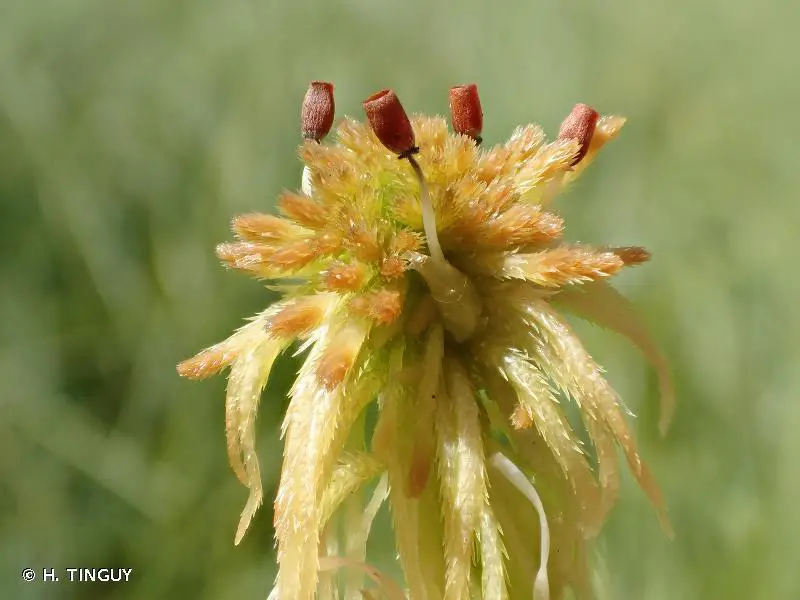

236117.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6746
Introduction
Welcome, fellow moss enthusiasts! Today, we’re going to delve into the fascinating world of Sphagnum fallax (H.Klinggr.) H.Klinggr., a remarkable moss species that belongs to the
sphagn19.jpg from: https://forums-naturalistes.forums-actifs.com/t1479-sphagnum-fallax-klinggr-klinggr
Sphagnaceae family, commonly known as Sphagnum. Prepare to be captivated by the intricate details and unique characteristics of this unassuming yet extraordinary plant.
Background
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of Sphagnum fallax, let’s set the stage with a brief introduction to the Bryophyta division, which encompasses mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. These ancient plants have been around for millions of years, predating even the dinosaurs! Despite their diminutive size, they play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation.
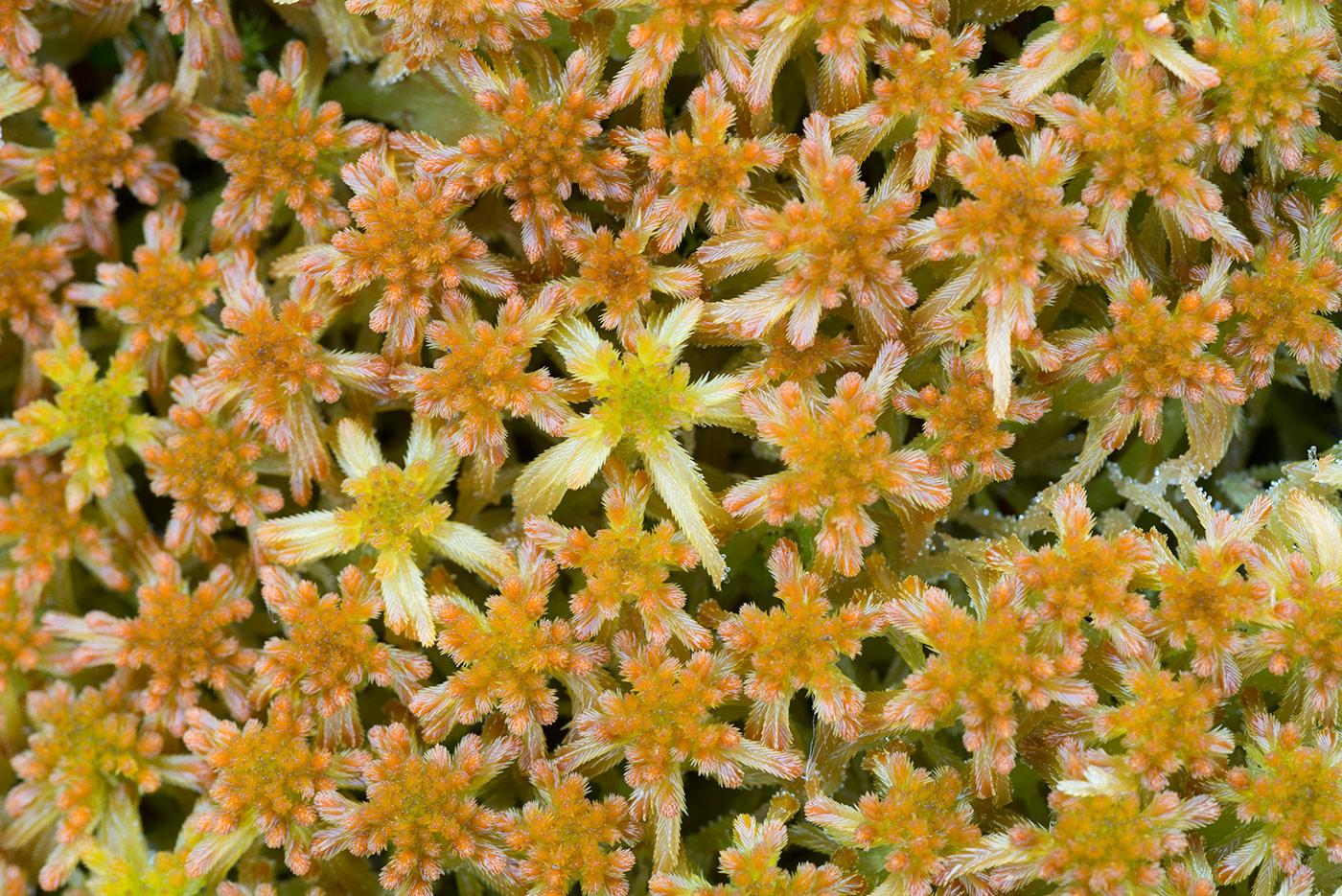

479631_0025ba04.jpg from: https://www.plantarium.ru/page/image/id/479631.html
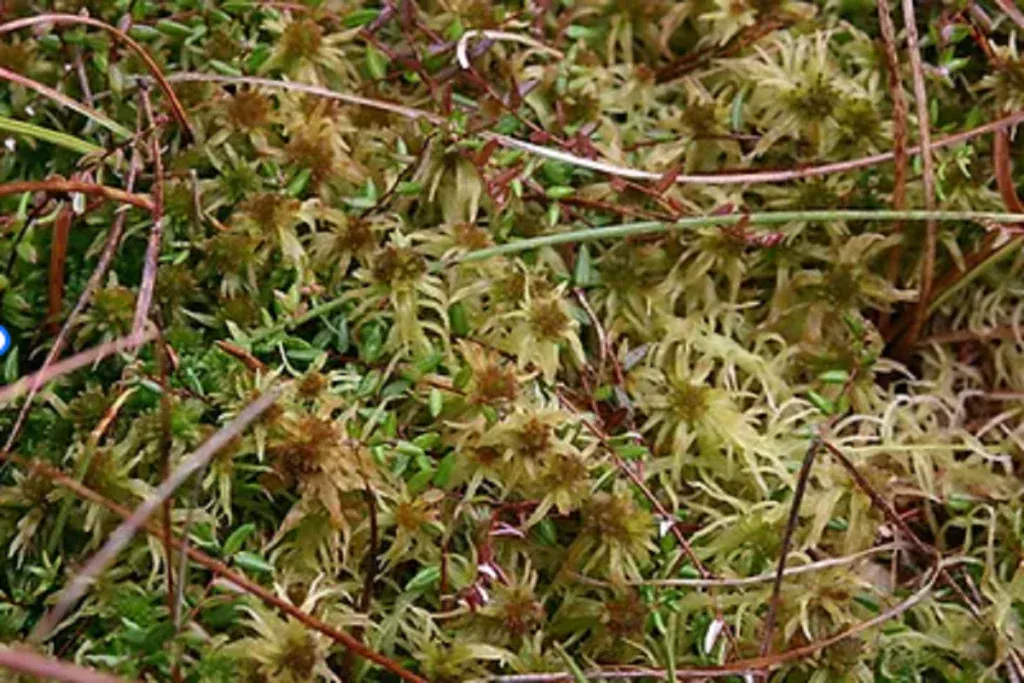

Torfowiec-konczysty-Sphagnum-fallax-H.-Klinggr.-1024×683.png from: https://prawanatury.com/artykul/torfowiec-konczysty-sphagnum-fallax-h-klinggr/
Main Content
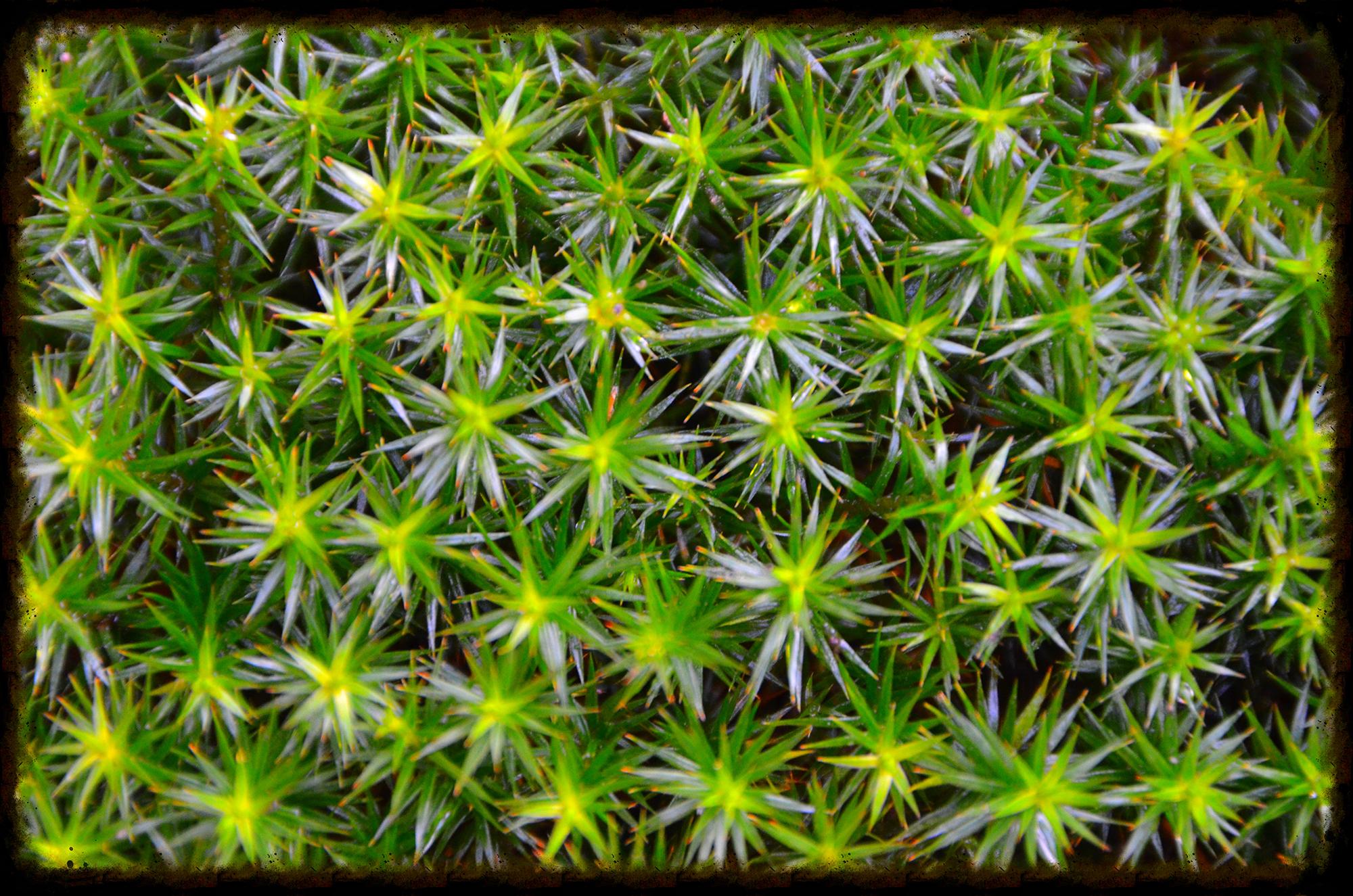
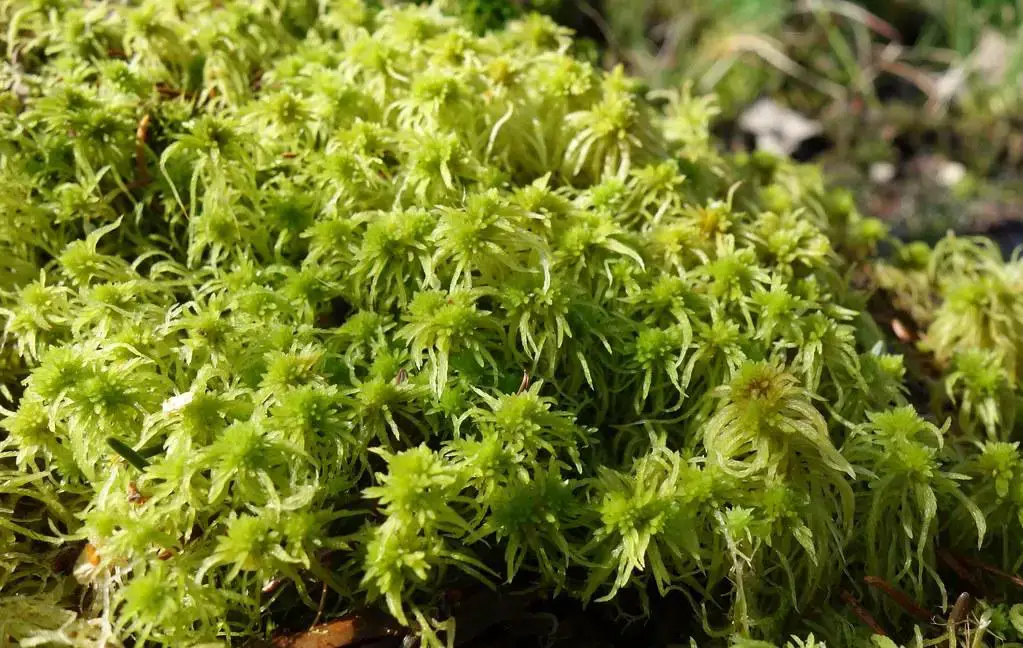
Morphology and Identification
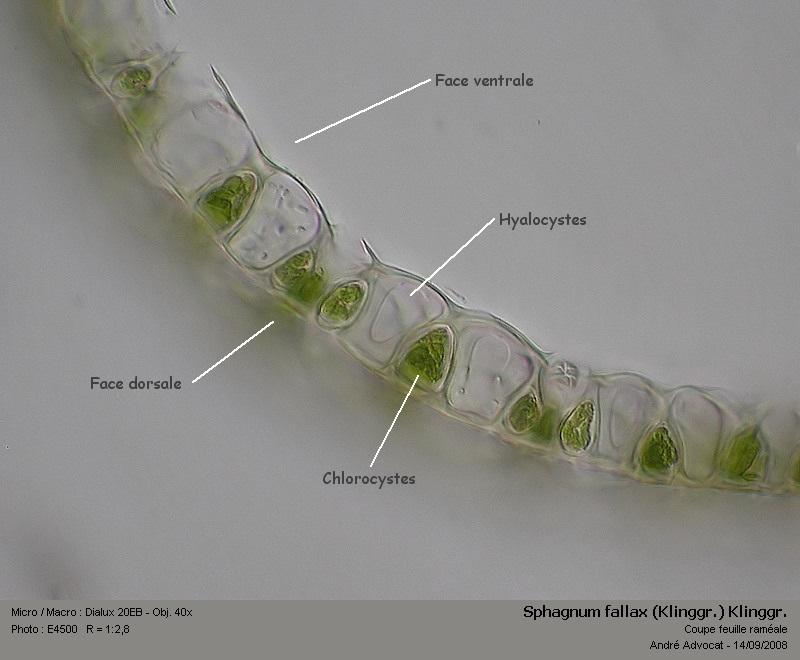
Sphagnum fallax is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems and branches grow horizontally. It forms dense, compact cushions or mats, with a vibrant green to yellowish-green hue. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate in shape, and the stem leaves are lingulate (tongue-shaped) with a truncate apex. One of the most distinctive features of this moss is its falcate (sickle-shaped) branch leaves, which give it a unique, curved appearance.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Sphagnum fallax is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, thriving in various habitats such as bogs, fens, swamps, and wet meadows. It’s particularly abundant in regions with cool, moist climates, such as northern Europe, North America, and parts of Asia. This moss prefers acidic, nutrient-poor environments, making it a common sight in
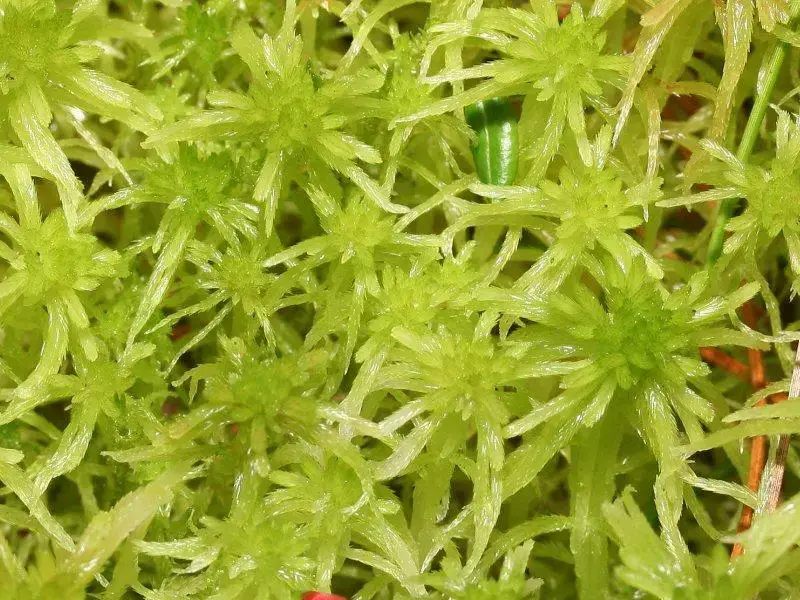

sphagnum_fallax..jpeg from: https://de.academic.ru/dic.nsf/dewiki/1310612
peatlands
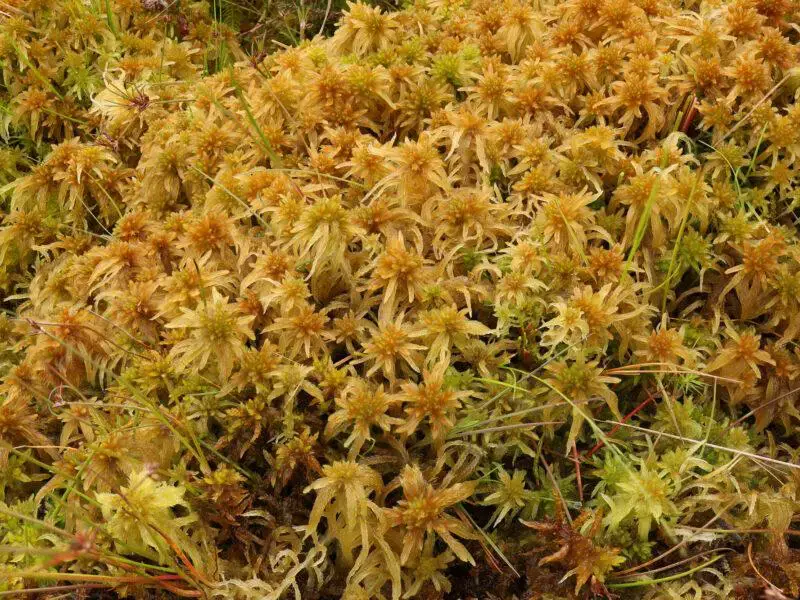

2020-09-05-10-16-35-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/sphagnum-fallax/
and other wetland areas.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Sphagnum mosses, including Sphagnum fallax, play a vital role in the formation and maintenance of peatlands. These mosses have an incredible ability to absorb and retain water, acting like tiny sponges. This unique adaptation allows them to create and sustain the waterlogged, acidic conditions that are essential for peatland ecosystems.
Moreover, Sphagnum fallax contributes to the
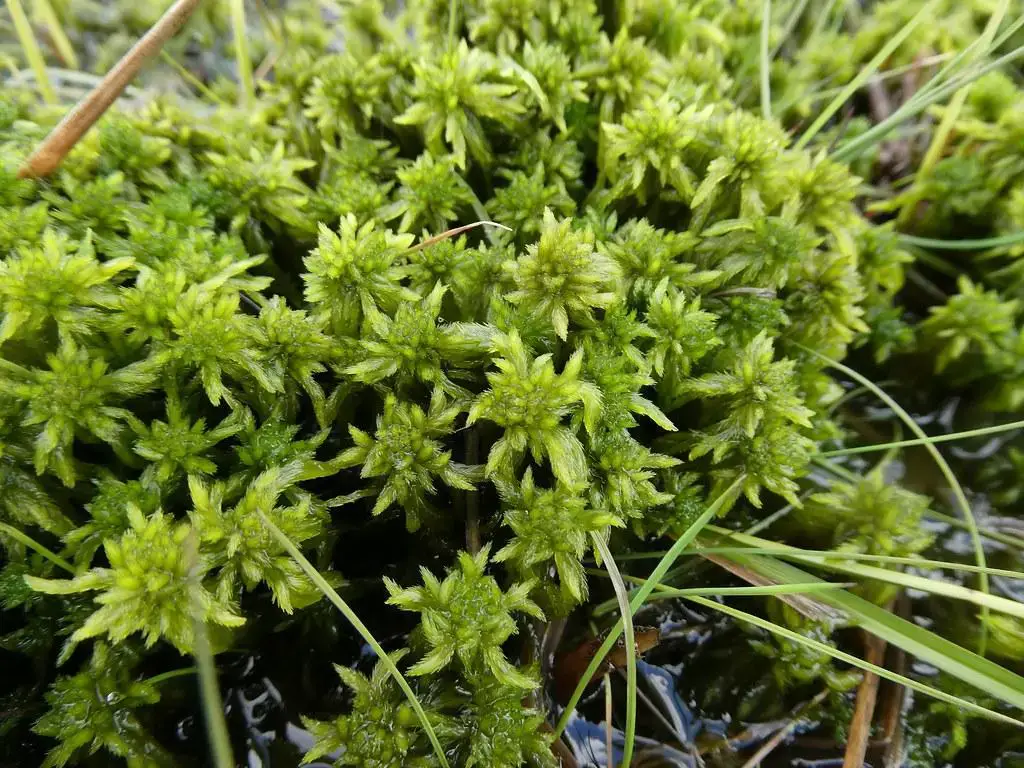

52881874861_cf346ea072_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/silybum/52881874861/
carbon cycle by accumulating and storing vast amounts of carbon in the form of peat. This process not only helps mitigate climate change but also provides a valuable resource for horticultural and industrial purposes.
Case Studies/Examples
In the Siberian Arctic, Sphagnum fallax
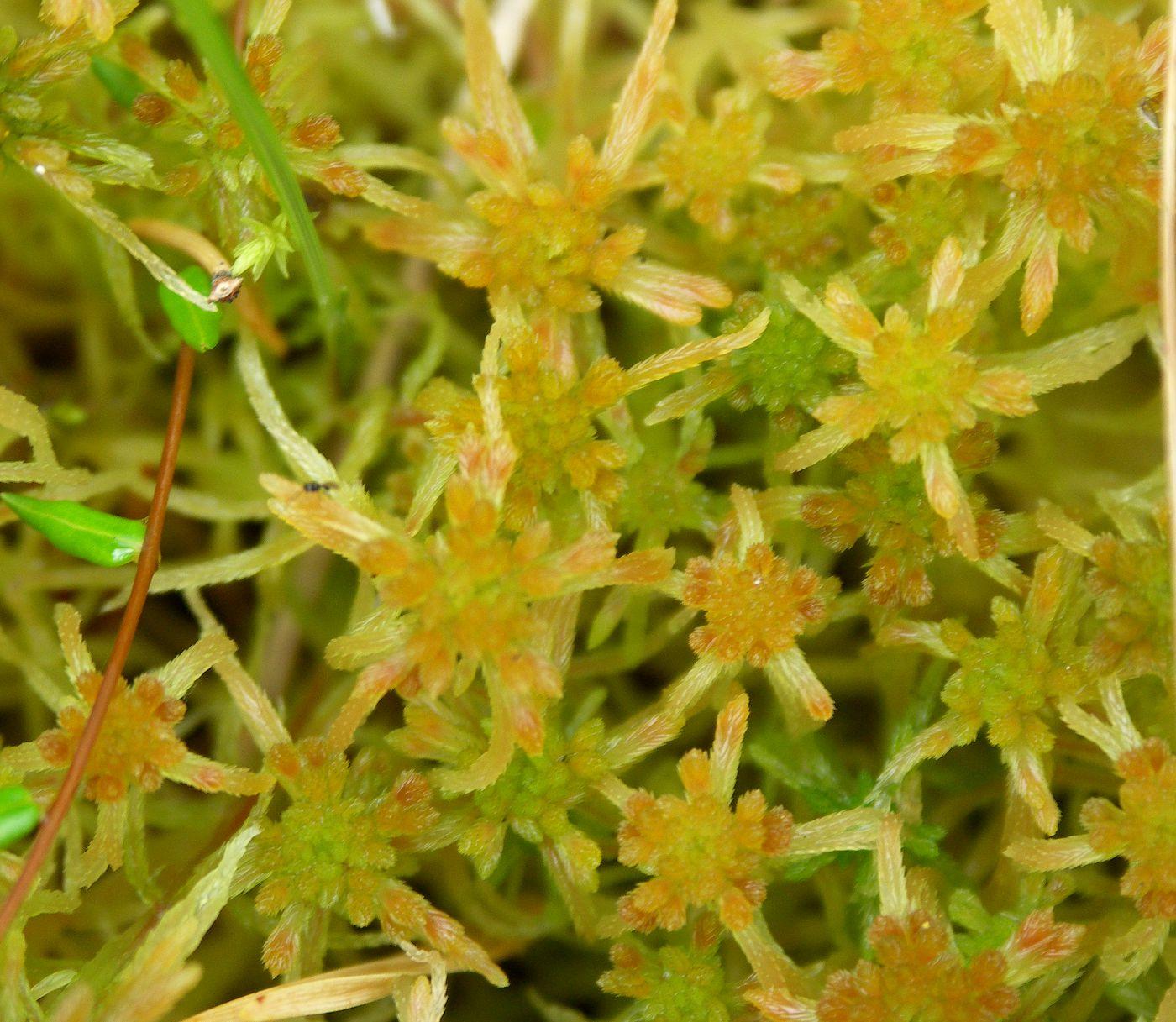

447682_9a1c1b2d.jpg from: https://www.plantarium.ru/page/image/id/447682.html
has been found to be a key indicator species for assessing the impacts of permafrost thaw on peatland ecosystems. Researchers have observed that as permafrost melts, Sphagnum fallax colonies expand, colonizing newly available habitats and altering the overall vegetation composition.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Sphagnopsida |
| Order | Sphagnales |
| Family | Sphagnaceae |
| Genus | Sphagnum |
| Species | Sphagnum fallax (H.Klinggr.) H.Klinggr.
 2k-Sphagnum-fallax-Karl-Ludwig-Poggemann-Flickr-CC-BY-2.0.jpg from: https://jgi.doe.gov/building-sphagnum-genomic-resources/2k-sphagnum-fallax-karl-ludwig-poggemann-flickr-cc-by-2-0/ |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate (stem leaves), Falcate (branch leaves) |
| Habitat | Bogs, fens, swamps, wet meadows |
Conclusion
Sphagnum fallax is a true marvel of the moss world, showcasing remarkable adaptations and playing a crucial role in shaping and sustaining delicate peatland ecosystems. From its unique morphology to its ecological significance, this unassuming plant deserves our utmost appreciation and protection. As we bid farewell to our moss adventure, ponder this: How can we, as enthusiasts and stewards of nature, contribute to the conservation of these invaluable ecosystems and the species that call them home?

32588615947_02c701bbc2_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/12639178@N07/32588615947/