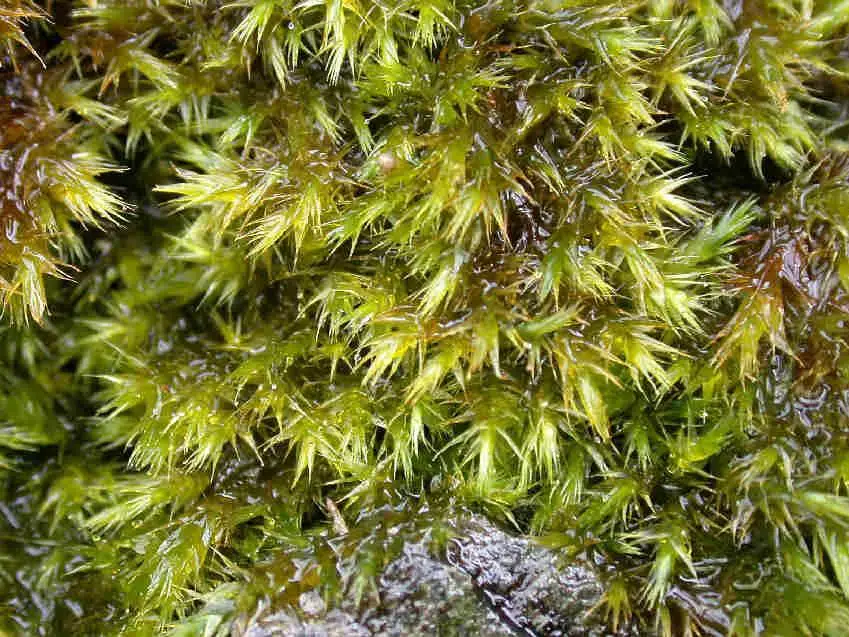

Drepanocladus_polygamus_001C.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Drepanocladus_polygamus.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Drepanocladus polygamus (Schimp.) Hedenäs moss stands out as a remarkable species. Belonging to the Amblystegiaceae family, this unassuming yet fascinating moss is also commonly known as

2022-09-21-17-01-09-Drep-poly.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/drepanocladus-polygamus/
Drepanocladus. Prepare to embark on a journey through the intricate details of this extraordinary plant, where we’ll unravel its secrets and appreciate its unique place in the natural world.
Background
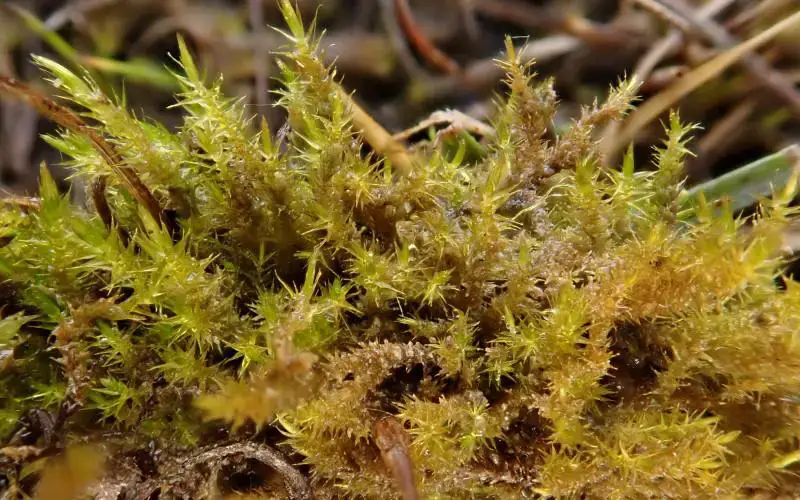

46133800.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/233043982?_popup=1
Before delving into the specifics of Drepanocladus polygamus, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
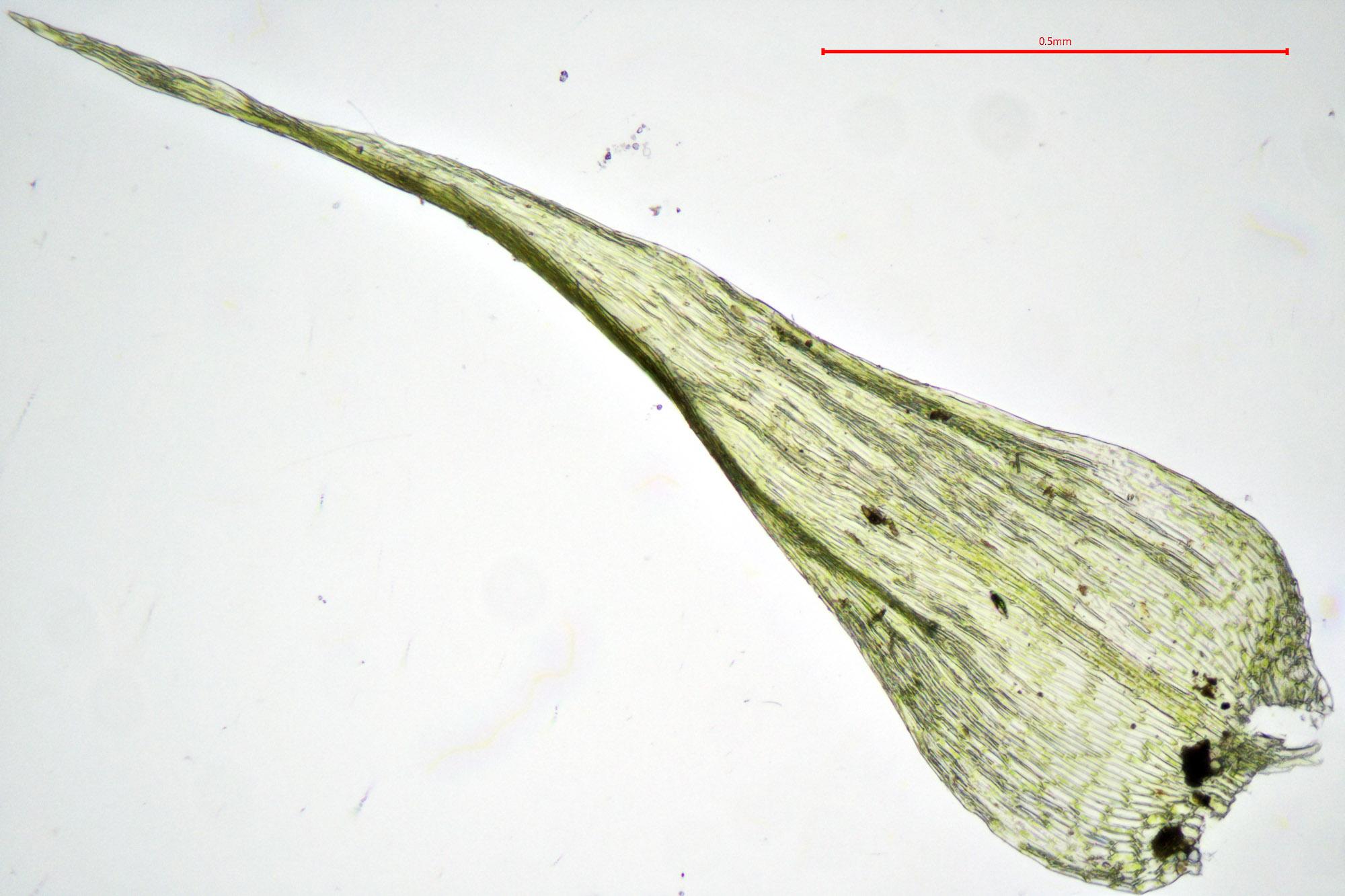
Drepanocladus polygamus is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems and branches grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, creeping stems can reach lengths of several centimeters, forming dense mats or cushions. The leaves are small, ovate to lanceolate in shape, and arranged spirally around the stem. When viewed under a microscope, the leaf cells reveal a distinctive pattern that aids in identification.

medium.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/461294-Drepanocladus-polygamus
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss species has a widespread distribution, occurring across various regions of the Northern Hemisphere, including Europe, Asia, and North America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, such as wetlands, bogs, fens, and along the banks of streams and rivers.
Drepanocladus_polygamus_4018.png from: https://vaplantatlas.org/index.php?do=plant&plant=4018&search=equisetum
Drepanocladus polygamus is well-adapted to moist and nutrient-rich environments, often forming lush carpets in these areas.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Drepanocladus polygamus plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating a suitable environment for other plants and organisms to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a habitat and food source for various invertebrates, further highlighting its ecological significance.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Drepanocladus polygamus is its ability to withstand periods of desiccation. During dry spells, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, only to revive and resume growth when moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to survive in environments with fluctuating water levels.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a peatland ecosystem, researchers found that Drepanocladus polygamus played a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of the wetland. Its dense mats helped regulate water levels, preventing excessive drying and ensuring the survival of other plant and animal species within the ecosystem.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Amblystegiaceae |
| Genus | Drepanocladus |
| Species | polygamus |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to lanceolate |
| Habitat | Wetlands, bogs, fens, stream banks |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere |
Conclusion
The Drepanocladus polygamus (Schimp.) Hedenäs moss, a member of the Amblystegiaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its unassuming appearance belies its remarkable adaptations, ecological significance, and resilience. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, this moss serves as a reminder of the intricate web of life that surrounds us, even in the smallest and most overlooked corners of our world. Perhaps the next time you encounter a lush carpet of moss, you’ll pause and wonder if Drepanocladus polygamus is among the hidden gems beneath your feet.