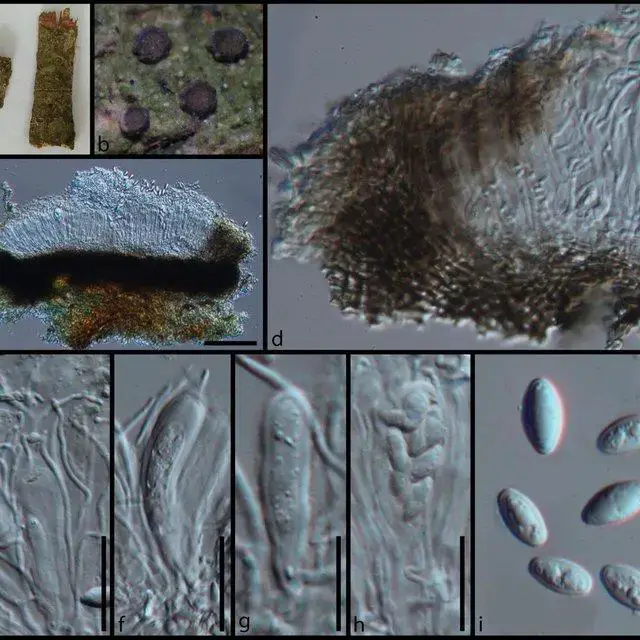
Morphology-of-Malmidea-subaurigera-MFLU-18-0692-a-Substrate-b-Ascomata-on-wood-c_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Morphology-of-Fitzroyomyces-cyperacearum-MFLU-18-0695a-a-Substrate-b-Ascomata-on_fig13_333058443
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Symbiezidium transversale (Sw.) Trevis. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Lejeuneaceae family. Often referred to simply as Symbiezidium

OpegraphaphysciariaNylDHawkswCoppins1606431065.jpg from: https://italic.units.it/index.php?procedure=taxonpage&num=2662
, this diminutive yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this extraordinary species.
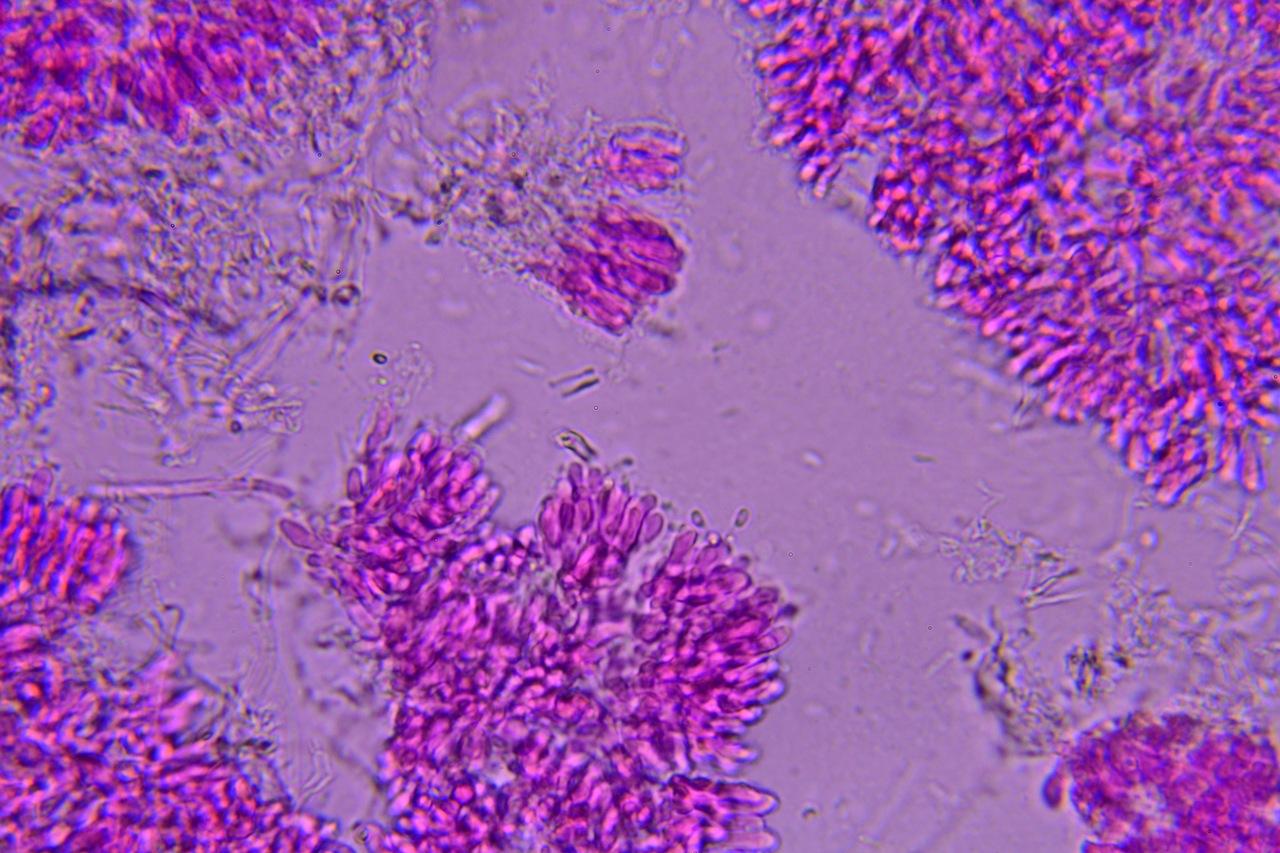
982670.jpg from: https://mushroomobserver.org/352187
Background
Before we explore the intricate details of Symbiezidium transversale, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. As members of the phylum

image-asset.jpeg from: https://www.exoticaesoterica.com/magazine/platycerium-madagascariense-waffles-and-dream
Marchantiophyta
d8bb15a9e461e19ddeec04227afb7acb–cross-section-jamur.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/109001253457552567/
and the class Jungermanniopsida, mosses like Symbiezidium are true marvels of nature, showcasing remarkable adaptations and ecological significance.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Symbiezidium transversale is a tiny, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on the surfaces it inhabits. Its delicate leaves are arranged in a distinctive spiral pattern, creating a visually striking and intricate tapestry. The leaves themselves are transversely inserted, a characteristic that lends this moss its specific epithet, “
Coupe-geologique-du-ravin-de-Facqueval-Hance-1984_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Coupe-transversale-SW-NE-schematique-a-travers-les-formations-du-Devonien-inferieur-aux_fig1_269697976
transversale.”
One of the most remarkable features of Symbiezidium is its ability to produce specialized reproductive structures called gemmae. These tiny, disc-shaped propagules are capable of developing into new moss plants, allowing for efficient dispersal and colonization of new habitats.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Symbiezidium transversale is widely distributed across various regions of the world, thriving in both tropical and temperate climates. It can be found growing on tree bark, rocks, and even soil, showcasing its adaptability to diverse substrates. This moss is particularly fond of moist, shaded environments, where it can take advantage of the consistent moisture and protection from direct sunlight.
A-D-Morphological-differentiation-of-symbiosomes-during-the-Rhizobium-etli-Phaseolus.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-D-Morphological-differentiation-of-symbiosomes-during-the-Rhizobium-etli-Phaseolus_fig3_12444290
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Symbiezidium transversale plays a vital role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it contributes to the formation of soil and the establishment of more complex plant communities. Additionally, its dense mats provide a microhabitat for various invertebrates, fungi, and other microorganisms, fostering biodiversity in the areas it inhabits.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Symbiezidium is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, this moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving itself once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments with fluctuating moisture levels, further contributing to its widespread distribution.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the tropical rainforests of Costa Rica, researchers discovered a diverse array of Symbiezidium species, including S. transversale, growing on the bark of various tree species. This study highlighted the importance of these mosses in maintaining the delicate balance of the ecosystem and providing microhabitats for other organisms.
Technical Table

Polychidium-muscicola_3_Sharnoff_1318_01.jpg from: https://lichenportal.org/portal/taxa/index.php?taxon=56014
sezione-trasversale-del-midollo-spinale-illustrazione-2gdjmdj.jpg from: https://www.alamy.it/fotos-immagini/midollo-spinale-3d.html?page=2

23611.jpg from: http://biogeodb.stri.si.edu/bioinformatics/dfm/metas/view/23611
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Lejeuneaceae |
| Genus | Symbiezidium |
| Species | transversale (Sw.) Trevis. |
| Growth Form | Creeping, forming dense mats or cushions |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spirally arranged, transversely inserted |
| Reproduction | Gemmae (specialized propagules) |
| Habitat | Tree bark, rocks, soil (moist, shaded environments) |
| Distribution | Widespread in tropical and temperate regions |
Conclusion
The Symbiezidium transversale (Sw.) Trevis. moss, a member of the Lejeuneaceae family, is a true testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. From its intricate morphology and specialized reproductive structures to its ecological significance and adaptations, this moss captivates the minds of enthusiasts worldwide. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, let us ponder: What other hidden gems await discovery in the realm of these unassuming yet remarkable plants?