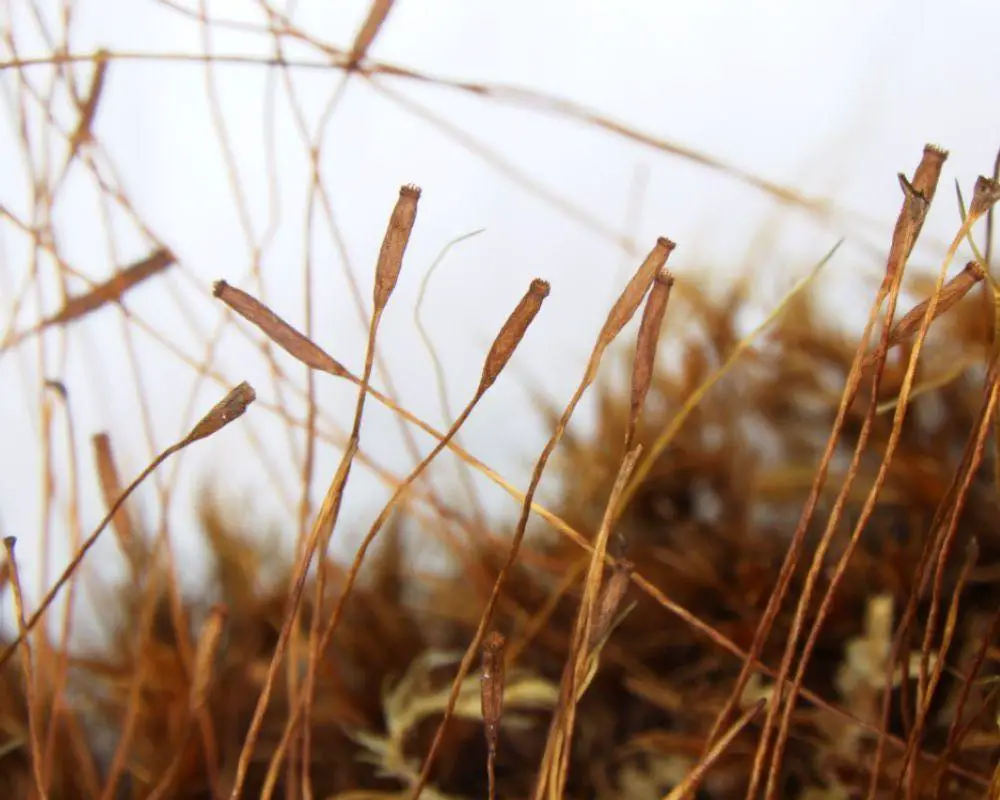

Dicranum_tauricum-sporangium-2.jpg from: https://blogs.ubc.ca/biology321/?page_id=987&cpage=1
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the Orthodicranum tauricum (Sapjegin) Smirnova. Belonging to the Dicranaceae family, this moss is commonly referred to as Orthodicranum. Let’s embark on an engaging journey to unravel the secrets of this fascinating plant.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Orthodicranum tauricum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are often overlooked due to their diminutive size, but their importance cannot be overstated.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Orthodicranum tauricum is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts. Its leaves are lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a
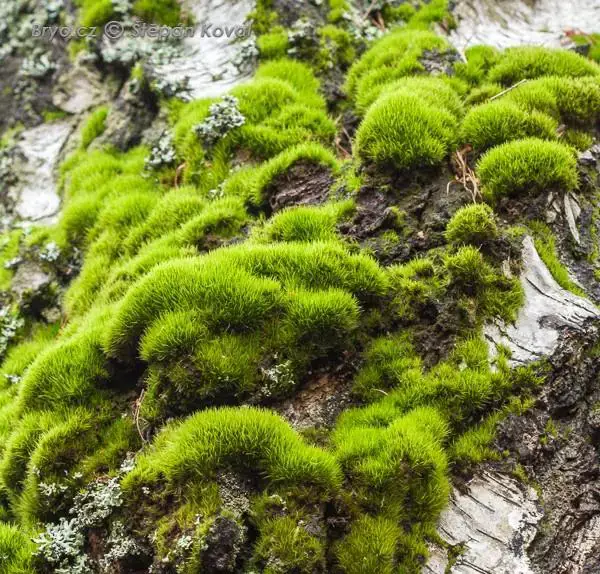

2293_Dicranum_tauricum_2009_03_13_0288.jpg from: https://www.bryo.cz/index.php?p=mechorosty_foto&site=default&gallery=dicranum_tauricum&id=2293
hair-like structure. This characteristic feature aids in the identification of this species. The sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) are relatively rare, but when present, they possess a curved seta (stalk) and a cylindrical capsule.
Global Distribution and Habitat
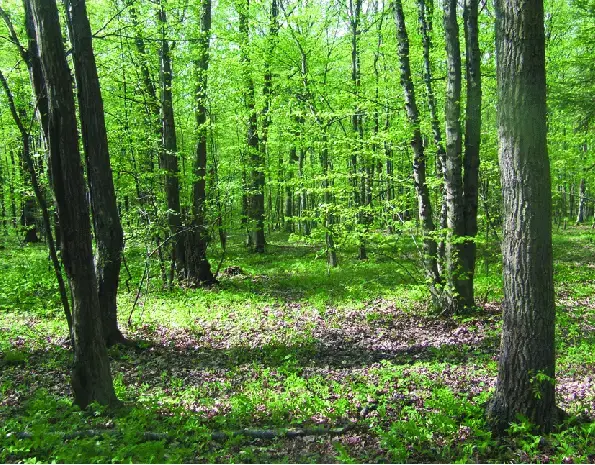
Orthodicranum tauricum is widely distributed across various regions, including Europe, Asia, and North America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, such as rocky outcrops, cliffs, talus slopes, and dry, exposed areas

Beech-forest-the-most-frequent-habitat-of-Orthodicranum-tauricum-Poland-Boze-Oczko.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Beech-forest-the-most-frequent-habitat-of-Orthodicranum-tauricum-Poland-Boze-Oczko_fig3_287007964
. This moss is particularly well-adapted to withstand harsh conditions, making it a resilient pioneer species in disturbed environments.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Orthodicranum tauricum plays a significant role in its ecosystem. It contributes to

Occurrence-of-Orthodicranum-tauricum-in-main-phytocoenosis-types-in-Central-East-Europe.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Occurrence-of-Orthodicranum-tauricum-in-main-phytocoenosis-types-in-Central-East-Europe_fig13_287007964
soil formation and moisture retention, creating favorable conditions for other plant species to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Orthodicranum tauricum is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments where water availability is limited.
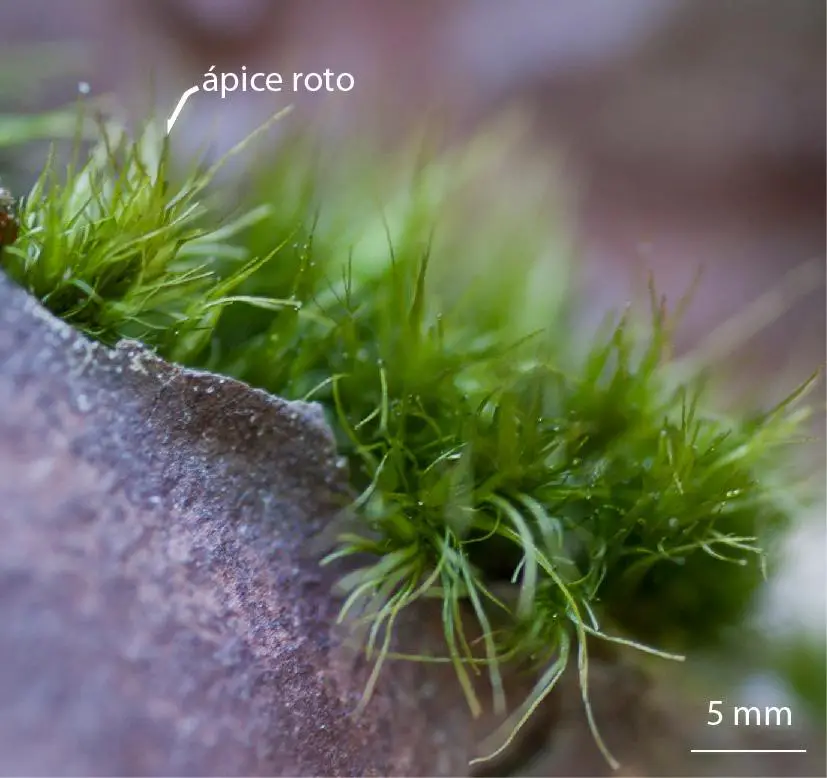
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the

Plants-of-Orthodicranum-tauricum-with-broken-tips-of-leaves-a-characteristic-feature-of_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plants-of-Orthodicranum-tauricum-with-broken-tips-of-leaves-a-characteristic-feature-of_fig8_287007964
Rocky Mountains of North America, researchers investigated the role of Orthodicranum tauricum in facilitating the establishment of vascular plants. The findings revealed that the moss acted as a nursery, providing a suitable microclimate and nutrient source for seedling growth, ultimately contributing to the overall biodiversity of the region.
Technical Table
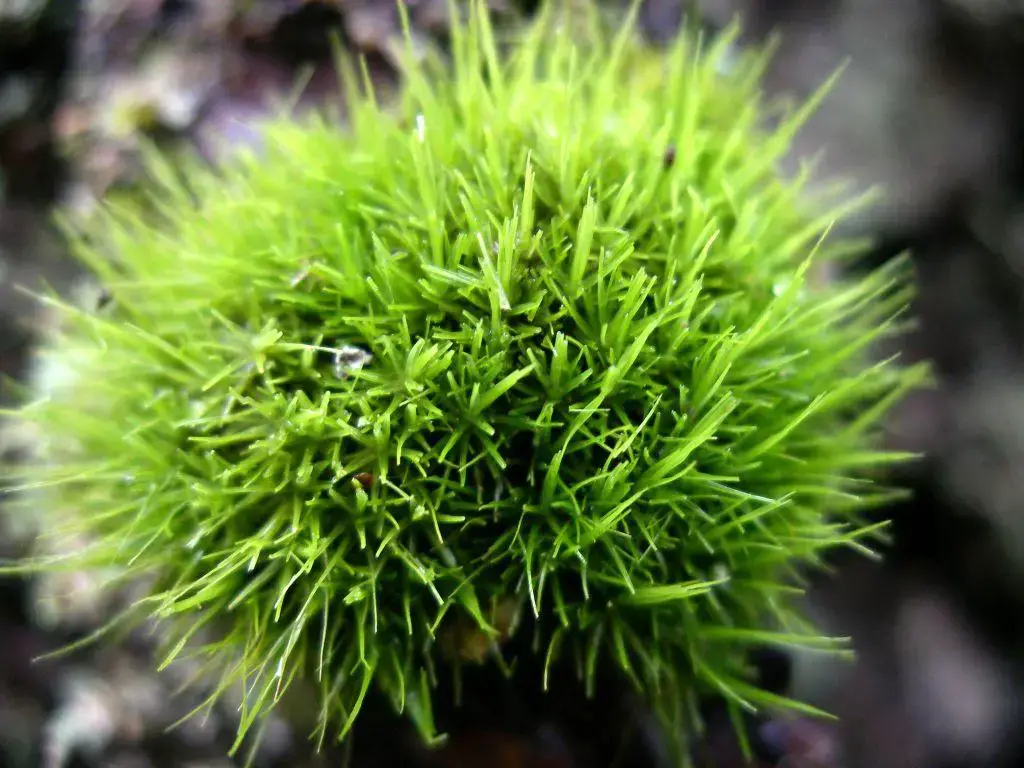

dicranum_tauricum.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Dicranaceae/dicranum-tauricum/en/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida
 2319285339_e9f83e6e92_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/maximillian_millipede/2319285339/ |
| Order | Dicranales |
| Family | Dicranaceae |
Genus
 Dicranum-tauricum-moss.jpg from: https://elmusgo.blogspot.com/2012/08/dicranum-tauricum.html |
Orthodicranum
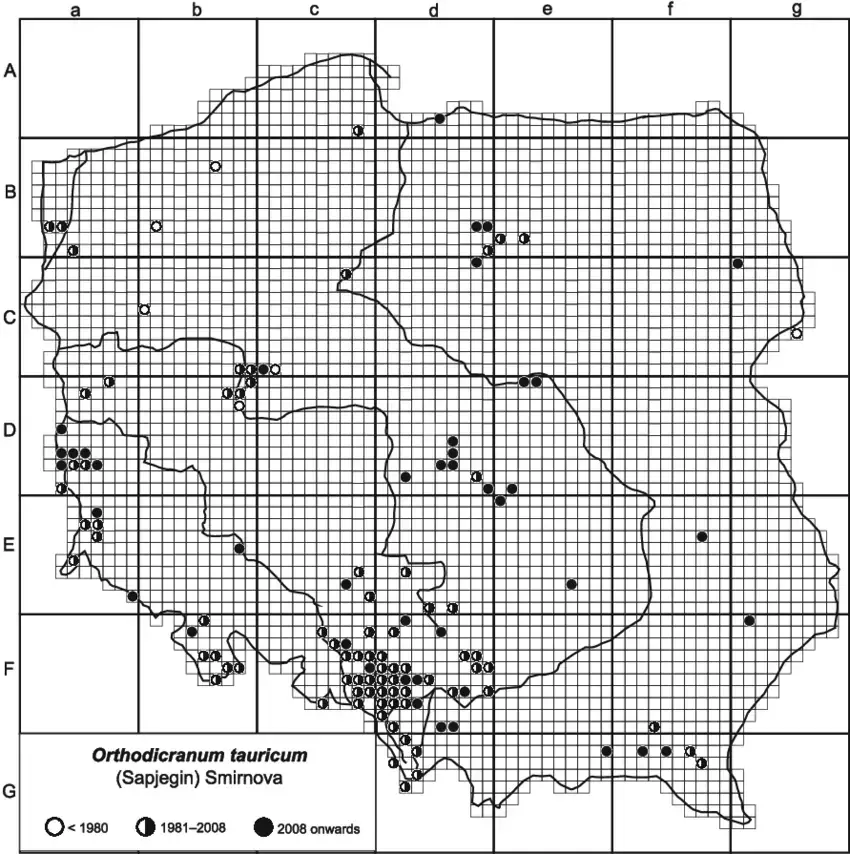 Distribution-of-Orthodicranum-tauricum-in-Poland.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Distribution-of-Orthodicranum-tauricum-in-Poland_fig10_287007964 |
| Species | tauricum |
Growth Form
 OS0144611_1549066243.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/portal/taxa/index.php?taxauthid=1&taxon=158733&clid=35 |
Acrocarpous |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate |
| Habitat | Rocky outcrops, cliffs, talus slopes |
Conclusion
The Orthodicranum tauricum (Sapjegin) Smirnova moss, a member of the Dicranaceae family, is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. Despite its unassuming appearance, this species plays a vital role in various ecosystems, contributing to soil formation, moisture retention, and biodiversity. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these often-overlooked yet invaluable components of our natural environments?