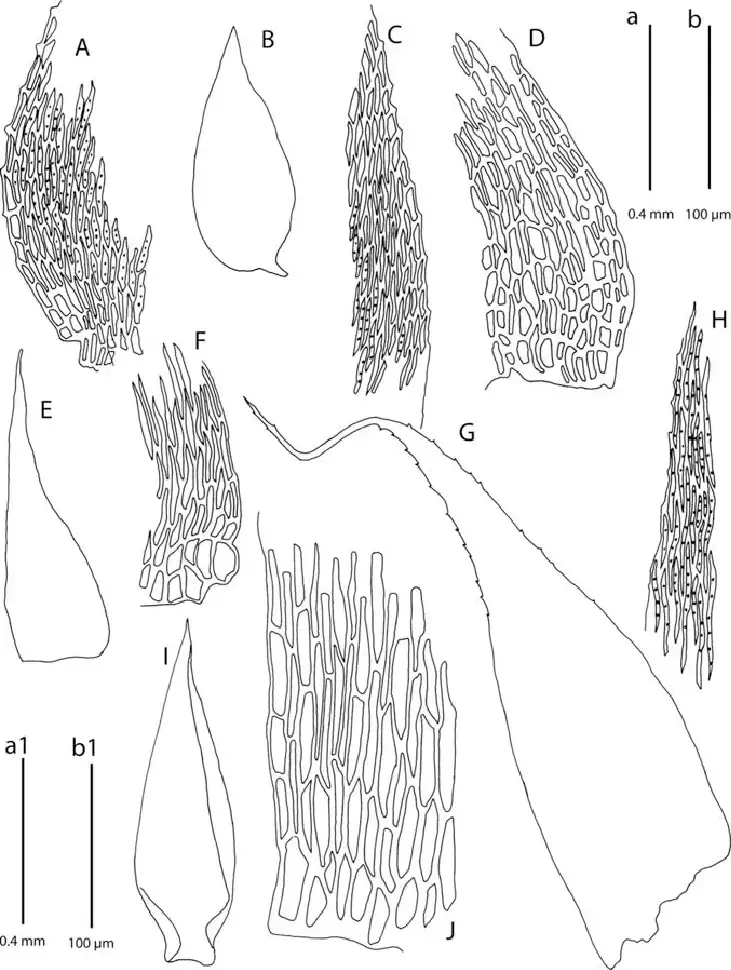
A-E-Taxithelium-kaernbachii-A-Alar-cells-B-Branch-leaf-C-Leaf-margin-cells-D.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-E-Taxithelium-kaernbachii-A-Alar-cells-B-Branch-leaf-C-Leaf-margin-cells-D_fig2_232683560
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Taxithelium kaernbachii (Broth.) Broth. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Pylaisiadelphaceae family. This unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide, offering a unique glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Taxithelium kaernbachii, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, collectively known as
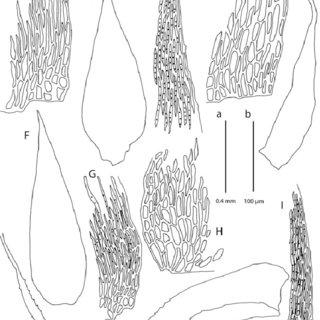
A-E-Taxithelium-vernieri-A-Alar-cells-B-Branch-leaf-C-Leaf-margin-cells-D_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Taxithelium-ramivagum-A-Alar-cells-B-Branch-leaf-C-Leaf-margin-cells-D_fig8_232683560
Bryophyta, encompass mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and play crucial roles in various ecosystems.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Taxithelium kaernbachii is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its delicate fronds form dense, velvety mats or cushions, often adorning tree trunks, rocks, or moist soil. The leaves are small, ovate to lanceolate in shape, and arranged in a spiral pattern along the stem. When viewed under a microscope, the leaf cells reveal a intricate pattern of hexagonal shapes, adding to the moss’s intricate beauty.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss species is widely distributed across various regions, including
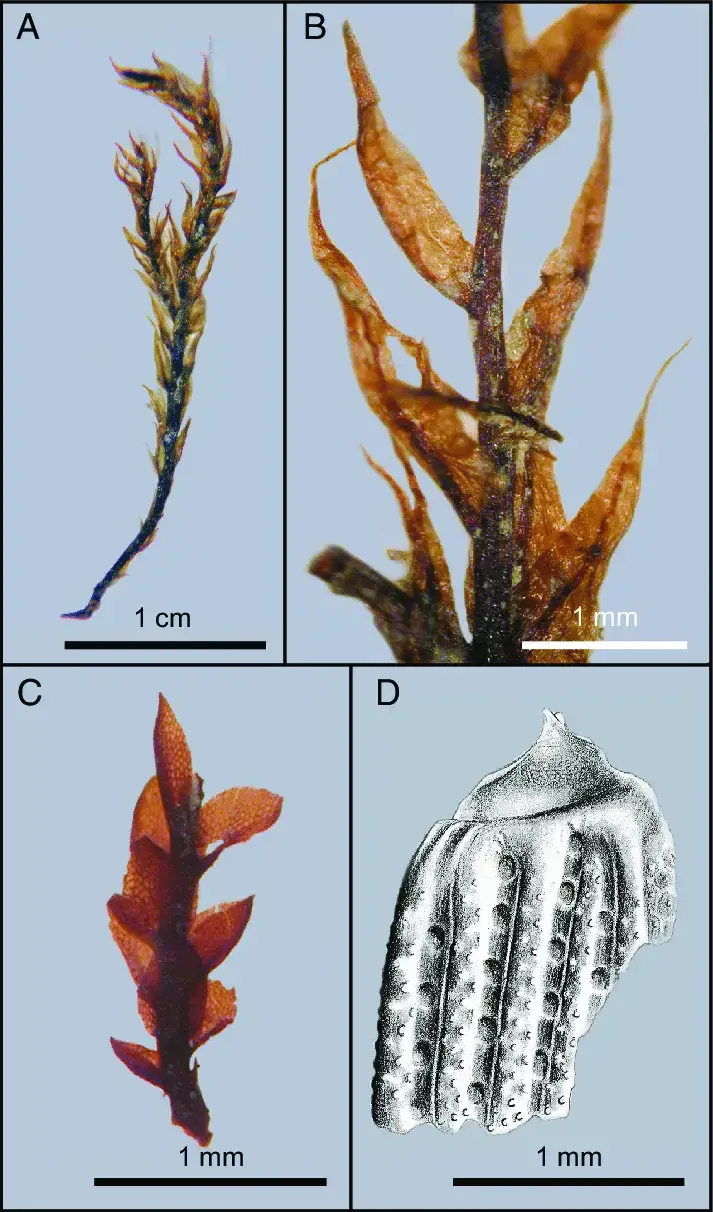
Fossil-mosses-and-a-beetle-A-Stem-and-leaves-of-the-semiaquatic-moss-Drepanocladus.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fossil-mosses-and-a-beetle-A-Stem-and-leaves-of-the-semiaquatic-moss-Drepanocladus_fig3_23148177
North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, such as forests, ravines, and stream banks, where it can access the necessary moisture and humidity levels. Taxithelium kaernbachii is often found growing in association with other bryophyte species, forming diverse and vibrant moss communities.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
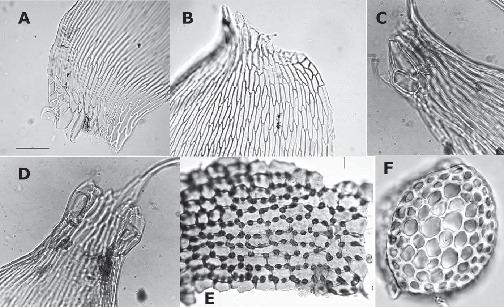
f01_07.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/systematic-botany/volume-36/issue-1/036364411X553081/A-Re-Circumscription-of-the-Moss-Genus-Taxithelium-Pylaisiadelphaceae-with/10.1600/036364411X553081.full
Despite its diminutive size, Taxithelium kaernbachii plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It acts as a sponge, absorbing and retaining moisture, creating a microhabitat for various invertebrates and providing a nursery for seedling establishment. Additionally, this moss contributes to soil formation and nutrient cycling, breaking down organic matter and releasing essential nutrients into the environment.
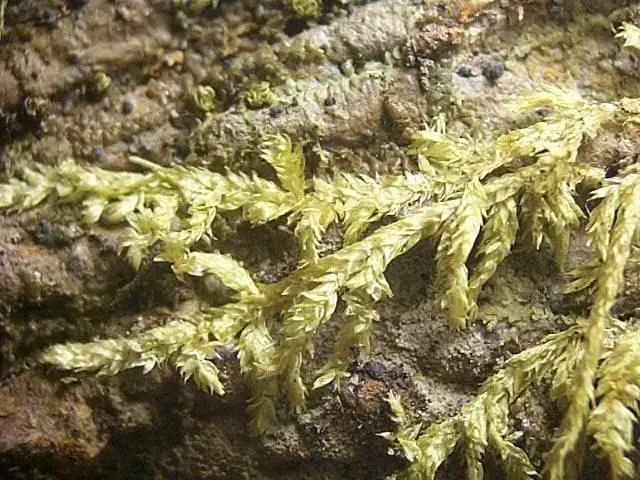

Taxithelium%2BPLANUM%2BC.jpg from: https://plantasdepuertorico.blogspot.com/2017/02/musgos-hypnales-taxithelium-planum.html
One of the remarkable adaptations of

taxithelium-mountain-forest-moss-background-260nw-2212821995.jpg from: https://www.shutterstock.com/image-photo/taxithelium-mountain-forest-moss-background-2212821995
Taxithelium kaernbachii is its ability to survive desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. Once moisture returns, it quickly revives, showcasing its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging conditions.
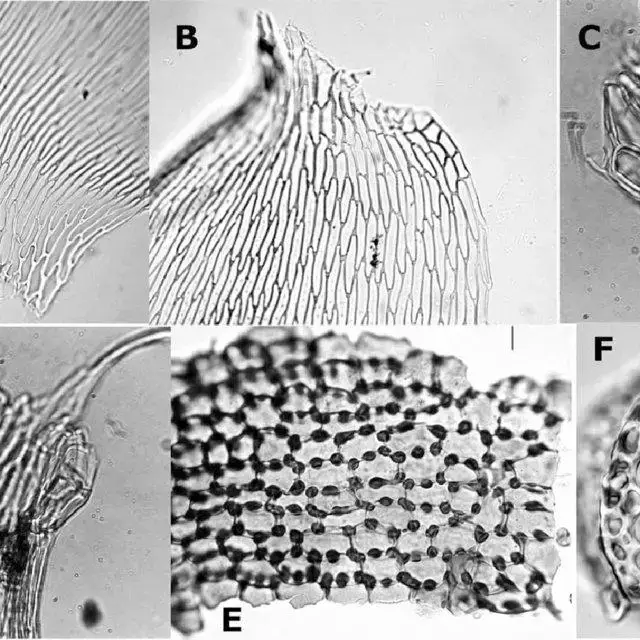
A-Poorly-developed-alar-cells-in-T-planissimum-400-B-Poorly-developed-alar-cells_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/232683560_A_Re-Circumscription_of_the_Moss_Genus_Taxithelium_Pylaisiadelphaceae_with_a_Taxonomic_Revision_of_Subgenus_Vernieri
Case Studies/Examples

392440.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5248

original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered a diverse array of bryophyte species, including Taxithelium kaernbachii, thriving in old-growth forests. These moss communities played a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of the ecosystem, providing habitat for various invertebrates and contributing to nutrient cycling.
Technical Table
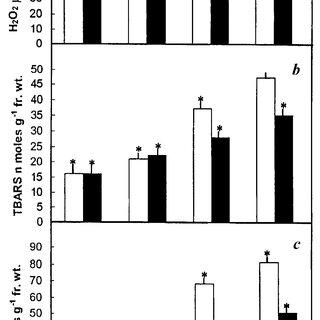
Changes-in-total-peroxide-a-TBARS-content-b-and-superoxide-anion-radical-production_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234129221_Induction_of_oxidative_stress_and_ultrastructuralchanges_in_moss_Taxitheliumnepalense_Schwaegr_Broth_underlead_and_arsenic_phytotoxicity
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Pylaisiadelphaceae |
| Genus | Taxithelium |
| Species | Taxithelium kaernbachii (Broth.) Broth. |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spiral |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to lanceolate |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | North America, Europe, Asia, Australia |
Conclusion
The Taxithelium kaernbachii (Broth.) Broth. moss, a member of the Pylaisiadelphaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its intricate beauty, ecological significance, and remarkable adaptations make it a fascinating subject for moss enthusiasts and nature lovers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the bryophyte world, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and preserve these delicate yet resilient organisms that play such vital roles in our ecosystems?