
jim__stasz_15711942854_13a5c8e9ac_b.jpg from: https://www.marylandbiodiversity.com/viewSpecies.php?species=10873
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out as a true marvel – the Acroporium rufum var. albidum J.Froehl. Belonging to the Sematophyllaceae family, this delicate yet resilient moss is commonly referred to as Acroporium. Prepare to embark on an enchanting journey as we delve into the intricate details of this remarkable plant.
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Acroporium rufum var. albidum J.Froehl., it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
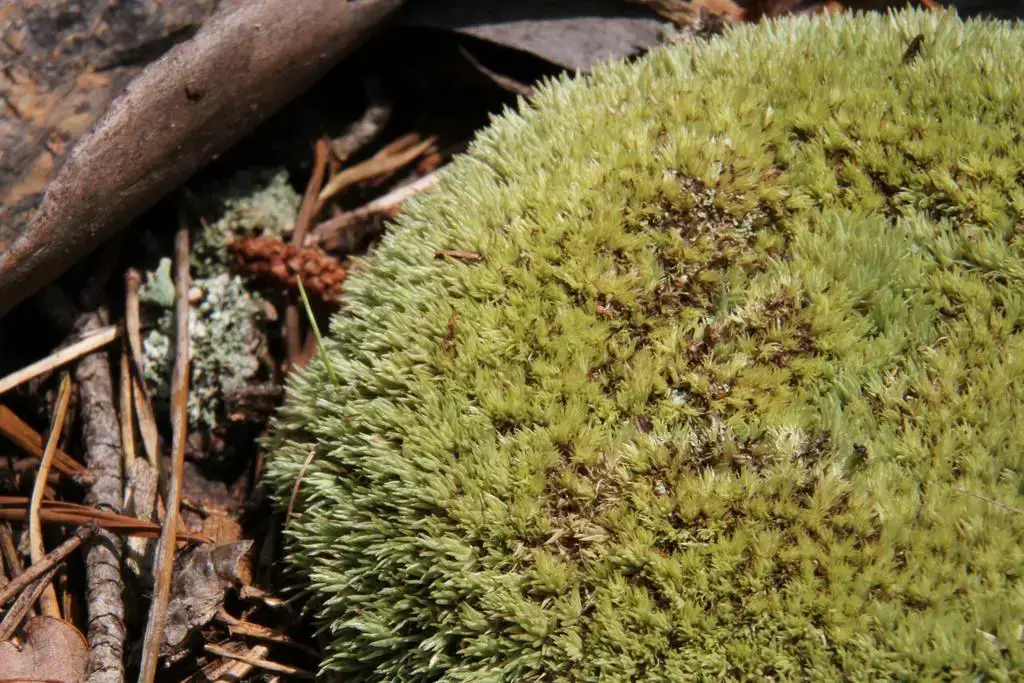
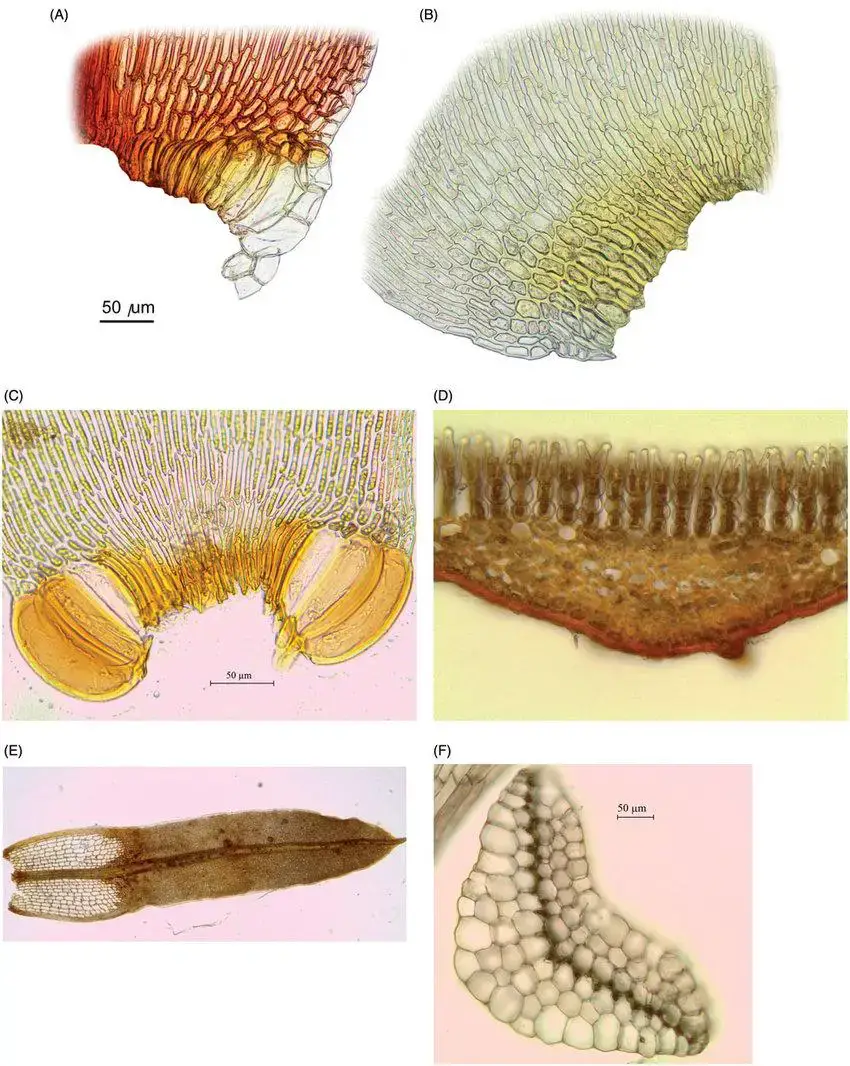
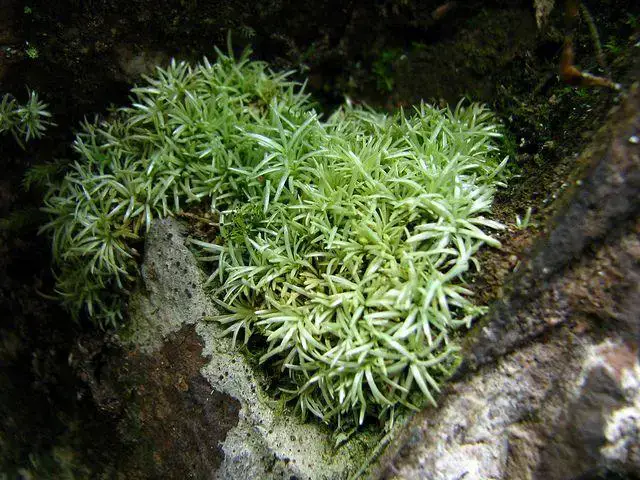
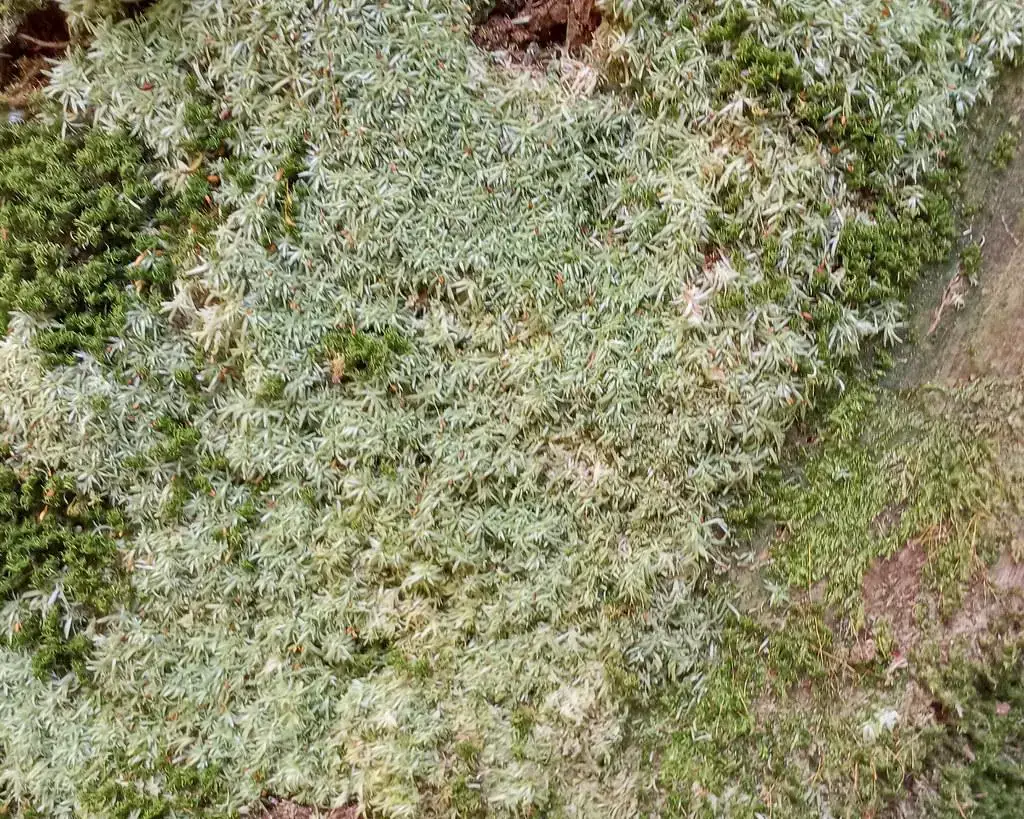
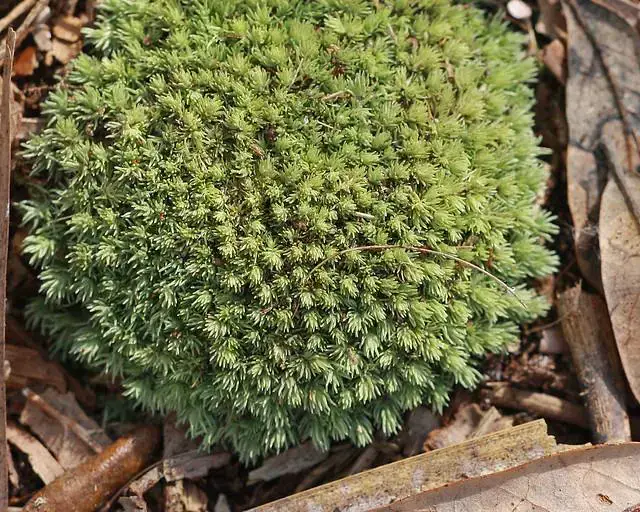
Acroporium rufum var. albidum J.Froehl. is a small, delicate moss that forms dense, cushion-like mats or tufts. Its slender stems are typically reddish-brown in color, while the leaves are pale green to whitish. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate in shape, with a single costa (midrib) that extends nearly to the leaf apex. One of the distinguishing features of this moss is its double-toothed leaf margins, which can be observed under a microscope.
Global Distribution and Habitat
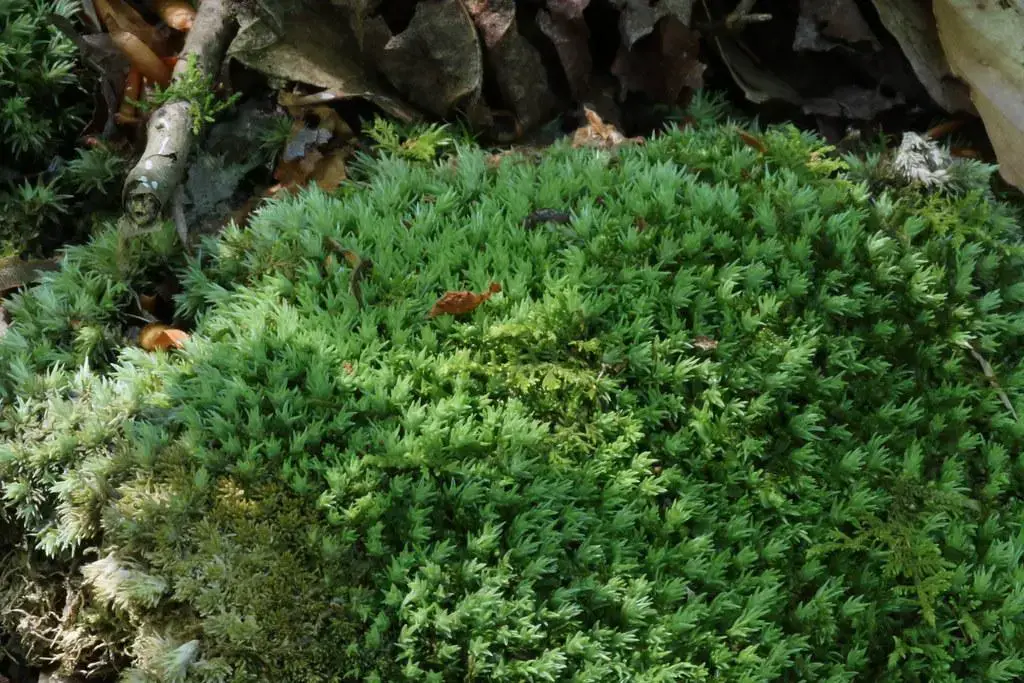
This moss species has a widespread distribution, occurring in various regions across the globe, including North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia

18465204224_273e45b4ed_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/26803925@N05/18465204224/
. It thrives in a variety of habitats, such as moist forests, rocky outcrops, stream banks, and even disturbed areas. Acroporium rufum var. albidum J.Froehl. is known for its ability to colonize both natural and human-made environments, making it a resilient and adaptable species.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Acroporium rufum var. albidum J.Froehl.

349647738480558080.jpeg from: https://www.picturethisai.com/ru/wiki/Leucobryum_albidum.html
plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating favorable conditions for other plants to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and food sources.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Acroporium rufum var. albidum J.Froehl. is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to survive in challenging environments and contributes to its widespread distribution.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that Acroporium rufum var. albidum J.Froehl. played a crucial role in the recovery of disturbed forest ecosystems. The moss’s ability to rapidly colonize and stabilize soil surfaces facilitated the establishment of other plant species, accelerating the overall restoration process.
Technical Table
Morphological-structures-connected-to-ectohydric-water-transport-A-Alar-groups-in.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Morphological-structures-connected-to-ectohydric-water-transport-A-Alar-groups-in_fig2_327550942

microglossum-rufum-2.jpg from: https://ultimate-mushroom.com/poisonous/959-microglossum-rufum.html

1b86144e31e828bf9522c373499eded9.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/50032245830323336/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Acroporium rufum var. albidum J.Froehl.
 51145390131_3433279081_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/38514062@N03/51145390131/ |
| Family | Sematophyllaceae |
| Common Name | Acroporium |
Growth Form
 8474082268_ff49d313de_z.jpg from: http://www.flickr.com/photos/38514062@N03/8474082268/ |
Dense cushions or tufts |
| Stem Color | Reddish-brown |
| Leaf Color | Pale green to whitish |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Margin | Double-toothed |
| Costa | Single, extending nearly to leaf apex |
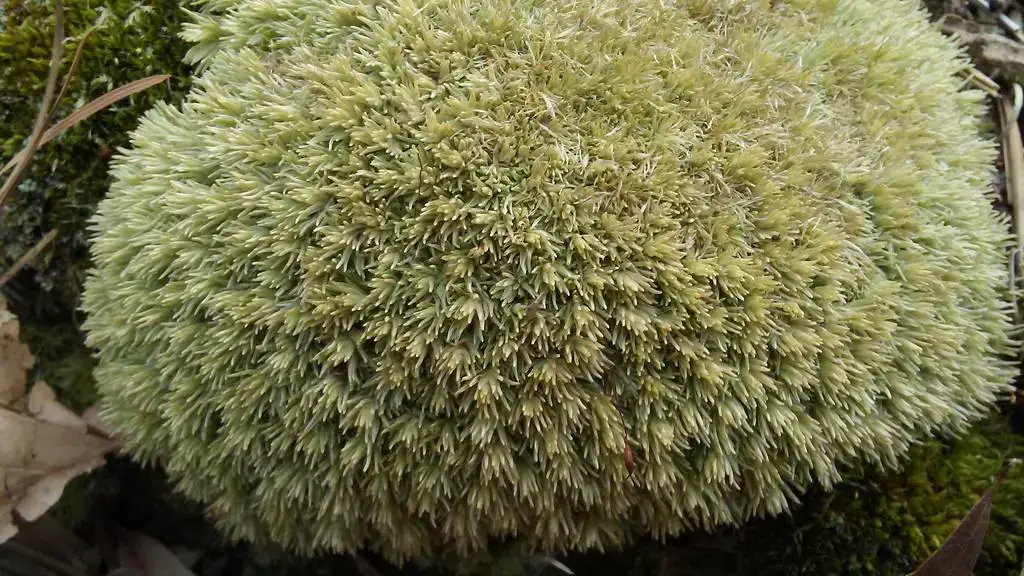
Conclusion
The Acroporium rufum var. albidum J.Froehl.

tyler_bell_33177812101_2e3ea350fd_b.jpg from: https://www.marylandbiodiversity.com/view/10873
, a remarkable member of the Bryophyta phylum, showcases the incredible diversity and resilience of mosses. From its delicate yet hardy nature to its vital ecological roles, this species serves as a testament to the importance of preserving and appreciating even the smallest components of our natural world. As we continue to explore the wonders of bryophytes, one question remains: What other hidden marvels await discovery in the intricate tapestry of life?

A-Allium-albidum-B-A-atroviolaceum-C-A-fuscoviolaceum-D-A-karsianum-E-A.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-Allium-albidum-B-A-atroviolaceum-C-A-fuscoviolaceum-D-A-karsianum-E-A_fig10_337167275