
Woolly-Fringe-moss-Racomitrium-lanuginosum-from-Teesdale-1500×1125.jpg from: https://www.nhsn.org.uk/the-hidden-world-of-bryophytes-in-the-north-east/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out as a true marvel – the Symbiezidium Trevis. moss. Belonging to the Lejeuneaceae family, this diminutive yet extraordinary plant is also commonly referred to as Symbiezidium. Prepare to embark on a fascinating journey through the intricate realm of this remarkable moss, where we’ll unravel its secrets and appreciate its unique place in the natural world.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Symbiezidium Trevis. moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. This moss belongs to the phylum

Schistidium-rivulare-immature-700×465.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/bryology-plants/
Marchantiophyta, which encompasses all liverworts, hornworts, and mosses. More specifically, it falls under the class Jungermanniopsida

il_1588xN.3170569044_kkgn.jpg from: https://www.etsy.com/uk/listing/1028598598/cinclidium-stygium-lurid-cupola-moss
, a group of leafy liverworts known for their intricate and delicate structures.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Symbiezidium Trevis. moss is a true masterpiece of nature, with its intricate and delicate morphology. This tiny plant boasts a creeping growth habit, forming dense mats or cushions on the surfaces it inhabits. Its leaves are incredibly small, often measuring just a few millimeters in length, and are arranged in a distinctive spiral pattern around the stem.

3d7ebb0f2a872823f18bb34396ee549d.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/394416879846478551/
One of the most remarkable features of Symbiezidium is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. During the sexual reproductive cycle, it produces specialized structures called archegoniophores and antheridiophores, which bear the female and male reproductive organs, respectively.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Symbiezidium Trevis. moss is widely distributed across various regions of the world, thriving in a diverse range of habitats. From the temperate forests of North America and Europe to the tropical rainforests of South America and Southeast Asia, this resilient moss can be found clinging to tree bark, rocks, and even soil.

Figure_25_03_07-300×212.jpg from: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wm-biology2/chapter/bryophytes/
Its ability to adapt to different environments is truly remarkable, as it can survive in both moist and relatively dry conditions. However, Symbiezidium tends to favor shaded and humid environments, where it can flourish and form dense carpets on the surfaces it colonizes.

berke17.jpg from: https://www.delta-intkey.com/britms/www/mniaceae.htm
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Symbiezidium Trevis. moss plays a crucial role in various ecosystems. These tiny plants act as pioneers, often being among the first to colonize bare surfaces and pave the way for other organisms to establish themselves.
br-179a10.jpg from: https://www.dorsetnature.co.uk/pages-bry/br-179.html
One of the most fascinating adaptations of Symbiezidium is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, these mosses can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This remarkable trait allows them to survive in environments where water availability is unpredictable.
Case Studies/Examples
To illustrate the significance of Symbiezidium Trevis. moss, let’s explore a case study from the temperate forests of North America. In these ecosystems, Symbiezidium often forms dense mats on the bark of trees, creating a microhabitat for a diverse array of invertebrates, such as mites, springtails, and even tiny snails.
These moss-dwelling communities play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and decomposition processes, contributing to the overall health and functioning of the forest ecosystem.
Technical Table
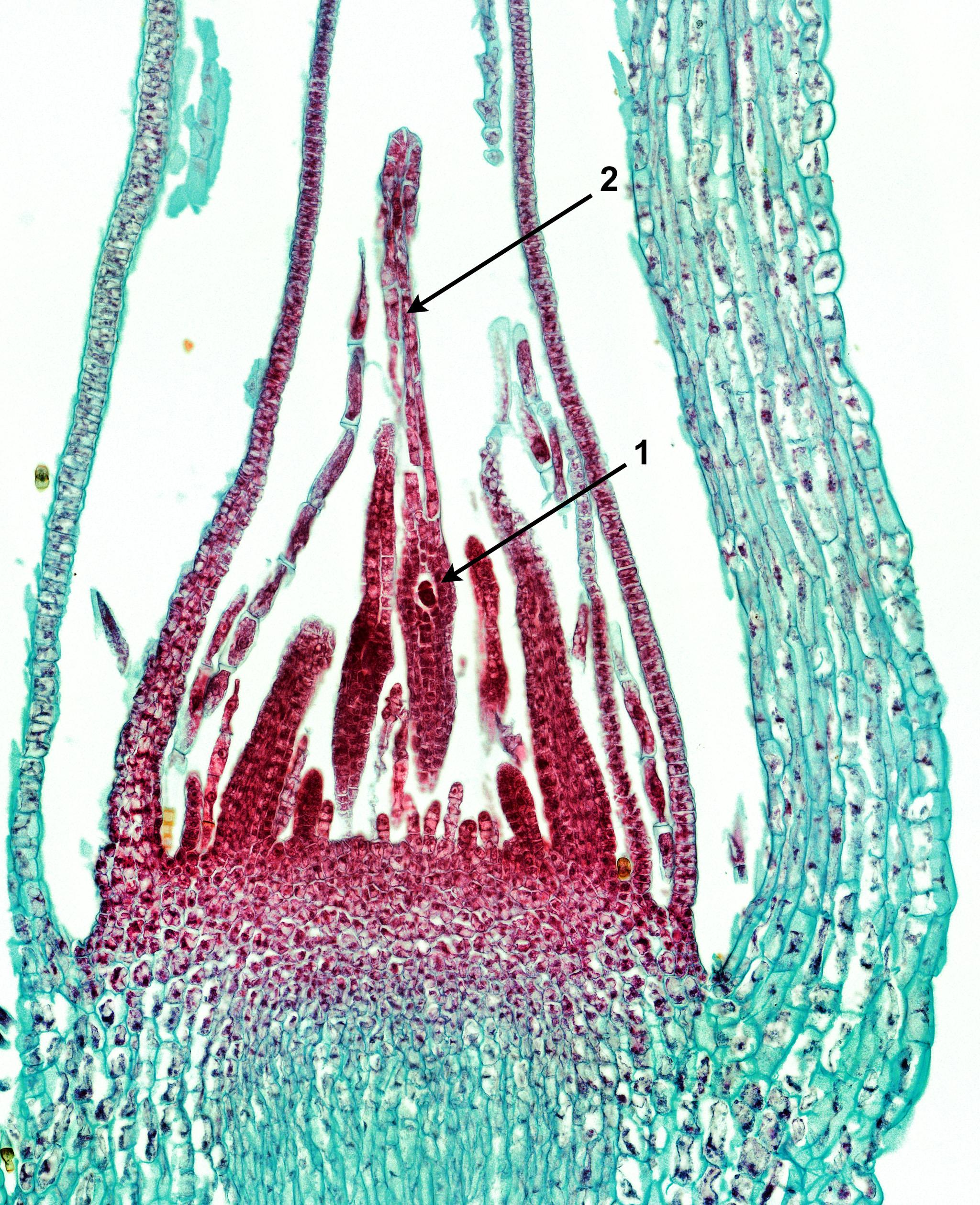
Moss-archegonium-egg-cell_zoom.jpg from: https://www.vcbio.science.ru.nl/virtuallessons/mosses/

35237c4e7f70daa558f4b9d25070ef26.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/465841155176765228/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Family | Lejeuneaceae |
| Common Name | Symbiezidium |
| Growth Habit | Creeping, forming mats or cushions |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spiral |
| Reproduction | Sexual and asexual |
| Habitat | Tree bark, rocks, soil |
| Distribution | Widespread globally |
| Ecological Role | Pioneer species, microhabitat provider |
| Adaptation | Desiccation tolerance |
Conclusion
Symbiezidium Trevis. moss, a true marvel of the bryophyte world, has captured our hearts and minds with its intricate beauty, remarkable adaptations, and vital ecological roles. From its delicate morphology to its global distribution and ability to withstand harsh conditions, this moss serves as a testament to the resilience and diversity of life on our planet.
As we bid farewell to this captivating journey, a thought-provoking question lingers: In a world where biodiversity is under constant threat, how can we ensure the preservation of these extraordinary yet often overlooked organisms, like Symbiezidium Trevis. moss, for generations to come?

Marchantiophyta-Lejeuneaceae-A-Ceratolejeunea-cornuta-B-Cheilolejeunea-rigidula-C_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Marchantiophyta-Lejeuneaceae-A-Ceratolejeunea-cornuta-B-Cheilolejeunea-rigidula-C_fig4_366700307