
30989426231_ebcf93c20f_b.jpg from: https://www.flickriver.com/photos/dinesh_valke/30989426231/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Dendroceros crispatus (Hook.) Nees moss stands out as a remarkable species. Belonging to the Dendrocerotaceae family, this moss is commonly referred to as Dendroceros. It is a member of the Anthocerotophyta
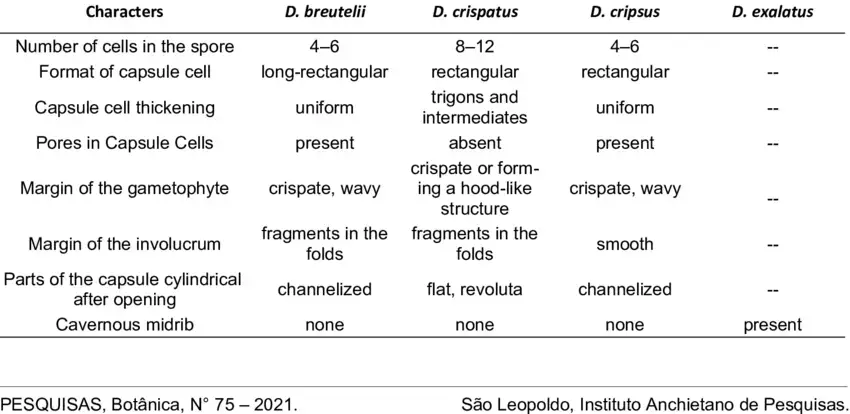
Morphological-comparison-of-the-four-Brazilian-species-of-Dendroceros-Nees.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Morphological-comparison-of-the-four-Brazilian-species-of-Dendroceros-Nees_tbl1_349894951
division, which encompasses the hornworts, a unique group of bryophytes known for their intricate life cycles and fascinating morphological features.
Background
The Anthocerotophyta division, to which Dendroceros crispatus belongs, is a small but significant group of bryophytes. These plants are often overlooked due to their diminutive size, yet they play crucial roles in various ecosystems. The Anthocerotopsida class, which includes the Dendrocerotaceae family, is characterized by its distinctive morphology and reproductive strategies.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Dendroceros crispatus is a thallose liverwort, meaning it grows in a flat, ribbon-like form. Its gametophyte, the dominant phase of its life cycle, consists of a green, irregularly branched thallus. The thallus is often crispate (curled or wavy) at the margins, lending the species its specific epithet “crispatus.” This moss is easily identifiable by its unique sporophyte structure, which resembles a slender, horn-like projection emerging from the thallus.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Dendroceros crispatus is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including tropical and subtropical areas. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, such as forest floors, rotting logs, and damp soil. This moss is often found in association with other bryophytes, forming intricate carpets or patches in suitable habitats.

58276_5d0516aa4970b.jpg from: https://www.reeflex.net/tiere/12141_Loxorhynchus_crispatus.htm
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Dendroceros crispatus plays vital roles in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating favorable conditions for other plants to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates and microorganisms, supporting biodiversity in its immediate surroundings.
Dendroceros crispatus exhibits remarkable adaptations to its environment. Its ability to withstand desiccation and rapidly rehydrate after periods of drought allows it to survive in challenging conditions. Furthermore, its unique reproductive strategies, involving the production of spores and specialized reproductive structures, contribute to its successful propagation and dispersal.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a tropical rainforest, researchers discovered that Dendroceros crispatus played a crucial role in facilitating the establishment of seedlings from various plant species. The moss’s ability to retain moisture and provide a suitable microhabitat for germination and early growth was found to be instrumental in promoting plant diversity within the ecosystem.
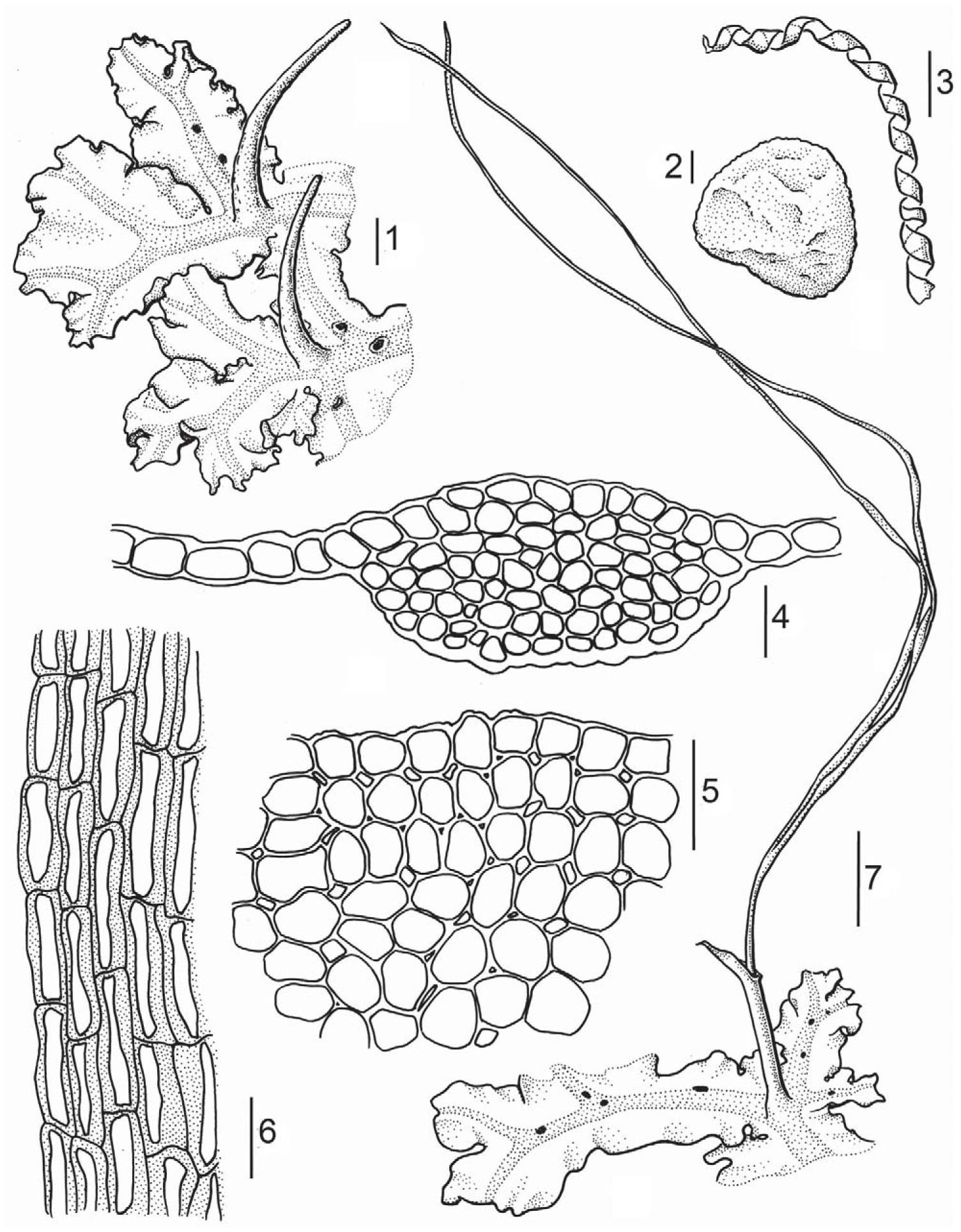
f01_03.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/cryptogamie-bryologie/volume-33/issue-1/cryb.v33.iss1.2012.003/The-Hornworts-Dendroceros-Nees-and-Megaceros-Campb-in-São-Tomé/10.7872/cryb.v33.iss1.2012.003.full
Technical Table

litswigh_09.jpg from: https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/14553

601.26028980.jpg from: https://eol.org/pages/5397803

Themeda-caudata-Nees-ex-Hook-Arn-A-Camus_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Themeda-caudata-Nees-ex-Hook-Arn-A-Camus_fig1_283889742

dendroceros-108.jpg from: https://www.cpbr.gov.au/bryophyte/photos-captions/dendroceros-108.html

5.jpg from: https://indiabiodiversity.org/observation/show/344805
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Division | Anthocerotophyta |
| Class | Anthocerotopsida |
| Family | Dendrocerotaceae |
| Species | Dendroceros crispatus (Hook.) Nees |
| Common Name | Dendroceros |
| Gametophyte | Thallose, green, irregularly branched thallus |
| Sporophyte | Slender, horn-like projection |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments (forest floors, rotting logs, damp soil) |
| Distribution | Tropical and subtropical regions worldwide |
Conclusion
The Dendroceros crispatus (Hook.) Nees moss, a member of the Dendrocerotaceae family, is a fascinating and ecologically significant species. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and adaptations to various habitats make it a captivating subject of study. As we delve deeper into the world of bryophytes, we are reminded of the intricate tapestry of life that exists even in the smallest of organisms. Perhaps the next time you encounter a patch of moss, you’ll pause and appreciate the wonders of

Litsea_elongata_JR43240.jpg from: https://lauraceae.myspecies.info/file/762
Dendroceros crispatus and its bryophyte kin.
Thought-provoking question: How might the study of bryophytes like Dendroceros crispatus contribute to our understanding of ecosystem resilience and conservation efforts?