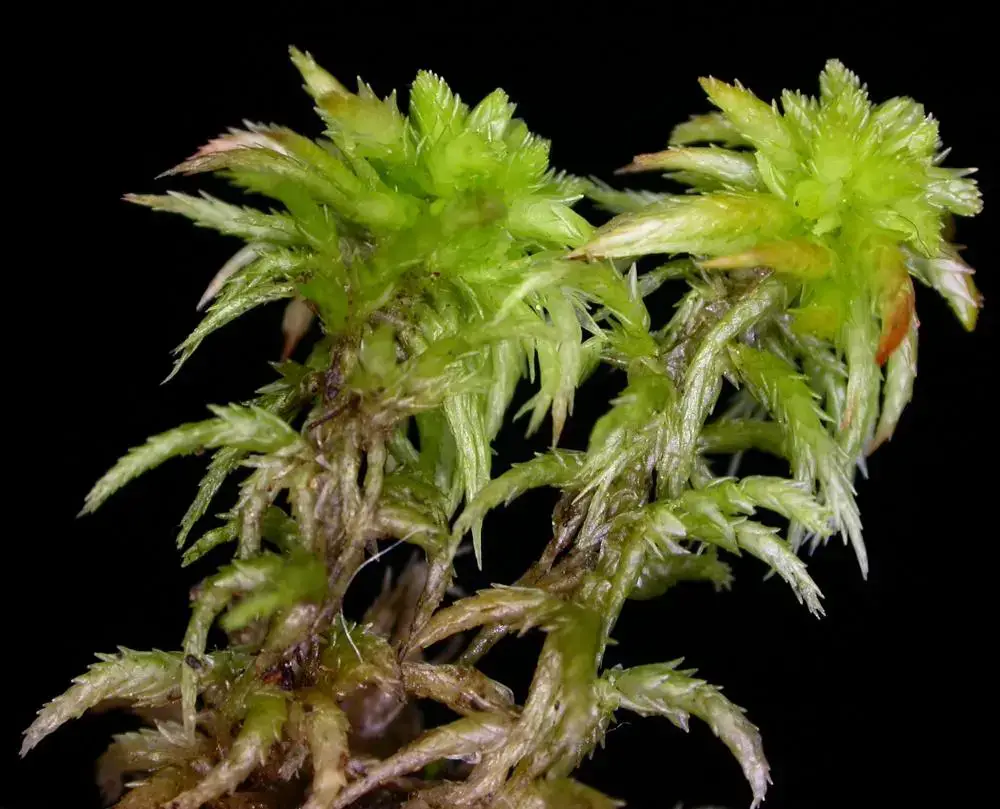

DT_Sphagnum_1_capitulum.jpg from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/52_Sphagnaceae_images.html
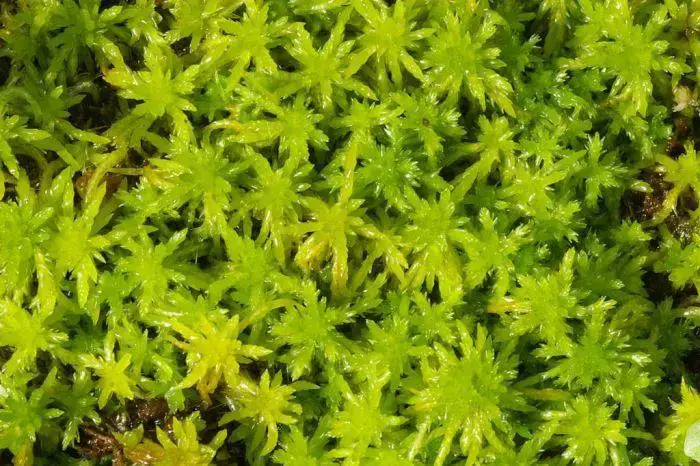

sphagnum.jpg from: https://bilingualbiology10.blogspot.com/2010/11/non-vascular-plants.html
is a species of moss belonging to the class Bryopsida in the plant division Bryophyta. Mosses are small, non-vascular plants that lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have leaf-like structures called phyllids that are only one cell layer thick. Mosses play important ecological roles, helping to retain moisture, prevent erosion, and provide habitat for tiny organisms.
Morphology and Identification
R. falcatulum forms dense mats with a glossy, golden-green appearance. Its stems are creeping to ascending, irregularly branched, and covered in falcate-secund (curved and pointing in one direction) leaves. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate with a slender acumen (tapering point) and have a single, short costa (midrib). Leaf margins are entire (smooth) and often recurved (curved back).
The species gets its name from the Latin words

largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311505414_Nuevo_registro_de_Sphagnum_falcatulum_Besch_Sphagnaceae_en_Isla_Navarino_Reserva_de_la_Biosfera_Cabo_de_Hornos
falcatum meaning “sickle-shaped” and ulum meaning “diminutive form”, referring to the small, curved leaves. R. falcatulum can be distinguished from similar species by its strongly falcate-secund leaves, short and double costa, and papillose (bumpy) leaf cells.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Rhaphidorrhynchium falcatulum has a pantropical distribution, found in tropical regions around the world including Central and South America, Africa, Southeast Asia, and Oceania. It typically grows as an epiphyte on tree trunks and branches in humid montane forests, but can also be found on rocks and logs. The species prefers shaded, moist habitats at elevations between 500-2000 meters.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other epiphytic mosses, R. falcatulum plays a role in nutrient cycling and water retention in forest ecosystems. Its mat-forming growth traps moisture, organic debris, and provides microhabitat for invertebrates. The strongly falcate-secund leaves help direct water down the stem to the growing tips. In addition, the papillose leaf cells may aid in water retention by increasing surface area.
R. falcatulum exhibits adaptations to its epiphytic lifestyle and tropical habitat:
- Tolerance of low light conditions in the forest understory
- Ability to absorb water and nutrients directly through leaves and stems
- Desiccation tolerance to withstand periodic drying
- Asexual reproduction via gemmae and fragmentation to aid dispersal
Conclusion
Image27W8large.jpg from: https://www.nzflora.info/factsheet/Taxon/Rhaphidorrhynchium-amoenum.html
The diminutive Rhaphidorrhynchium falcatulum

0717-6643-gbot-75-02-00667-gf2.jpg from: https://www.scielo.cl/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0717-66432018000200667
may be easily overlooked, but it is a fascinating and ecologically important member of tropical forest communities worldwide. Next time you’re walking through a humid tropical forest, take a closer look at the trees and rocks – you might just spot this marvelous moss! What other tiny wonders are waiting to be discovered in the world of bryophytes?

mcw269f1.jpg from: https://www.botany.one/2017/07/single-peat-moss-individuals-include-allelic-diversity-sphagnum/

2174e69b73594fa0c620e8af5924f136.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/bf7e5eeaf8a578b6413d823dbe679935