
ede20439e369289b11e9dce53b55edd0.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/437834395003016595/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one tiny moss species stands out as a true marvel – the Micromitrium tomentosum (Hornsch.) Paris. Belonging to the Orthotrichaceae family, this diminutive plant is commonly referred to as Micromitrium. Despite its unassuming size, this moss holds a wealth of fascinating information and plays a crucial role in its ecosystem.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of

website_image_template_-_with_copywrite_15_6.jpg from: https://www.benaranurseries.com/gompholobium-tomentosum
Micromitrium tomentosum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth. They have been around for over 400 million years, predating even the earliest vascular plants.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
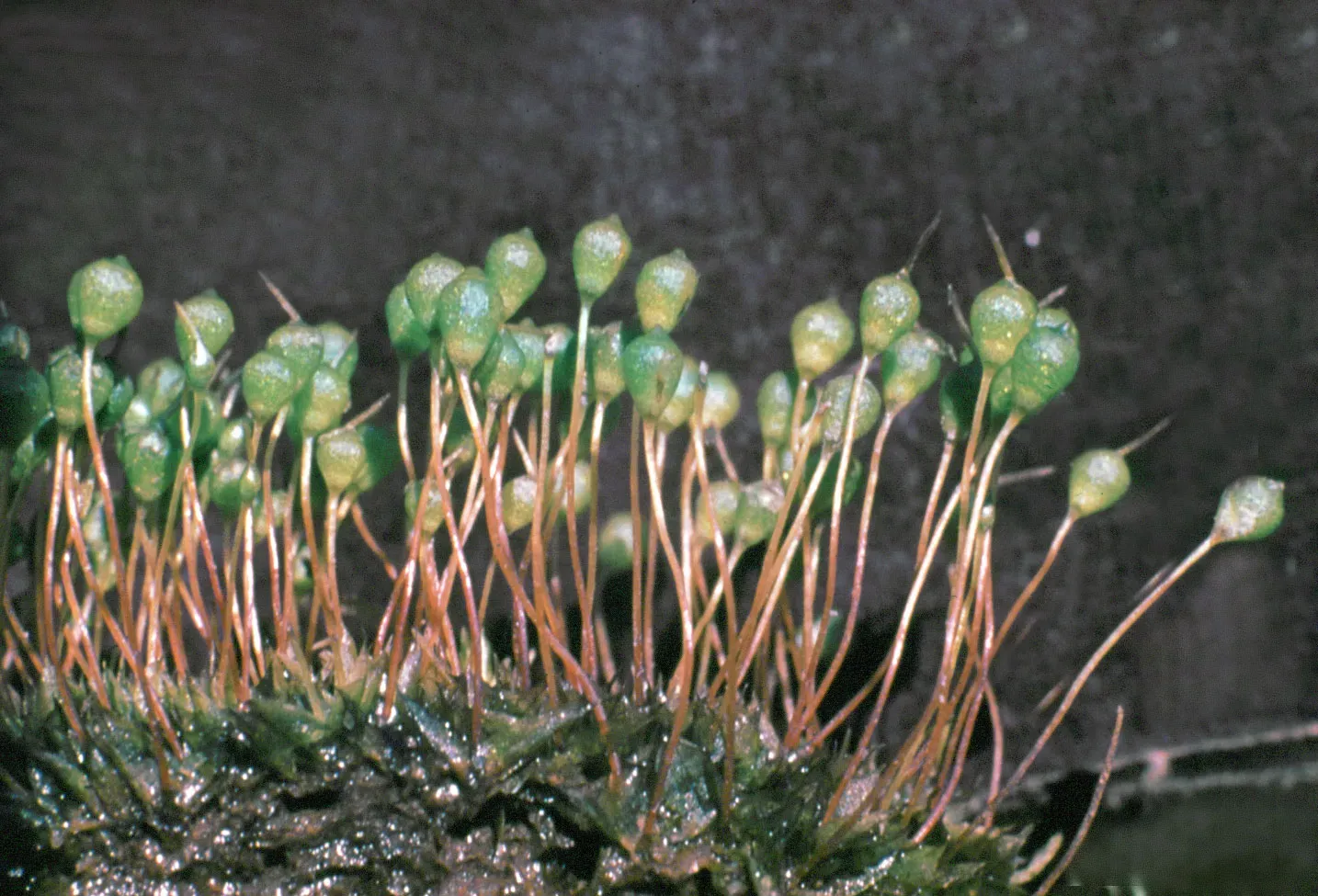
Micromitrium tomentosum is a tiny acrocarpous moss, meaning its sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) grow at the tips of the stems. It forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats, with stems reaching only a few centimeters in height. The leaves are small, ovate to lanceolate in shape, and often have a distinctive tomentose (woolly) appearance due to the presence of numerous hair-like structures called papillae.
One of the key identifying features of Micromitrium tomentosum is its unique calyptra – a cap-like structure that covers the developing sporophyte. In this species, the calyptra is mitriform (cone-shaped) and deeply furrowed, giving it a distinctive appearance.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Micromitrium tomentosum is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and North America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from tree bark and rocks to soil and decaying wood. This moss is particularly fond of calcareous (calcium-rich) substrates, making it a common sight on limestone outcrops and old walls.

sempervivum-arachmoideum-tomentosum-2.jpg from: https://www.farmyardnurseries.co.uk/shop/Sempervivum-arachnoideum-ssp-tomentosum-Minor-M4260

Pelargonium_tomentosum_fleurs_floraison_printemps_balcon_Paris_mai_2022_0-e1653922225868.jpg from: https://www.pariscotejardin.fr/2022/05/la-floraison-discrete-du-pelargonium-tomentosum/
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Micromitrium tomentosum plays a vital role in its ecosystem. Like other bryophytes, it helps to regulate moisture levels, prevent soil erosion, and provide a microhabitat for various invertebrates and microorganisms.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Micromitrium tomentosum is its ability to survive in dry conditions. When moisture is scarce, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves and slowing down its metabolic processes. Once water becomes available again, it quickly revives and resumes its growth and reproduction.

rhododendron-tomentosum-syn-ledum-palustre-commonly-known-as-marsh-labrador-tea-northern-labrador-tea-wild-rosemary-78436314.jpg from: https://www.dreamstime.com/stock-photos-rhododendron-tomentosum-syn-ledum-palustre-image19993143
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the United Kingdom, researchers found that Micromitrium tomentosum played a crucial role in the colonization of newly exposed calcareous substrates. Its ability to establish itself quickly on these surfaces paved the way for other plant species to follow, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
Technical Table

spc_000010336_000071599.jpg from: https://www.orchidroots.com/detail/information/?pid=462934&role=
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
Class
 14442303703_d782674a49_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/mercadanteweb/14442303703 |
Bryopsida |
| Order | Orthotrichales |
| Family | Orthotrichaceae |
| Genus | Micromitrium
 Gompholobium-tomentosum-Yallingup-Siding-21Nov2020-2-RClark.jpg from: https://gcln.org.au/product/gompholobium-tomentosum/ |
| Species | tomentosum
 c77948d9b4f3731ff5c132842c7cbe44.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/189221621818449443/ |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to lanceolate |
| Calyptra | Mitriform, deeply furrowed |
Conclusion
Micromitrium tomentosum (Hornsch.) Paris may be small in stature, but its impact on the natural world is undeniable. This remarkable moss species serves as a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the plant kingdom, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: What other hidden marvels await our discovery in the intricate tapestry of life?
Urn-moss.jpg from: https://www.britannica.com/plant/top-moss