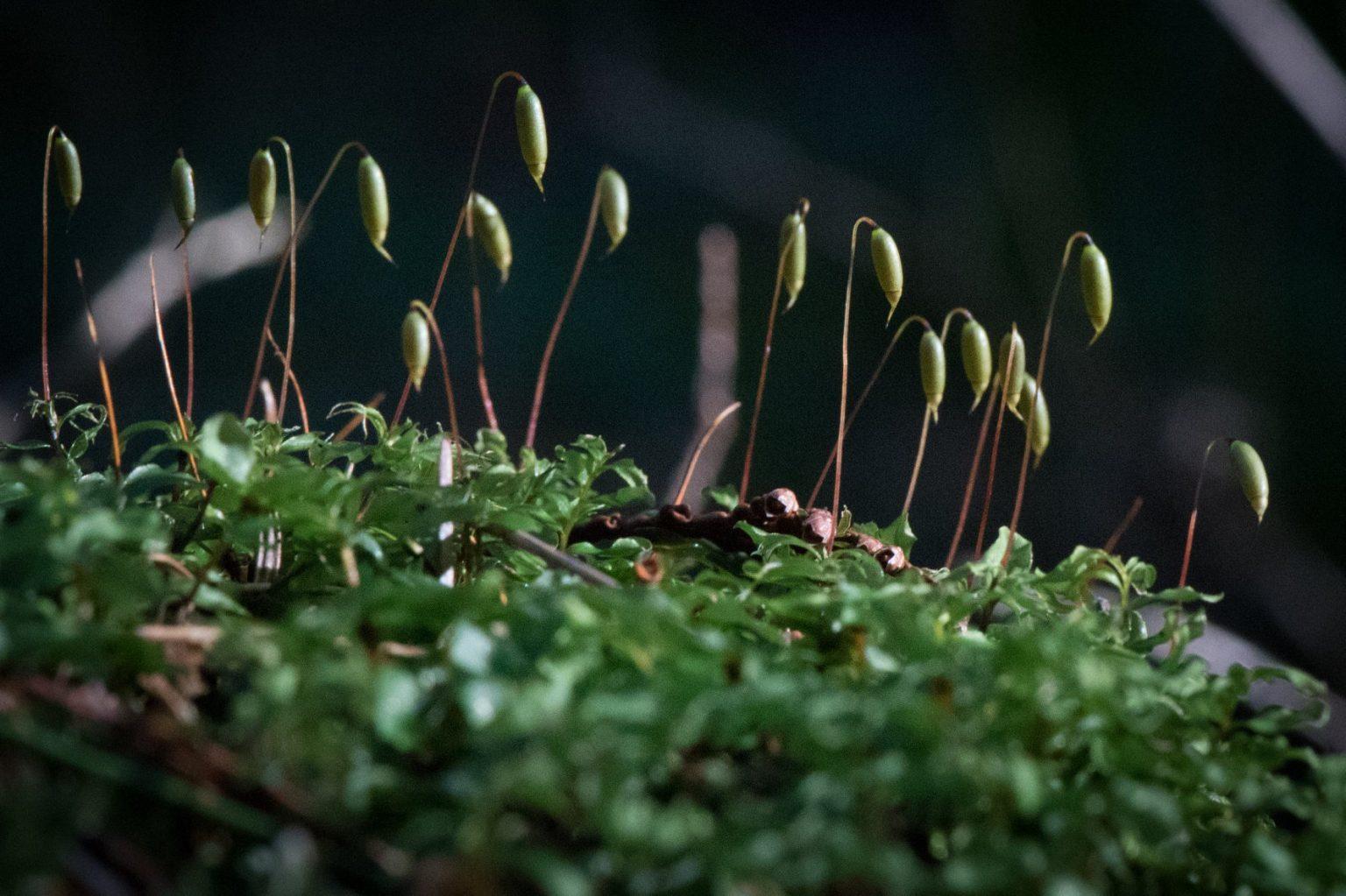

50497970_10161254999610133_1237573793887551488_n-1536×1023.jpeg from: https://blogs.ubc.ca/biology321/?page_id=514
Rhizomnium hattorii: A Remarkable Moss of the Mniaceae Family
Introduction
The world of mosses is full of fascinating species, each with their own unique characteristics and ecological roles. One particularly noteworthy moss is Rhizomnium hattorii T.J.Kop., also known simply as Rhizomnium. This moss belongs to the Mniaceae family and has some remarkable features. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at Rhizomnium hattorii and explore what makes it so special.
Background on Mosses
Before diving into the specifics of Rhizomnium hattorii, let’s briefly review what mosses are. Mosses are small, non-vascular plants that belong to the division Bryophyta.
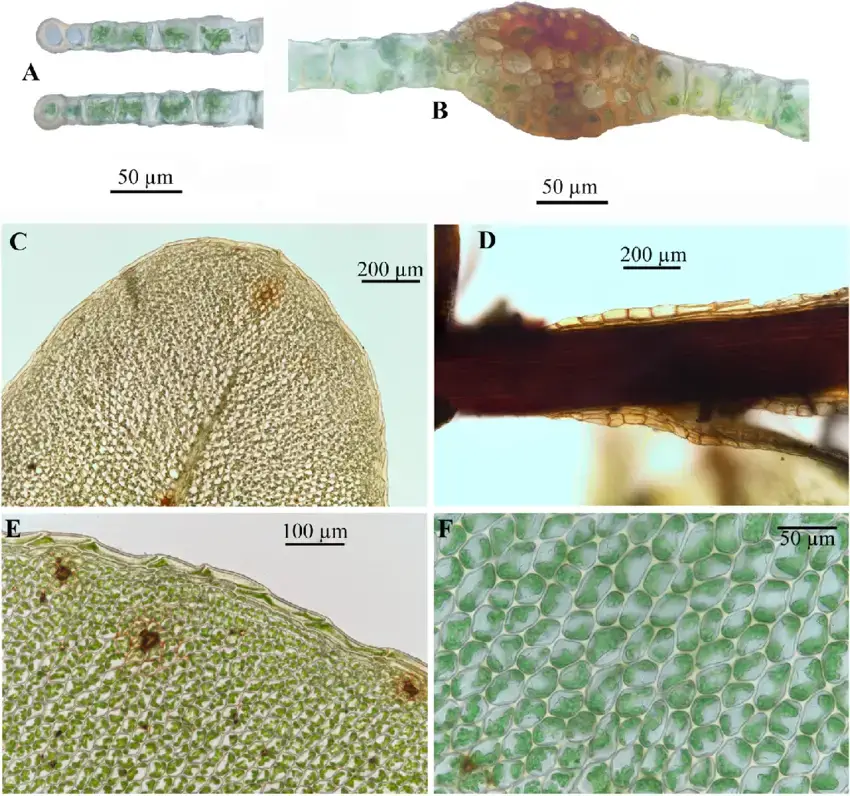
Rhizomnium-mieheanum-Frank-Muell-TJKop-A-Cross-section-of-leaf-border-B.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Rhizomnium-mieheanum-Frank-Muell-TJKop-A-Cross-section-of-leaf-border-B_fig2_362722152
They lack true roots, stems, and leaves, instead having structures that serve similar functions. Mosses play important ecological roles, helping to retain moisture, prevent erosion, and provide habitat for other organisms.
Morphology and Identification of Rhizomnium hattorii
Rhizomnium hattorii is a relatively large moss, with shoots that can reach 5-10 cm tall. The leaves are oblong to obovate in shape and have a distinct border of elongated cells. The leaf tips are rounded to obtuse. Rhizomnium hattorii is dioicous, meaning male and female reproductive structures are on separate plants.
One of the most distinctive features of Rhizomnium hattorii is the presence of rhizoids, root-like structures, on the stems. These rhizoids are reddish-brown in color and help the moss anchor itself to the substrate and absorb water and nutrients. The presence of these rhizoids is a key identification feature for this species.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Rhizomnium hattorii has a wide global distribution, being found in Asia, Europe, North America, and South America. In North America, it occurs in the western United States and Canada, as well as in the Appalachian Mountains.
This moss typically grows on damp soil, rocks, or rotten logs in shaded forests. It prefers humid environments and is often found near streams or in other moist microhabitats. Rhizomnium hattorii can form extensive mats on the forest floor.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Rhizomnium hattorii plays important roles in its ecosystem. It helps to retain moisture in the soil, which benefits other plants growing nearby. The mats formed by this moss also stabilize the soil and prevent erosion.
Rhizomnium hattorii also provides habitat for various small invertebrates, which in turn support other organisms higher up the food chain. Some birds, such as the Winter Wren, use mosses like Rhizomnium hattorii to build their nests.
To survive in the shaded, humid environments it prefers, Rhizomnium hattorii has several adaptations:
- Rhizoids for anchoring and absorbing water and nutrients
- Leaves with a distinct border that helps regulate moisture loss
- Dioicous reproduction to promote genetic diversity
Conclusion
Rhizomnium hattorii is a remarkable moss with a wide distribution and important ecological roles. Its distinct morphological features, like the reddish rhizoids and bordered leaves, make it a fascinating species to observe and study. Next time you’re walking through a humid forest, keep an eye out for mats of Rhizomnium hattorii – you may be surprised at the diversity of life this small moss supports! What other secrets do you think the world of mosses holds?