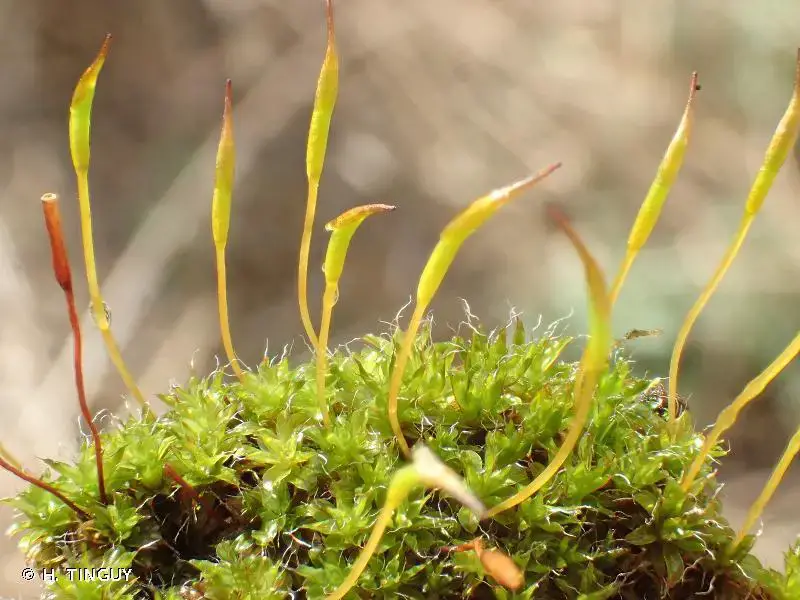

254333.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/434233?lg=en
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its resilience and adaptability – the Syntrichia laevipila Brid., also known simply as Syntrichia. This unassuming yet remarkable member of the Pottiaceae family has carved out a niche for itself across diverse habitats, playing a crucial role in various ecosystems.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Syntrichia laevipila Brid., it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but are vital components of many terrestrial ecosystems. They act as pioneers, colonizing bare surfaces and paving the way for more complex plant communities to thrive.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
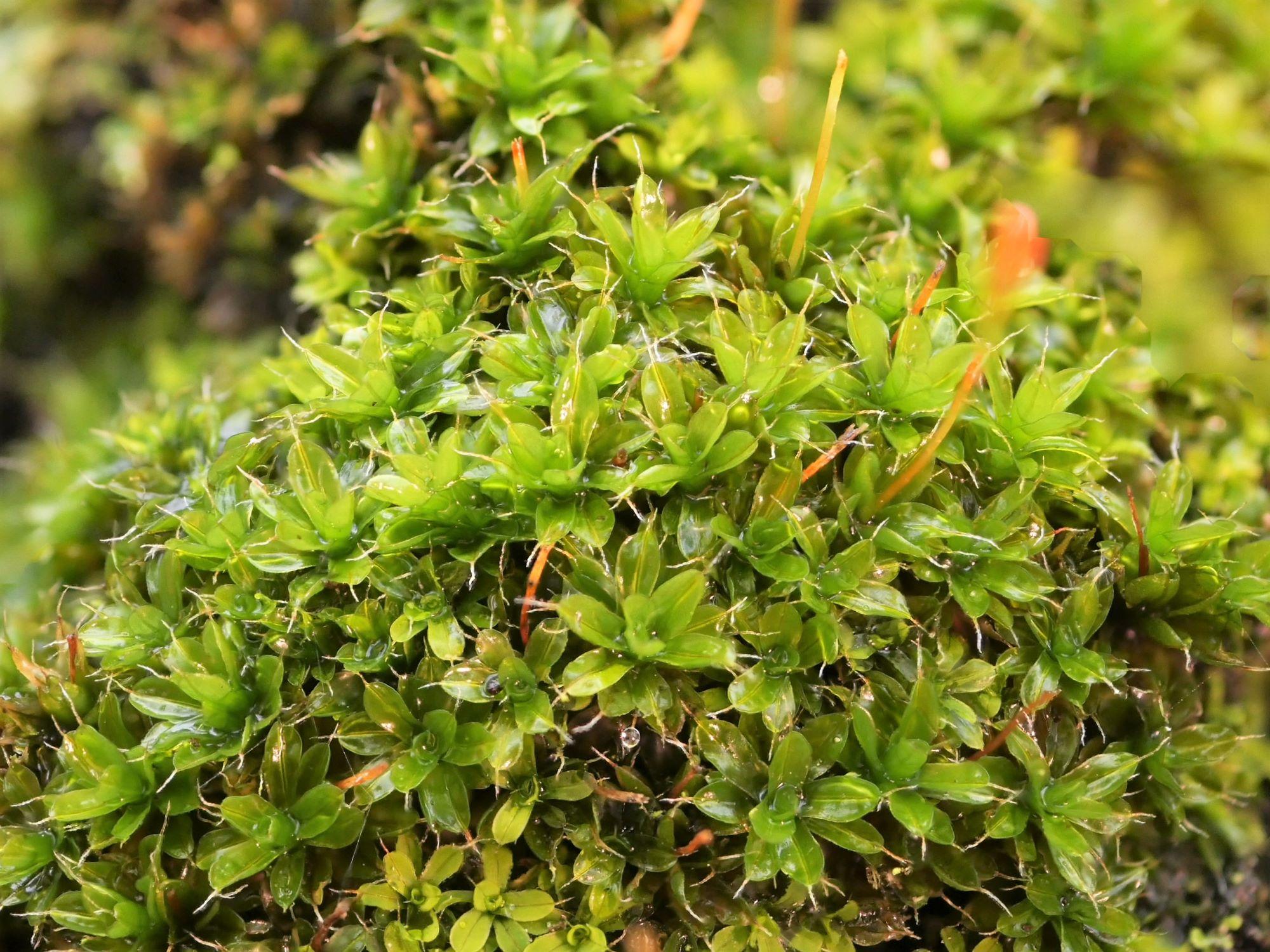

Syntrichia-laevipila-1.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/syntrichia-laevipila/
Syntrichia laevipila Brid. is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are
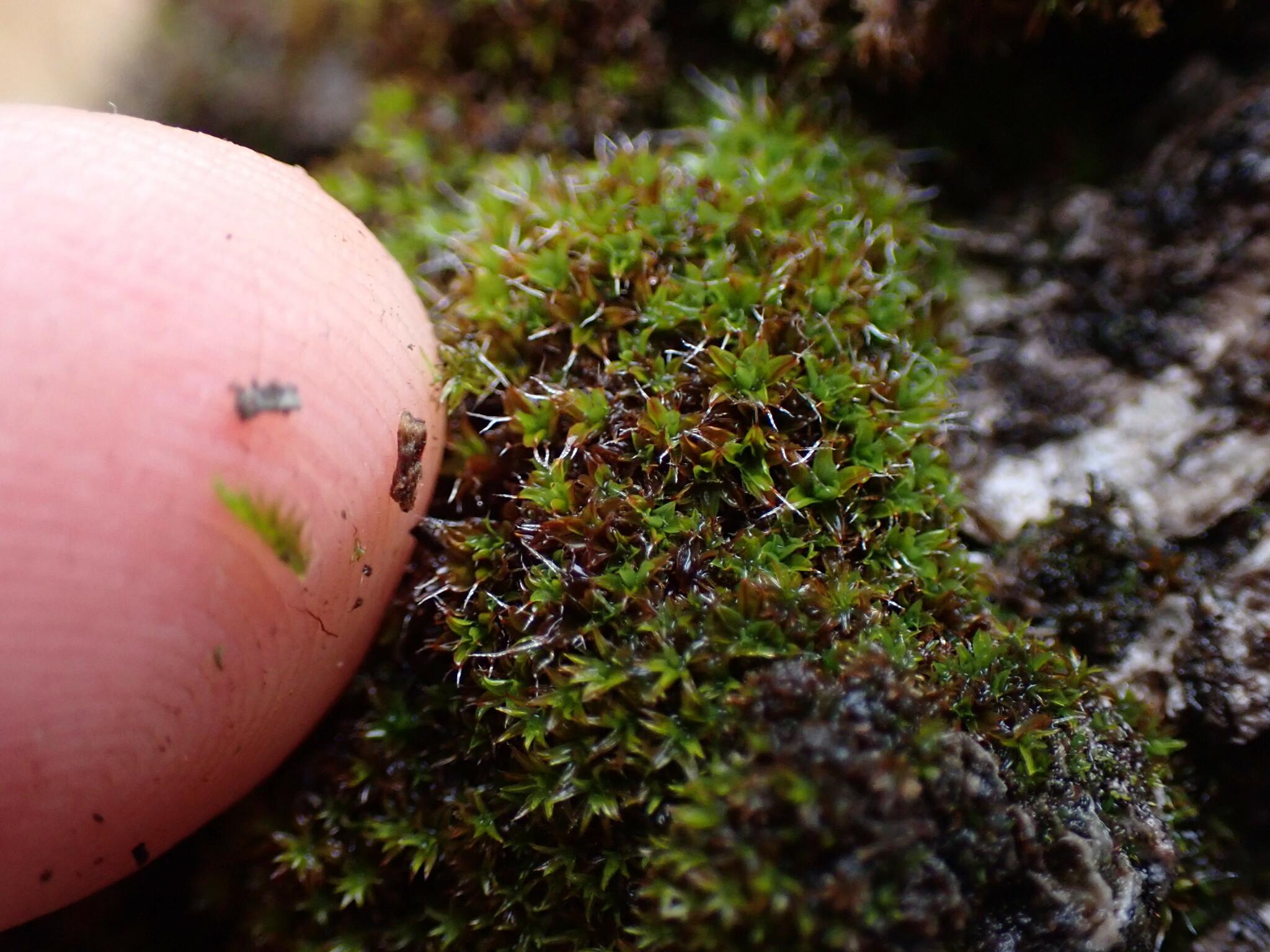

original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2671290
lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a short hair point. The capsules, which contain the spores, are cylindrical and erect, supported by a reddish-brown seta (stalk).
Global Distribution and Habitat
This resilient moss species has a cosmopolitan distribution, meaning it can be found on almost every continent, thriving in a wide range of habitats. From arid and semi-arid regions
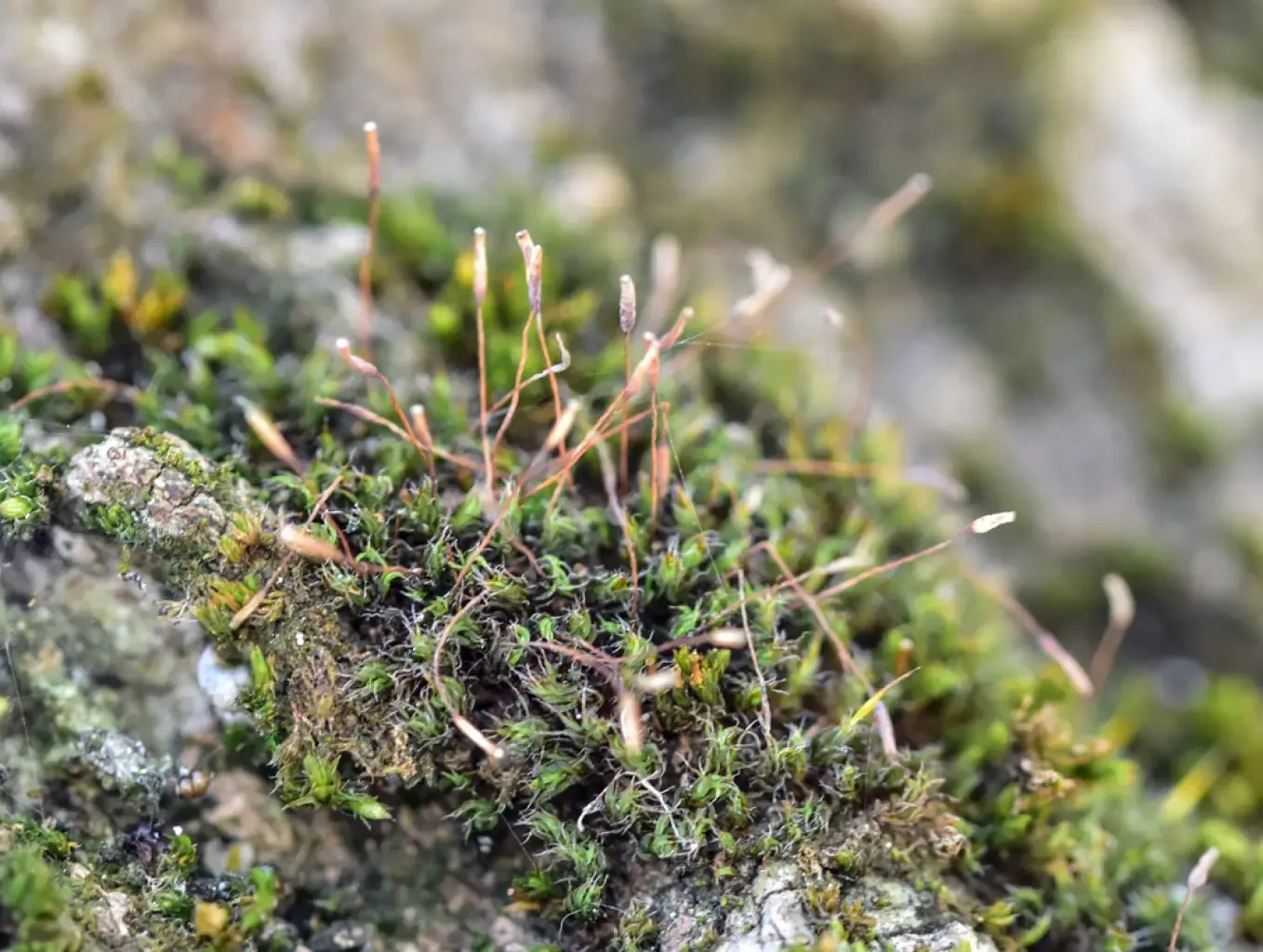

b9370be1f171991498a494026b5d671c.jpg from: https://www.asturnatura.com/fotografia/flora/syntrichia-laevipila-1-de-6/40051.html
to temperate and boreal zones, Syntrichia laevipila Brid. has adapted to survive in diverse environments. It commonly grows on soil, rocks, tree bark, and even concrete surfaces, showcasing its remarkable ability to colonize various substrates.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size,
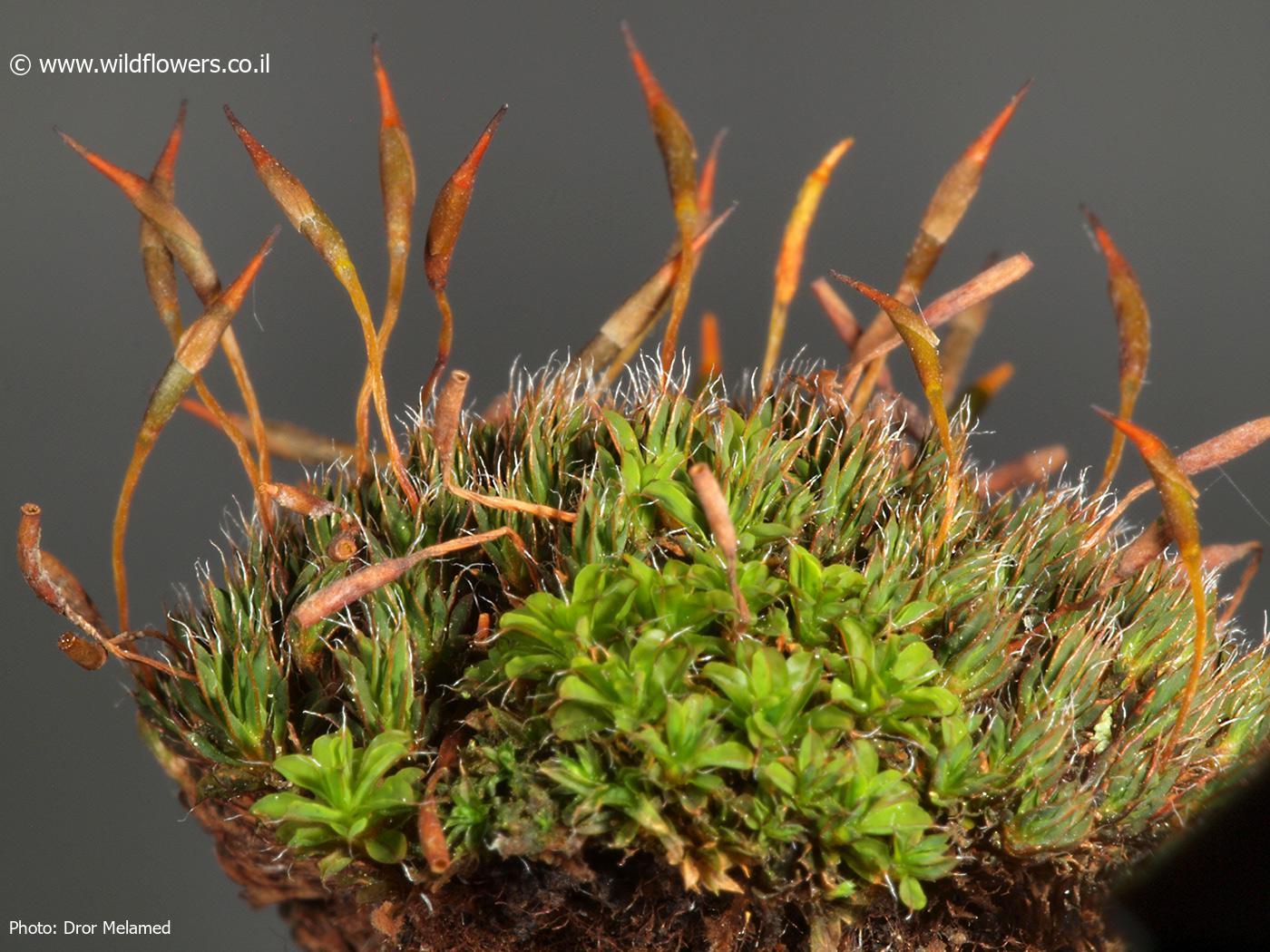

3286-l-3.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=20105
Syntrichia laevipila Brid. plays a vital role in ecosystem functioning. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, facilitating the establishment of other plants. Additionally, it serves as a microhabitat
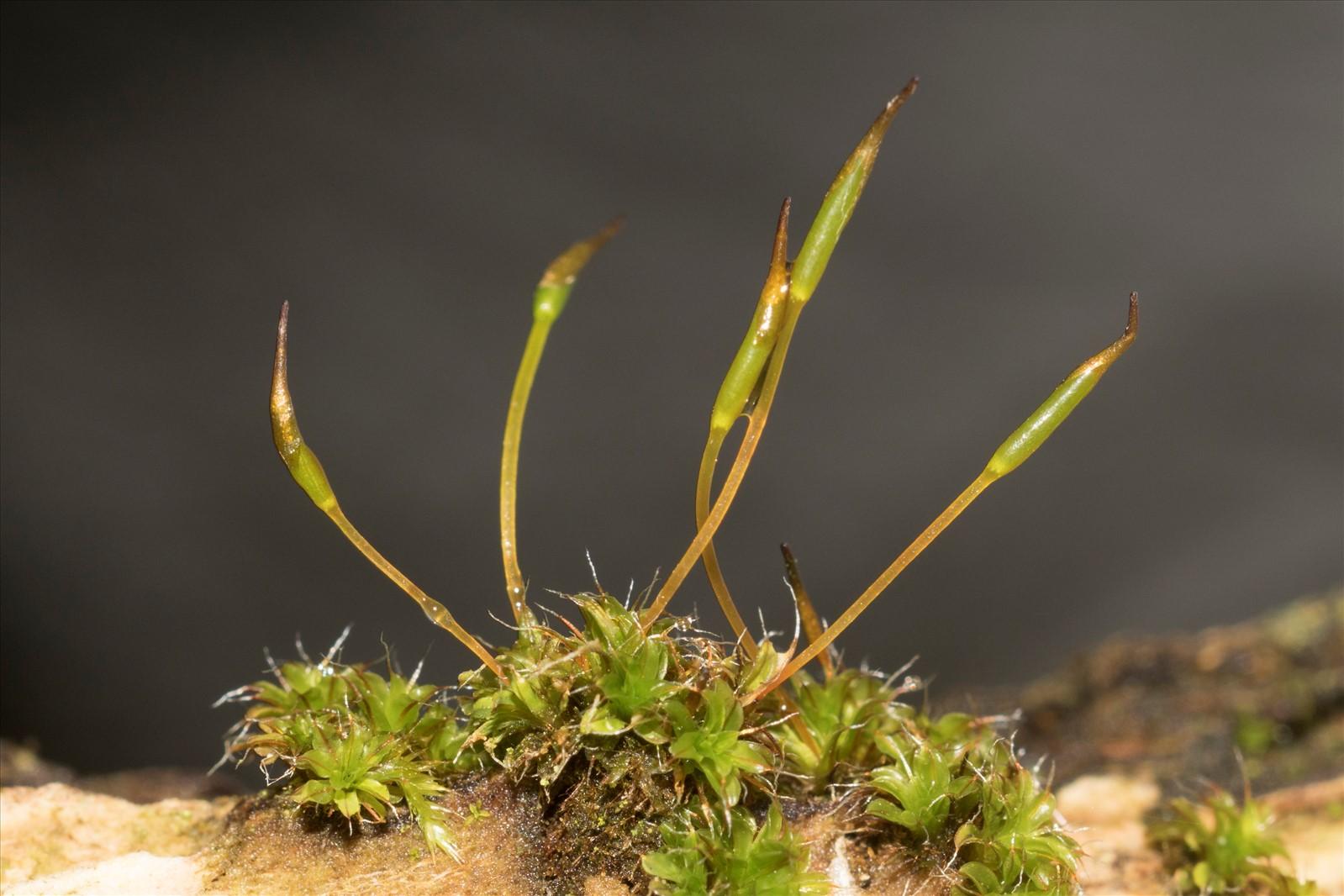

DSC04495_1600.jpg from: https://www.preservons-la-nature.fr/flore/taxref/43158.html
for numerous invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the key adaptations that enable Syntrichia laevipila Brid. to thrive in harsh environments is its ability to undergo desiccation tolerance. During periods of drought, the moss can essentially “shut down” its metabolic processes and enter a state of dormancy, only to revive when moisture becomes available again. This remarkable trait allows it to survive in areas where water is scarce.
Case Studies/Examples
The versatility and resilience of Syntrichia laevipila Brid. have been demonstrated in various studies and observations. For instance, researchers have documented its ability to colonize post-mining sites, playing a crucial role in the early stages of ecological restoration. Additionally, this moss has been found growing on historic buildings and monuments, highlighting its ability to adapt to human-made environments.
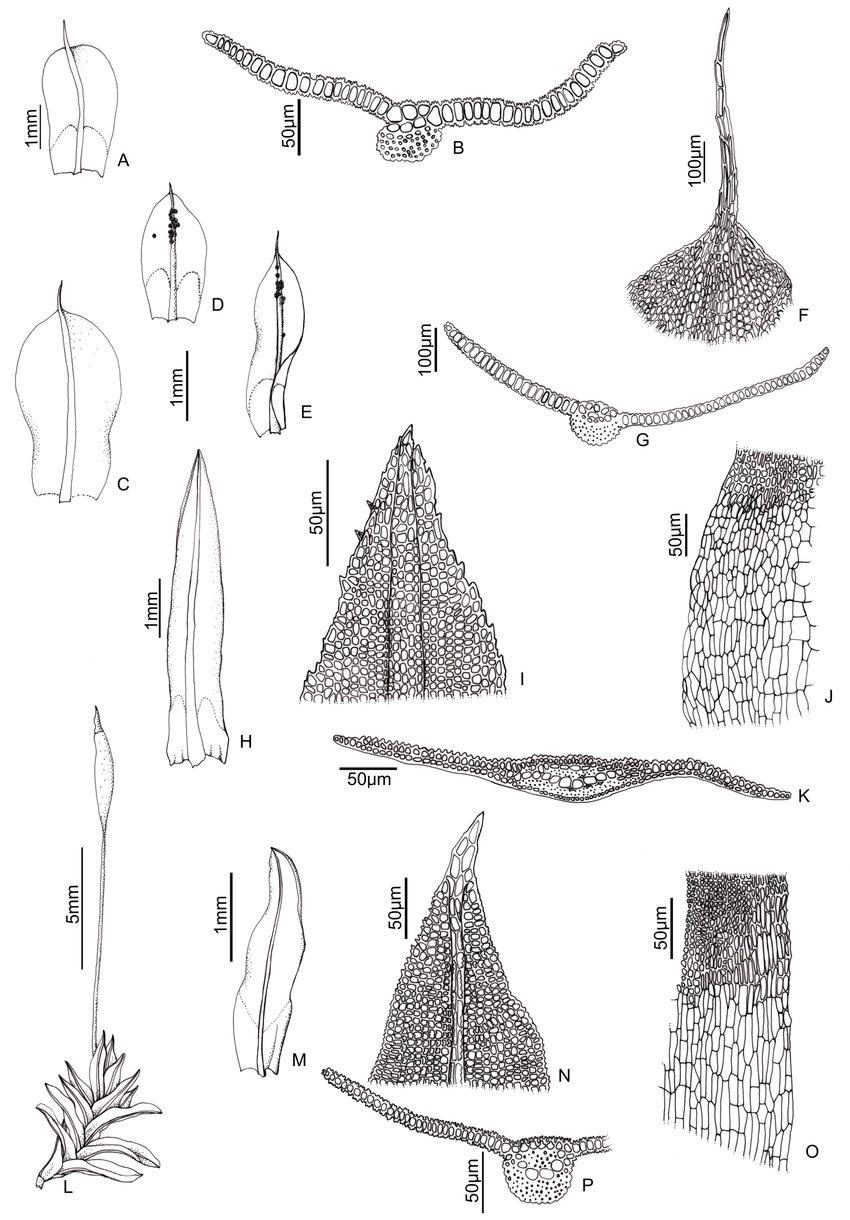
Syntrichia-laevipila-Brid-A-Leaf-B-Leaf-section-Syntrichia-papillosa-Wils-ex.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Syntrichia-laevipila-Brid-A-Leaf-B-Leaf-section-Syntrichia-papillosa-Wils-ex_fig8_296705710
Technical Table
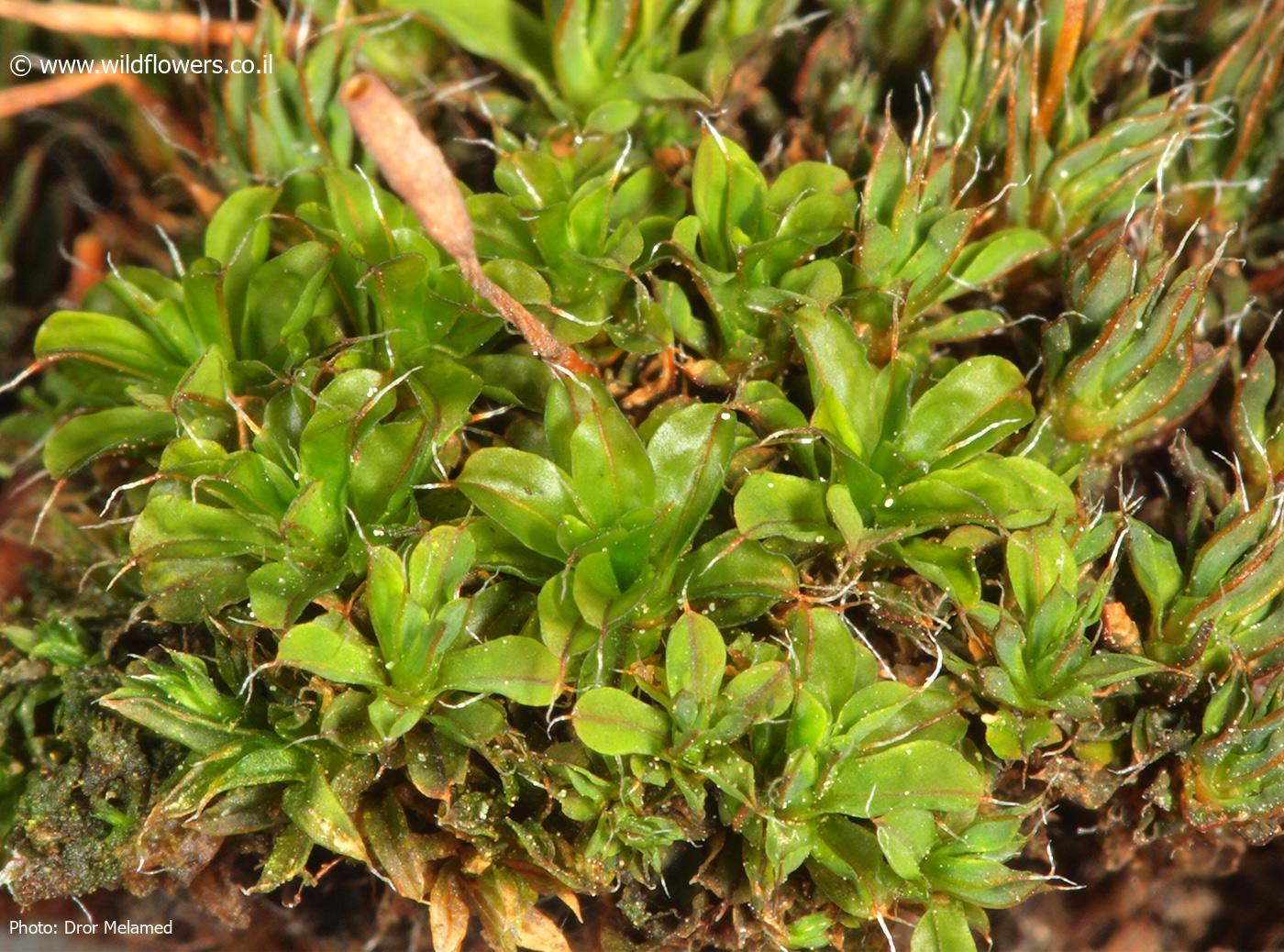

3286-l-5.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=20107
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Syntrichia |
| Species | laevipila Brid. |
| Growth Form | Dense cushions or mats |
Leaf Shape
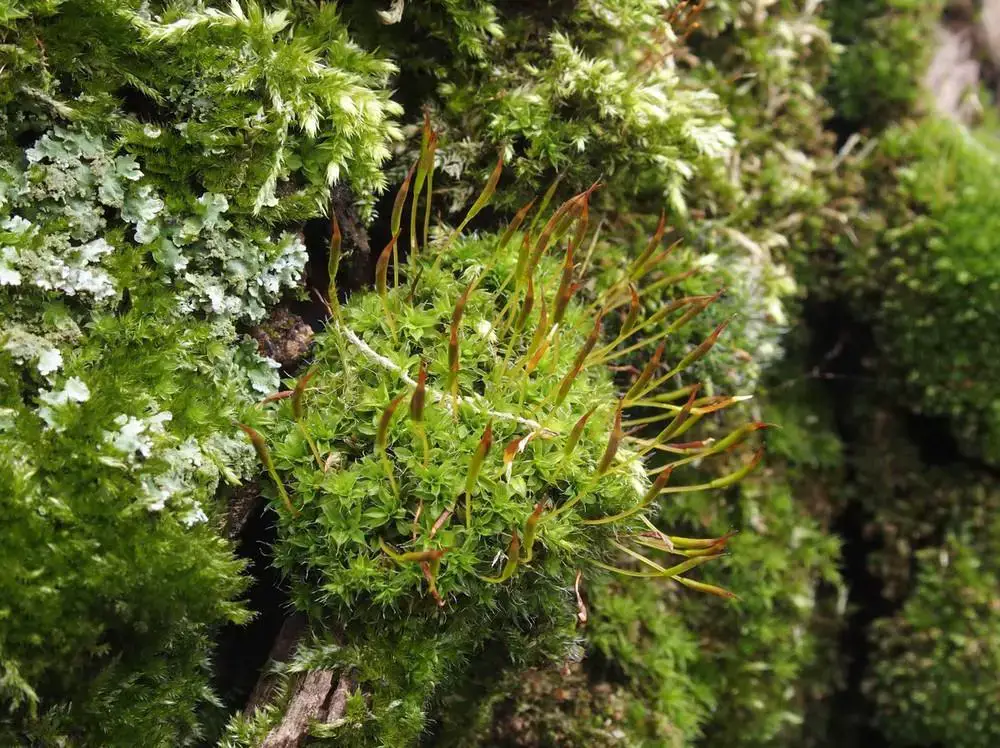 33794275.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/208704773?_popup=1 |
Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Capsule | Cylindrical, erect |
| Seta | Reddish-brown |
Conclusion
In the intricate tapestry of bryophytes, Syntrichia laevipila Brid. stands as a testament to the remarkable adaptability and resilience of these often-overlooked organisms. From its ability to colonize diverse habitats to its vital ecological roles, this moss species reminds us of the importance of appreciating and preserving even the smallest components of our natural world. As we continue to explore and understand the wonders of bryophytes, perhaps the question we should ask ourselves is: What other hidden gems await discovery in the realm of these unassuming yet extraordinary plants?

s._laevipila_by_erika_almeida4.jpg from: https://www.viva.fct.unl.pt/liquenes/syntrichia-laevipila