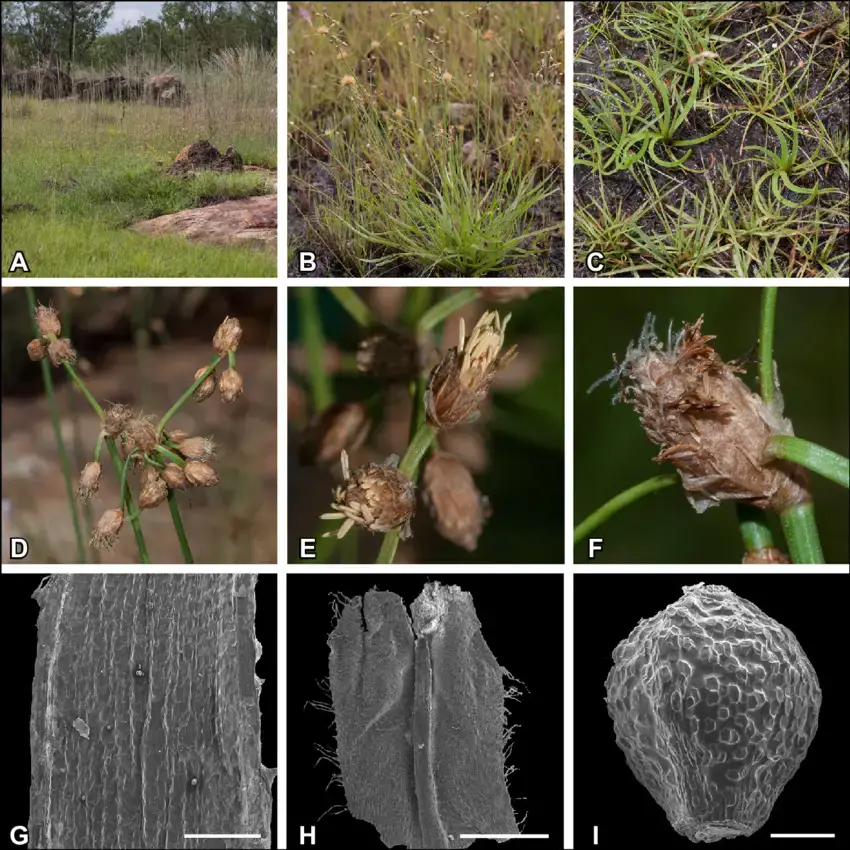

Fimbristylis-helicophylla-A-habitat-B-habit-C-leafy-rosettes-with-twisted.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fimbristylis-helicophylla-A-habitat-B-habit-C-leafy-rosettes-with-twisted_fig6_283486876
Schlotheimia badiella var. helicophylla: A Fascinating Moss of the Orthotrichaceae Family
Introduction
Today we’re diving into the captivating world of Schlotheimia badiella var. helicophylla Besch., a unique moss species of the Orthotrichaceae family. This tiny but mighty plant, also simply known as Schlotheimia, may be small in stature but it plays important ecological roles. Let’s explore what makes this moss so special!
Background on Mosses
Before we get into the specifics of Schlotheimia, let’s review some moss basics. Mosses are non-vascular plants in the division
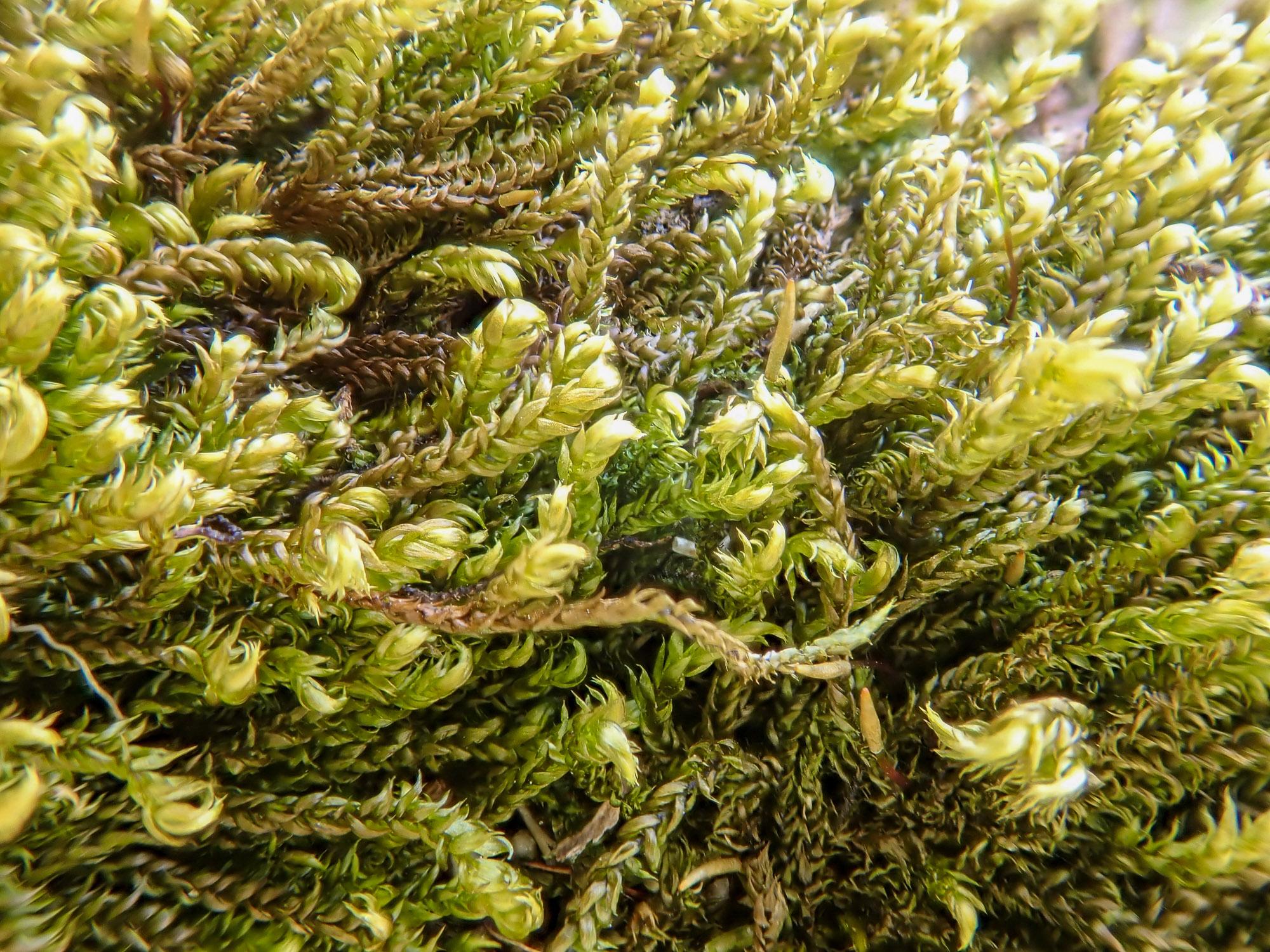
Schlotheimia-badiella-Besch-a-c-habit-dry-b-capsule-d-branch-leaves-e.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Schlotheimia-badiella-Besch-a-c-habit-dry-b-capsule-d-branch-leaves-e_fig2_281108486
Bryophyta. Unlike other plants, they lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have rhizoids, a stem-like structure, and leaf-like appendages. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in diverse habitats worldwide.

2021-04-18-14-14-07.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/hygrohypnum-luridum/

Helodium_blandowii_HEBL2-8_Shovel_Creek_Meadows_KlamathNF_MLenz_lg.jpg from: https://www.fs.usda.gov/wildflowers/beauty/California_Fens/diversity/mosses.shtml
Morphology and Identification
Schlotheimia badiella var. helicophylla is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning it has a branching, creeping growth habit. Its scientific name comes from its reddish-brown color (badiella) and spiraling, propeller-shaped leaves (helicophylla). The leaves are lanceolate with a costa (midrib) and serrated margins. Capsules are cylindrical and peristomate.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss has a pantropical

fauriella-tenuis.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Theliaceae/fauriella-tenuis/en/
distribution, found in tropical regions across multiple continents. It grows as an

DSC_7319.JPG from: https://aquamoss.blogspot.com/2013/05/callicostella-papillata-var-prabaktiana.html
epiphyte on tree bark and branches in moist, shady forests. The ability to grow on vertical surfaces helps it compete for space and avoid being smothered by leaf litter on the forest floor.

Weissia+controversa+var.+densifolia+%2528Thick-leaved+Stubble-moss%2529+Oxwich+02apr11+%25283a%2529.jpg from: https://moonmoths.blogspot.com/2011/04/underhill-cottage.html
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, Schlotheimia plays important roles in its ecosystem:
- Nutrient cycling: It helps trap and recycle nutrients that might otherwise be lost from the forest.

moss-hypnum-cupressiforme-close-up-shot-local-focus-182232202.jpg from: https://www.dreamstime.com/moss-hypnum-andoi-rock-beech-forest-tara-mountain-serbia-moss-hypnum-andoi-rock-image139265857

sagina-subulata-var-glabrata-aurea-scotch-moss-im-bluhenden-naturlichen-gartenpflanzenportrait-2d03bym.jpg from: https://www.alamy.de/sagina-subulata-var-glabrata-aurea-scotch-moss-im-bluhenden-naturlichen-gartenpflanzenportrait-image378703352.html
- Water retention: Moss mats absorb and slowly release water, regulating moisture.
- Microhabitats: It provides shelter and foraging grounds for invertebrates.
- Substrate stabilization: Moss anchors to bark, reducing erosion and stabilizing the microenvironment.
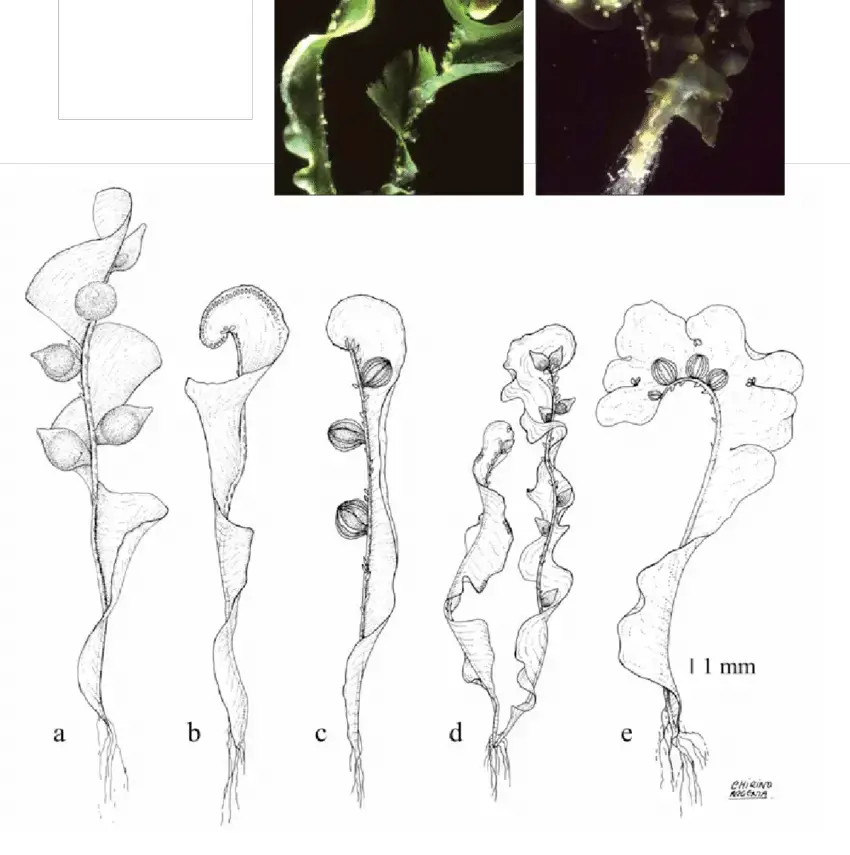
Figura-51-Aspecto-general-de-Riella-helicophylla-izquierda-con-un-pie-masculino.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-51-Aspecto-general-de-Riella-helicophylla-izquierda-con-un-pie-masculino_fig3_262562573
Schlotheimia has several adaptations for its epiphytic lifestyle:
- Desiccation tolerance: It can survive periods of drying out, then rehydrate.
- Lightweight spores: Spores are dispersed by wind to reach new tree habitats.
- Rhizoids: Help anchor the moss to bark surfaces.
Conclusion
From its spiraling propeller leaves to its important ecological roles, Schlotheimia badiella var. helicophylla is a prime example of how tiny but mighty mosses help shape their environments. Next time you’re in a tropical forest, take a closer look at the trees – you might just spot this fascinating moss! What other secrets of the miniature world await discovery?