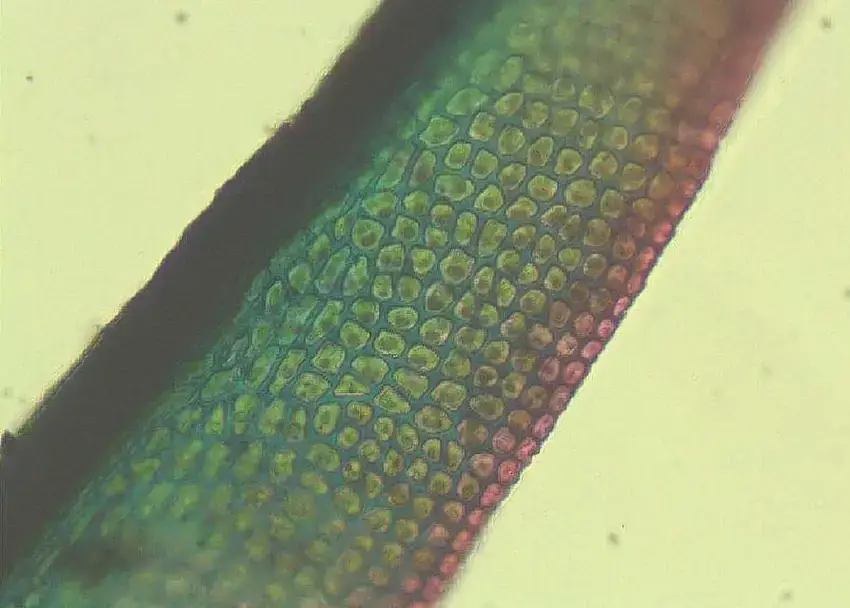
Hymenostylium-aurantiacum-distal-leaf-portion-showing-blue-green-collenchymatous-cells.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Hymenostylium-aurantiacum-distal-leaf-portion-showing-blue-green-collenchymatous-cells_fig9_289991659
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Hymenostylium dicranelloides Broth. ex Dixon moss stands out as a fascinating member of the Pottiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Hymenostylium, this unassuming yet resilient moss has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this remarkable plant and uncover its secrets.
343955.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5330?lg=en
Background
Before we explore the specifics of Hymenostylium dicranelloides, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.

Hymenostylium_recurvirostrum_011.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Hymenostylium_recurvirostrum_var_recurvirostrum.html
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
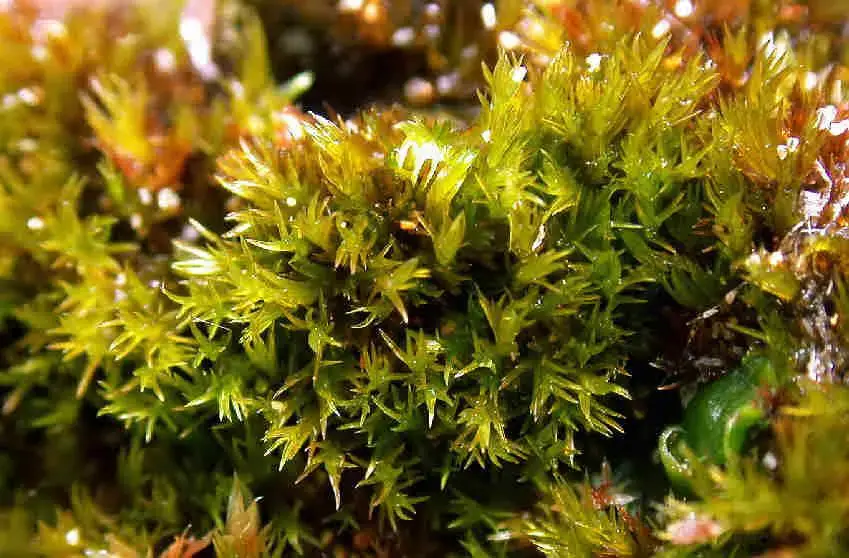
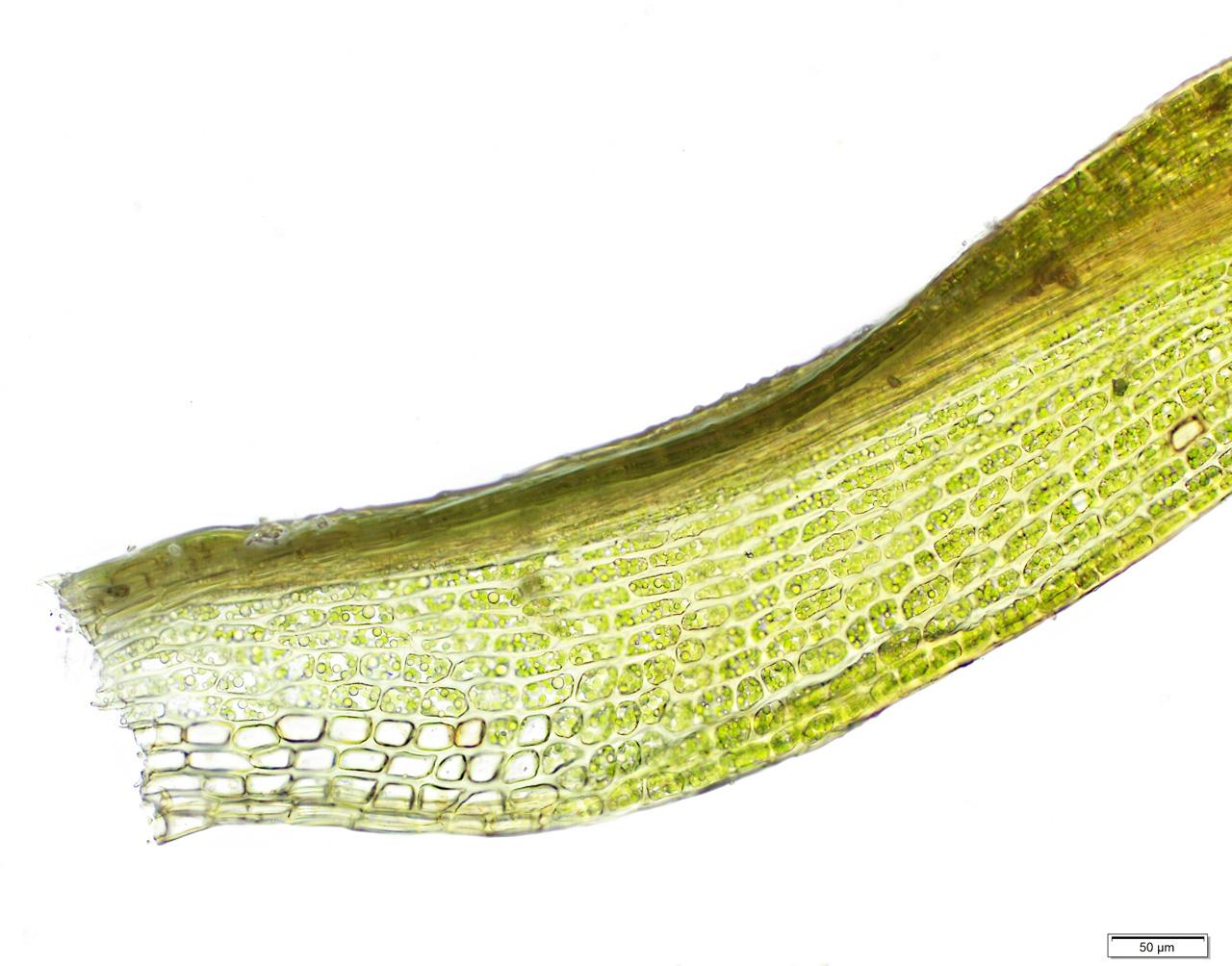
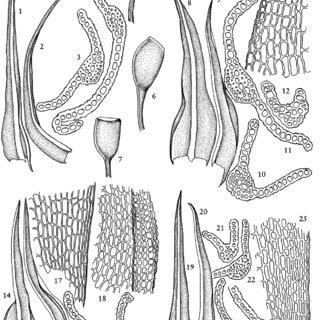
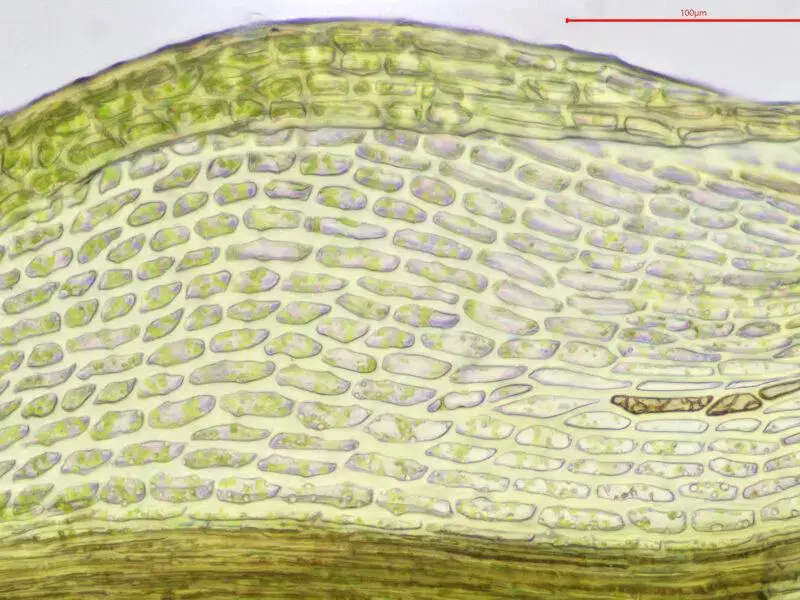
Hymenostylium dicranelloides is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its stems are typically unbranched, and the leaves are arranged in a spiral pattern. The leaves themselves are lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive midrib that extends to the leaf apex. One of the key identifying features of this moss is the presence of a hyaline (transparent) hair-point at the leaf tip.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss species has a widespread distribution, occurring on various continents, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and North America. It thrives in a range of habitats, from exposed soil and rock surfaces to disturbed areas such as roadsides and construction sites. Hymenostylium dicranelloides is particularly well-adapted to dry and nutrient-poor environments, making it a true survivor in challenging conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
209657.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5330
Despite its diminutive size, Hymenostylium dicranelloides plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and stabilization, helping to prevent erosion and providing a suitable environment for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, fungi, and other microorganisms, contributing to biodiversity.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Hymenostylium dicranelloides is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. When moisture becomes available again, it quickly revives, demonstrating its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the United Kingdom, researchers found that Hymenostylium dicranelloides played a crucial role in the colonization of newly created habitats, such as quarries and construction sites. Its ability to rapidly establish itself on bare soil and rock surfaces made it a pioneer species, paving the way for other plants to follow.
Technical Table

h_recurvirostrum1.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/hymenostylium_recurvirostrum.html
Ganoderma-curtisii-a-b-Sporocarp-showing-abhymenial-and-hymenial-surface-c.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Ganoderma-curtisii-a-b-Sporocarp-showing-abhymenial-and-hymenial-surface-c_fig5_322159030
Microscopic-structures-of-Xylodon-macrosporus-holotype-a-basidiospores-b-basidia.ppm from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Microscopic-structures-of-Xylodon-macrosporus-holotype-a-basidiospores-b-basidia_fig7_356215324
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Hymenostylium |
| Species | dicranelloides Broth. ex Dixon |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, with a hyaline hair-point |
| Habitat | Exposed soil, rock surfaces, disturbed areas |
| Distribution | Widespread across Europe, Asia, Africa, and North America |
Conclusion
The Hymenostylium dicranelloides Broth. ex Dixon moss, a member of the Pottiaceae
Hymenostylium-recurvirostrum-var-insigne-1-4-Guatemala-Steyermark-49998a-1-2_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Global-distribution-of-Hymenostylium-recurvirostrum-var-insigne_fig2_237495670
family, is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. Despite its unassuming appearance, this moss plays a vital role in its ecosystem, contributing to soil formation, providing microhabitats, and serving as a pioneer species in disturbed areas. Its ability to withstand desiccation and rapidly revive when moisture becomes available is a testament to its evolutionary success.

hymenostylium-recurvirostru.240×240-u1i1s1q90f1.jpg from: https://www.nzpcn.org.nz/flora/species/hymenostylium-recurvirostrum/
As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, the Hymenostylium dicranelloides serves as a reminder of the intricate web of life that surrounds us, even in the most unexpected places. Perhaps the next time you encounter a small, cushion-like moss, you’ll pause and appreciate the incredible journey of this unassuming yet remarkable plant.
2023-09-28-18-09-10-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/hymenostylium-recurvirostrum/