
010555711_1-d02ede7d9447e2c20a7809f1cd171241-768×994.png from: https://studylib.net/doc/10555711/rare-moss-and-lichen-surveys-of-blm-vale-district-aloina-…
Introduction
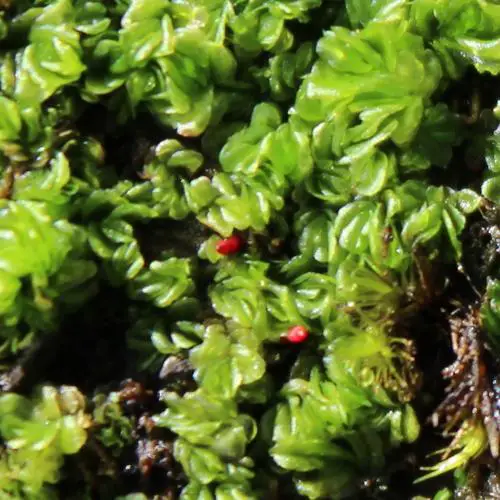
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one tiny moss stands out as a true marvel – the Aloina bifrons (De Not.) Delgad., commonly known as

medium.JPG from: https://enciclovida.mx/especies/147218-aloina-bifrons

largepreview.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274301744_Aloina_bifrons_De_Not_Delgad_Pottiaceae_Musci_in_Russia
Aloina. This diminutive plant belongs to the Pottiaceae family and is a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience found in the realm of mosses.
Background
Before we delve into the fascinating details of Aloina bifrons, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems worldwide. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
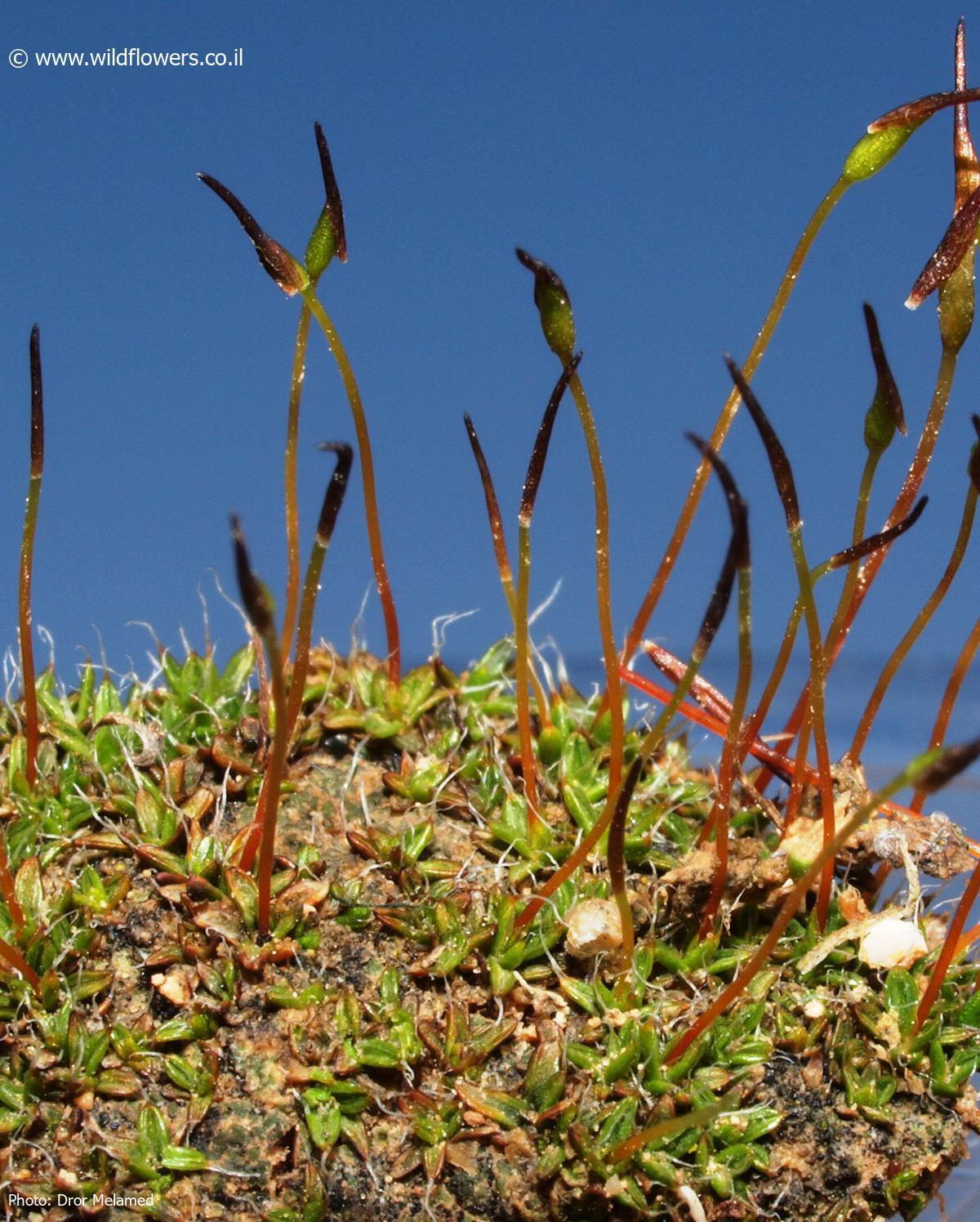
Aloina bifrons is a small acrocarpous moss, typically forming dense tufts or cushions. Its leaves are lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive bifid (split into two parts) apex. The leaf margins are entire (smooth), and the costa (midrib) is excurrent
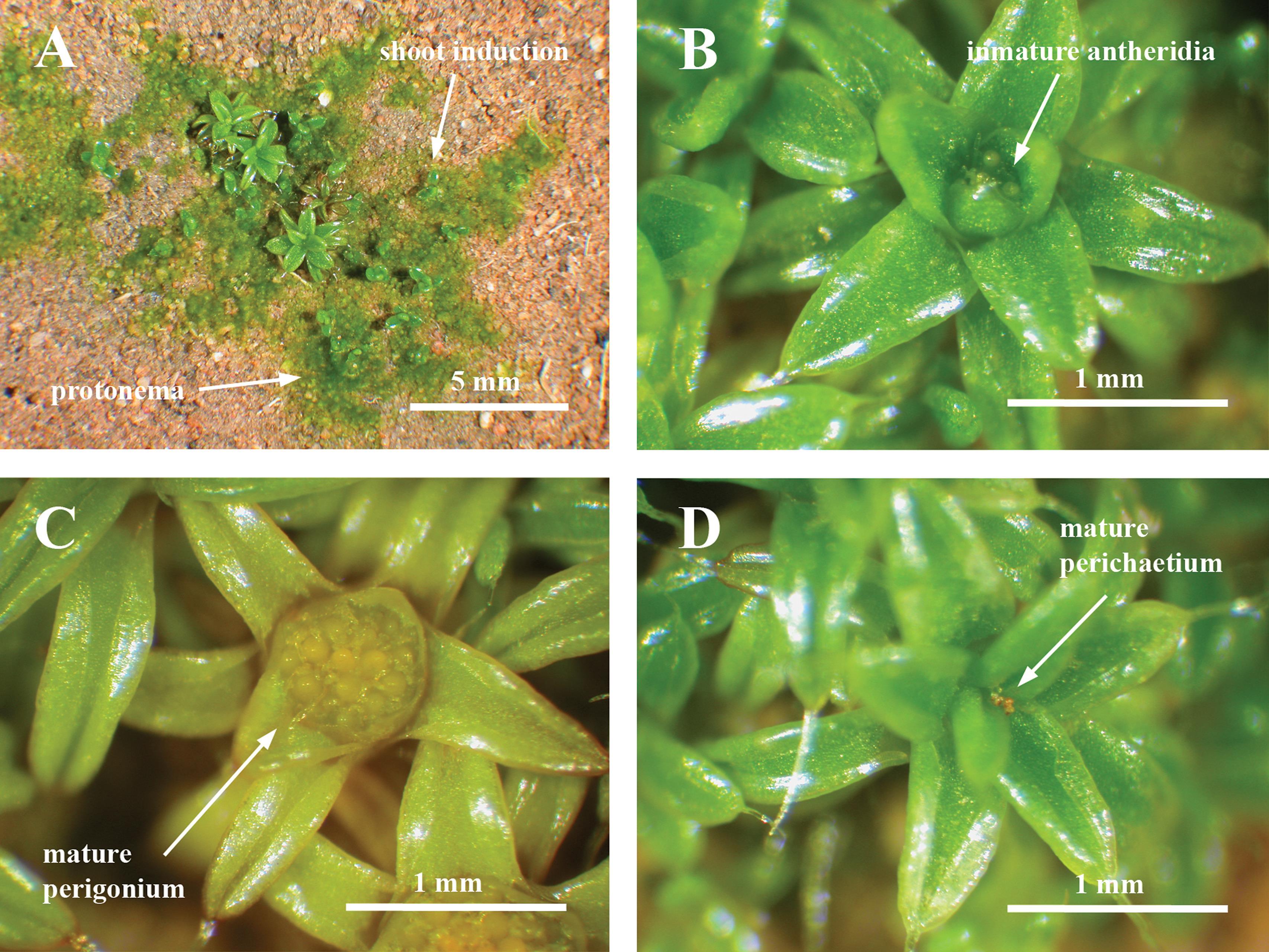
i0007-2745-116-1-43-f01.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/the-bryologist/volume-116/issue-1/0007-2745-116.1.043/An-experimental-demonstration-of-rhizautoicy-self-incompatibility-and-reproductive-investment/10.1639/0007-2745-116.1.043.full
(extending beyond the leaf apex). The sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) are borne on short setae (stalks), and the capsules are erect and cylindrical.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss has a cosmopolitan distribution, meaning it can be found on almost every continent. Aloina bifrons thrives in a wide range of habitats, from arid and semi-arid regions to temperate and Mediterranean climates. It is often found growing on soil

zzzPTER_Solanopteris_bifrons_CV9710C2.JPG from: https://plantidtools.fieldmuseum.org/pt/nlp/catalogue/3373230
, rocks, walls, and

A-bifrons-rio-Cachito-MTE.JPG from: https://chileanendemics.rbge.org.uk/es/taxa/argylia-bifrons-phil
disturbed areas, showcasing its adaptability and resilience.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
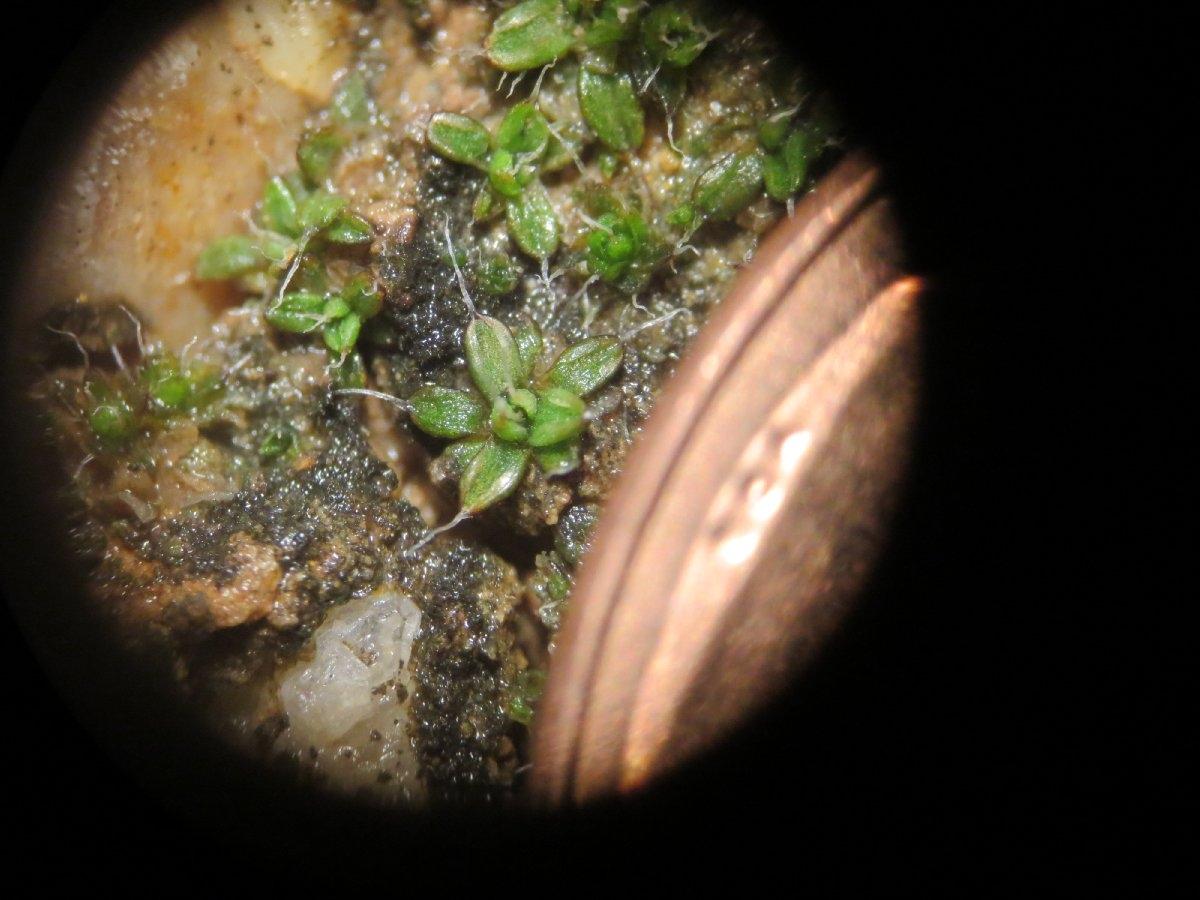
Despite its diminutive size, Aloina bifrons plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It contributes to soil formation and stabilization, helps retain moisture, and provides a microhabitat for various tiny organisms. Additionally, this moss exhibits remarkable adaptations to survive in harsh environments, such as desiccation tolerance

144892.jpg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=13684
(the ability to withstand prolonged periods of dryness) and poikilohydry (the ability to revive from a dried state upon rehydration).
Case Studies/Examples
One fascinating example of Aloina bifrons‘s resilience can be found in the Atacama Desert in Chile, one of the driest places on Earth. This moss has been observed to revive and resume growth after receiving just a few millimeters of rainfall, showcasing its incredible ability to survive in extreme conditions.
Technical Table

98390225387661199b39.jpeg from: https://m-r-g-r.com/items/5f116ddc4adba033ecdc9a0d

3279-l.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=19505
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Aloina |
| Species | bifrons
 aloina-aloe.jpg from: https://aloevivo.com/aloina/ |
| Growth Form | Dense tufts or cushions |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Apex | Bifid (split into two parts) |
| Leaf Margins | Entire (smooth) |
| Costa | Excurrent (extending beyond leaf apex) |
| Sporophytes | Borne on short setae |
| Capsules | Erect and cylindrical |
Conclusion
The Aloina bifrons (De Not.) Delgad., or simply Aloina, is a true marvel of the bryophyte world. Its ability to thrive in diverse habitats, its ecological significance, and its remarkable adaptations make it a fascinating subject of study. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, this unassuming moss serves as a reminder of the incredible resilience and beauty that can be found in even the smallest of organisms. Perhaps the next time you encounter a patch of Aloina bifrons, you’ll pause and reflect on the wonders it holds, leaving you with a newfound appreciation for the marvels of nature that often go unnoticed.