
original.jpg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2680758
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Sematophyllum subpinnatum (Brid.) E.Britton moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Sematophyllaceae family. This unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate beauty and resilience of the bryophyte kingdom.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of this moss, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. Bryophytes, a group that includes mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest and most primitive land plants on Earth. These resilient organisms have played a crucial role in the colonization of terrestrial environments, paving the way for the evolution of more complex plant life.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
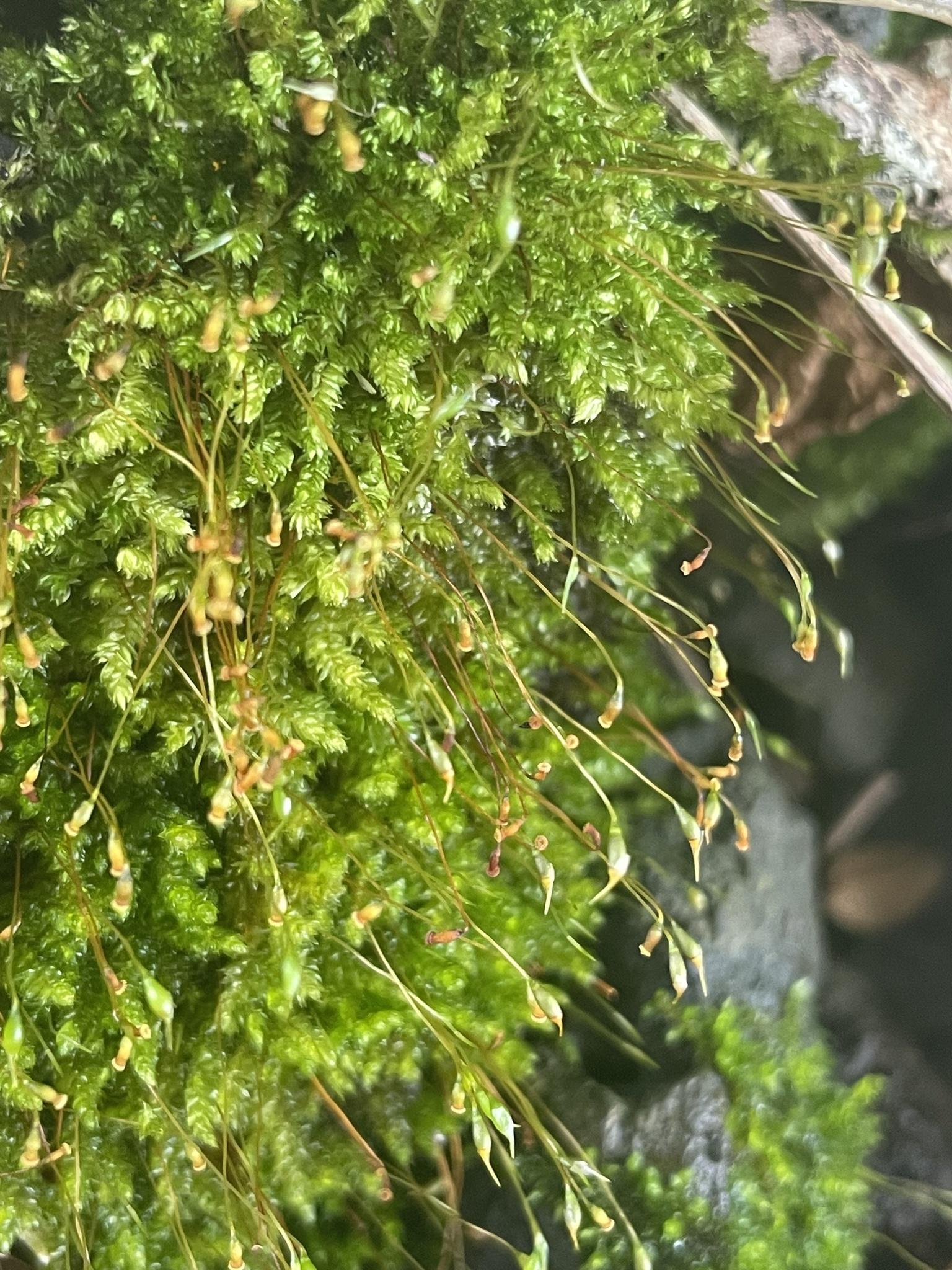
The Sematophyllum subpinnatum moss is a striking representative of the Bryopsida class, characterized by its delicate, feathery appearance. Its slender stems are adorned with
Distribution-map-for-Sematophyllum-subpinnatum-Brid-E-Britton.ppm from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Distribution-map-for-Sematophyllum-subpinnatum-Brid-E-Britton_fig8_334452850
pinnately arranged leaves, creating a intricate and visually appealing pattern. The leaves themselves are ovate-lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive acuminate tip that sets them apart from other moss species.
One of the most remarkable features of this moss is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. During the sexual reproductive cycle, the moss produces sporophytes bearing capsules that release spores, enabling the dispersal and propagation of the species. Asexually, the moss can also spread through fragmentation and the formation of gemmae, specialized reproductive structures that allow for rapid colonization of new habitats.
Global Distribution and Habitat
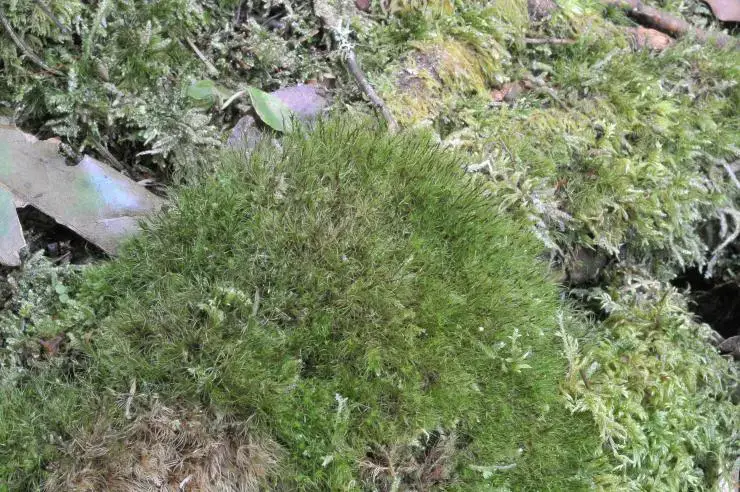
The Sematophyllum subpinnatum moss is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, and Asia. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist and shaded forests to rocky outcrops and even urban environments, showcasing its remarkable adaptability.

386eba63a73f4235727ee7927128bb85.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/f205d365e2ca7e50d564abc51281d7f6
This moss is particularly fond of acidic substrates, such as decaying logs, tree bark, and soil rich in organic matter. Its ability to colonize these environments is facilitated by its tolerance for low nutrient levels and its capacity to absorb water and nutrients directly from the surrounding air and precipitation.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
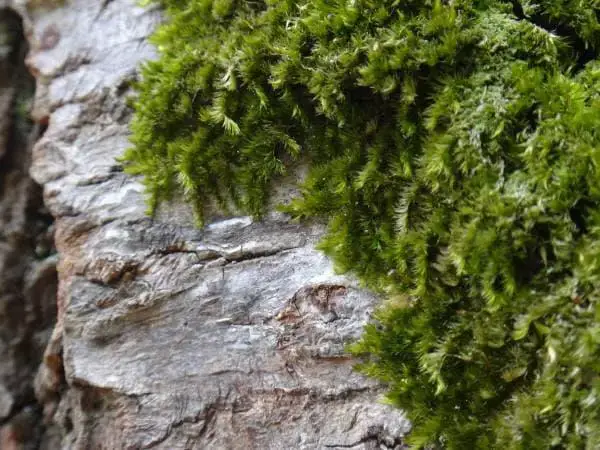
Despite its diminutive size, the Sematophyllum subpinnatum moss plays a vital role in various ecosystems. It contributes to soil formation and nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter and providing a suitable habitat for a myriad of microscopic organisms, such as fungi and bacteria.
largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/357506613_Aposporic_development_of_gametophyte_in_Sematophyllum_subpinnatum_Brid_E_Britton_Sematophyllaceae_from_capsule_wall
Moreover, this moss serves as a crucial microhabitat for numerous invertebrates, including insects, spiders, and other arthropods. Its intricate structure offers shelter, nesting sites, and a source of moisture, supporting the biodiversity of these ecosystems.
One of the remarkable adaptations of the Sematophyllum subpinnatum moss is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, effectively shutting down its metabolic processes until favorable conditions return. This remarkable resilience allows the moss to thrive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels, ensuring its survival and propagation.
Case Study: Urban Moss Gardens
In recent years, the Sematophyllum subpinnatum moss has gained popularity in the realm of urban gardening and green infrastructure. Its ability to colonize various substrates, including concrete and brick, has made it a valuable addition to moss gardens and living walls. These innovative projects not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of urban spaces but also contribute to air purification, temperature regulation, and biodiversity conservation.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Sematophyllum subpinnatum (Brid.) E.Britton |
| Family | Sematophyllaceae |
| Class | Bryopsida |
Growth Form
 18f919b5a0113c0e96757fbd476cd00c.jpg from: http://blog.goo.ne.jp/mossphoenix/e/ce0245c8622108cf7f057a537e673ea0 |
Pleurocarpous (horizontally growing) |
| Leaf Arrangement | Pinnate |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate, acuminate tip |
| Reproduction | Sexual (sporophytes, spores) and Asexual (fragmentation, gemmae) |
| Habitat | Moist forests, rocky outcrops, urban environments |
| Substrate Preference | Acidic, organic-rich substrates |
| Ecological Roles | Soil formation, nutrient cycling, microhabitat provision |
Adaptations
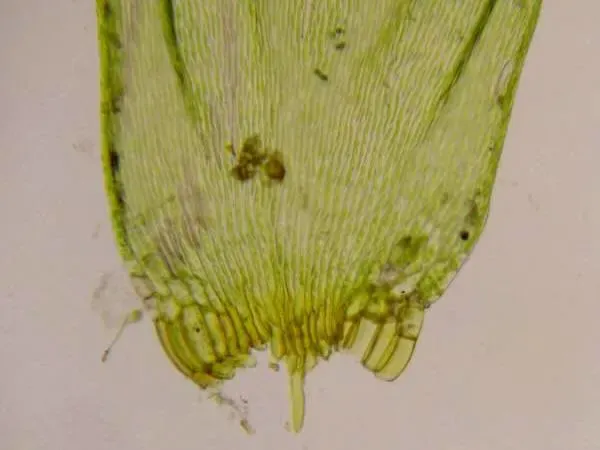 d1fb042d56d8fa121690d7613c5c8bfa.jpg from: https://blog.goo.ne.jp/mossphoenix/e/58a09a0f9594ab500e01773dcd923bd3 |
Desiccation tolerance, dormancy |
Conclusion
The Sematophyllum subpinnatum (Brid.) E.Britton
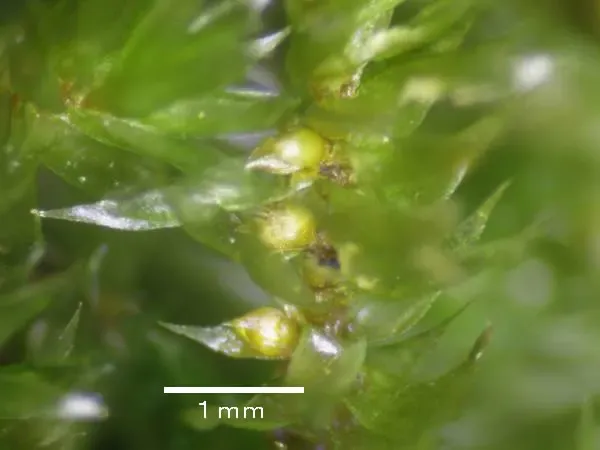

6fec1baa9f14c2a3951b1af404a69490.jpg from: https://blog.goo.ne.jp/mossphoenix/e/0561d393bd70ca9294b363c5949e7de9
moss is a true marvel of nature, showcasing the incredible diversity and resilience of the bryophyte kingdom. From its intricate morphology and adaptations to its ecological significance and potential applications, this moss continues to captivate and inspire moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike. As we delve deeper into the world of bryophytes, we are reminded of the intricate tapestry of life that surrounds us, and the importance of preserving and appreciating these often-overlooked wonders of the natural world.
21398216688_6c51d2c9fd_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/48126735@N03/21398216688/

f98a099bec9746963ec8f2431ce30df5.jpg from: https://blog.goo.ne.jp/mossphoenix/e/3197388033cd01ab691c25e25065e979

a-Fossombronia-sp-Gametophyte40x-b-Sematophyllum-subpinnatum-Brid-EGBritton.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-Fossombronia-sp-Gametophyte40x-b-Sematophyllum-subpinnatum-Brid-EGBritton_fig6_344717960
Thought-provoking question: In an era of rapid urbanization and environmental challenges, how can we leverage the remarkable adaptations of mosses like the Sematophyllum subpinnatum to create more sustainable and resilient urban environments?