
400886.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6809
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Anthoceros agrestis Paton moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Anthocerotaceae family, also known as the Anthoceros or hornwort family. This unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a unique glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s diversity.
Background

4be31130f4deb931d3bc8dbfc9e5085e.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/anthoceros-agrestis-care-growing-guide–1152569729612463854/
The Anthocerotaceae family belongs to the division Anthocerotophyta, which is one of the three main groups of bryophytes, alongside mosses (
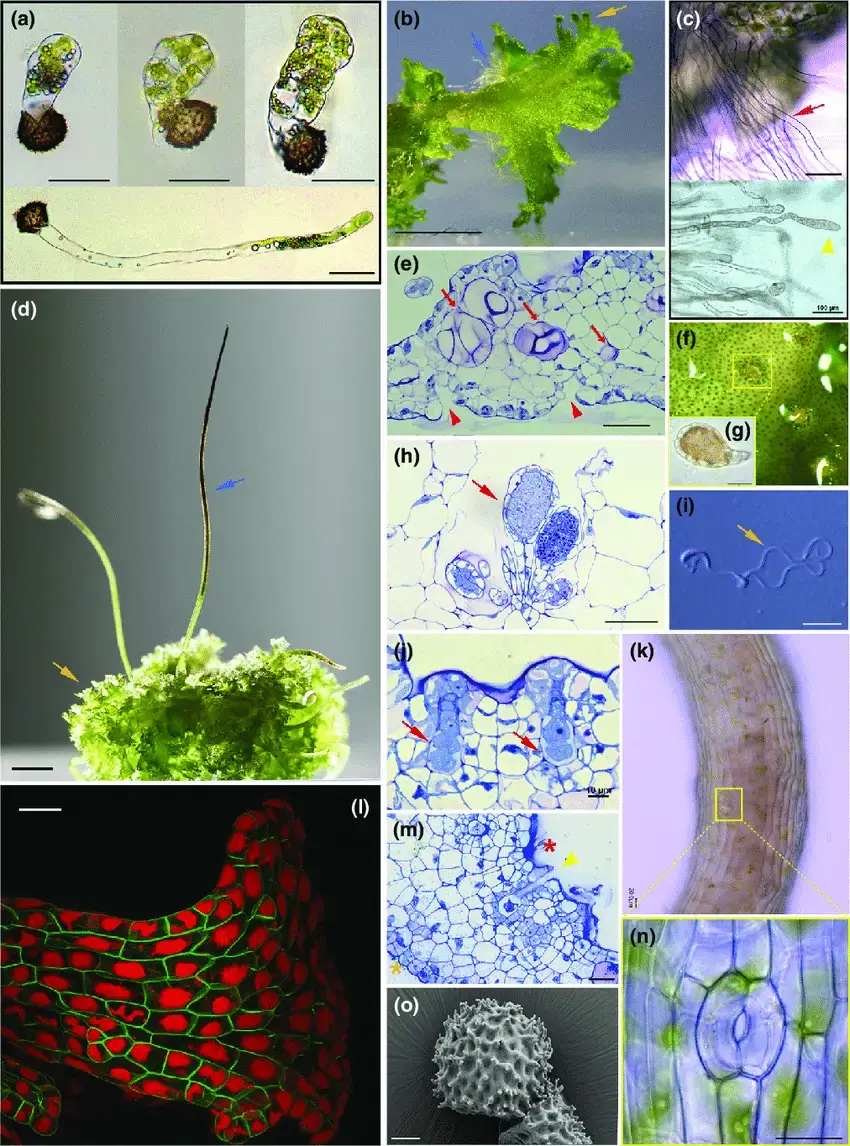
Key-morphological-features-of-Anthoceros-agrestis-a-Light-micrograph-LM-of.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Key-morphological-features-of-Anthoceros-agrestis-a-Light-micrograph-LM-of_fig2_343642257
Bryophyta

836073.jpg from: https://www.bio-forum.pl/messages/3280/836068.html
) and liverworts (Marchantiophyta). These diminutive yet resilient plants have played a crucial role in the evolution of land plants, serving as a bridge between aquatic and terrestrial environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
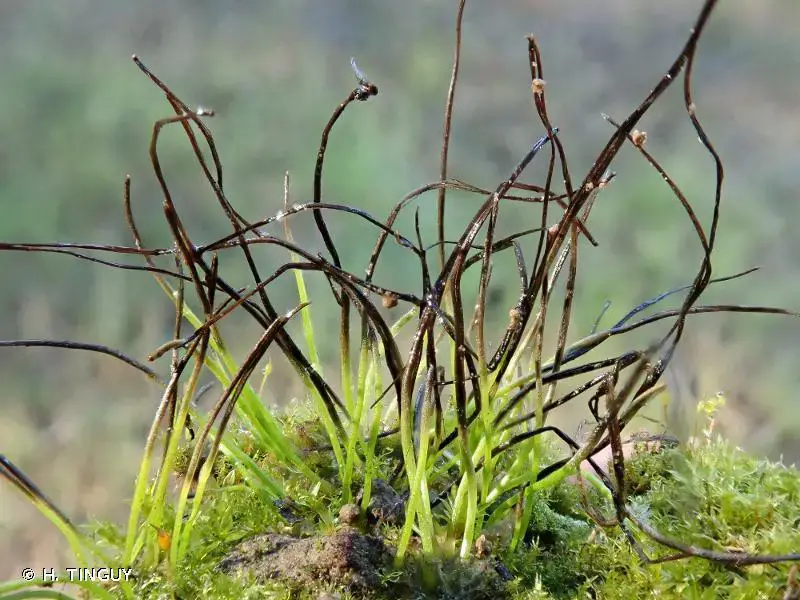
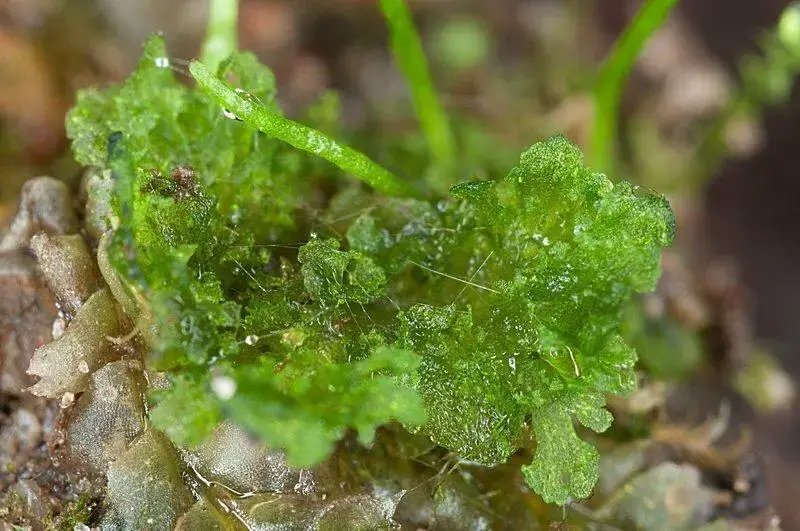
The Anthoceros agrestis Paton moss is a thallose liverwort, meaning it grows in a flattened, ribbon-like form. Its gametophyte, the dominant phase of its life cycle, consists of a green, irregularly branched thallus that creeps along the substrate. One of the most distinctive features of this moss is the presence of
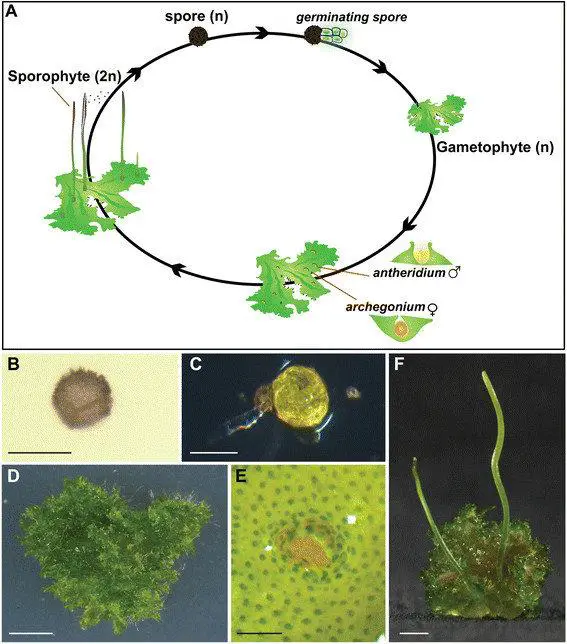
Life-cycle-of-the-hornwort-Anthoceros-agrestis-The-life-cycle-of-A-agrestis-A-starts.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Life-cycle-of-the-hornwort-Anthoceros-agrestis-The-life-cycle-of-A-agrestis-A-starts_fig1_274947363
hornlike structures called sporophytes, which emerge from the thallus and bear spores for reproduction.
Global Distribution and Habitat
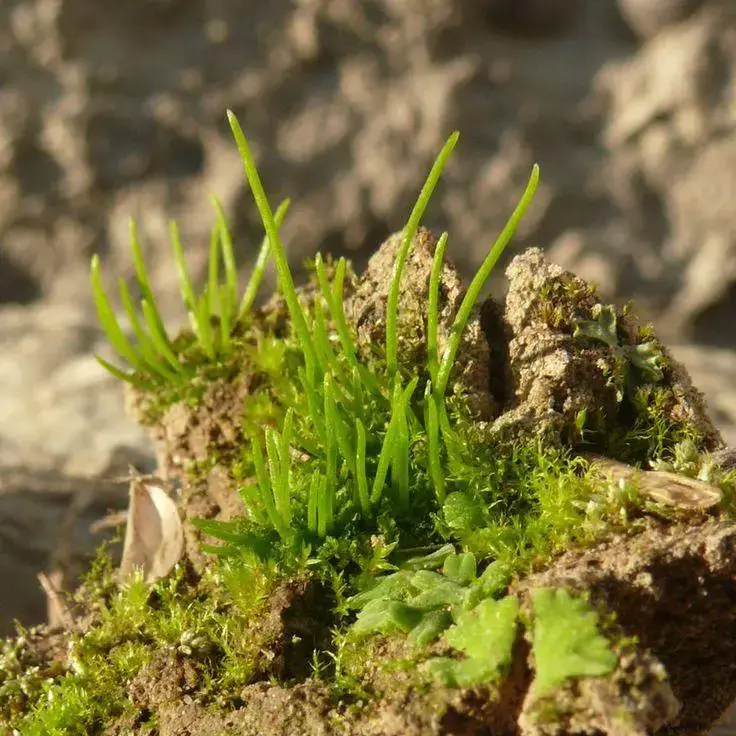
Anthoceros agrestis Paton is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, North America, and parts of Asia. It thrives in moist, shaded environments, often found growing on soil, decaying wood, or in the crevices of rocks and tree bark. This moss prefers habitats with high humidity and moderate temperatures, making it a common sight in forests, woodlands, and other damp, sheltered areas.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Anthoceros agrestis Paton plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating a suitable environment for other plants and organisms to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a food source and habitat for various invertebrates, further enhancing biodiversity.

The-target-species-Field-hornwort-Anthoceros-agrestis-Paton-Carolina-hornwort_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-target-species-Field-hornwort-Anthoceros-agrestis-Paton-Carolina-hornwort_fig3_349924023
One of the remarkable adaptations of Anthoceros agrestis Paton is its ability to survive periods of drought by entering a dormant state. When conditions become unfavorable, the moss can dry out and remain in a state of suspended animation until moisture returns, allowing it to quickly revive and continue its growth.
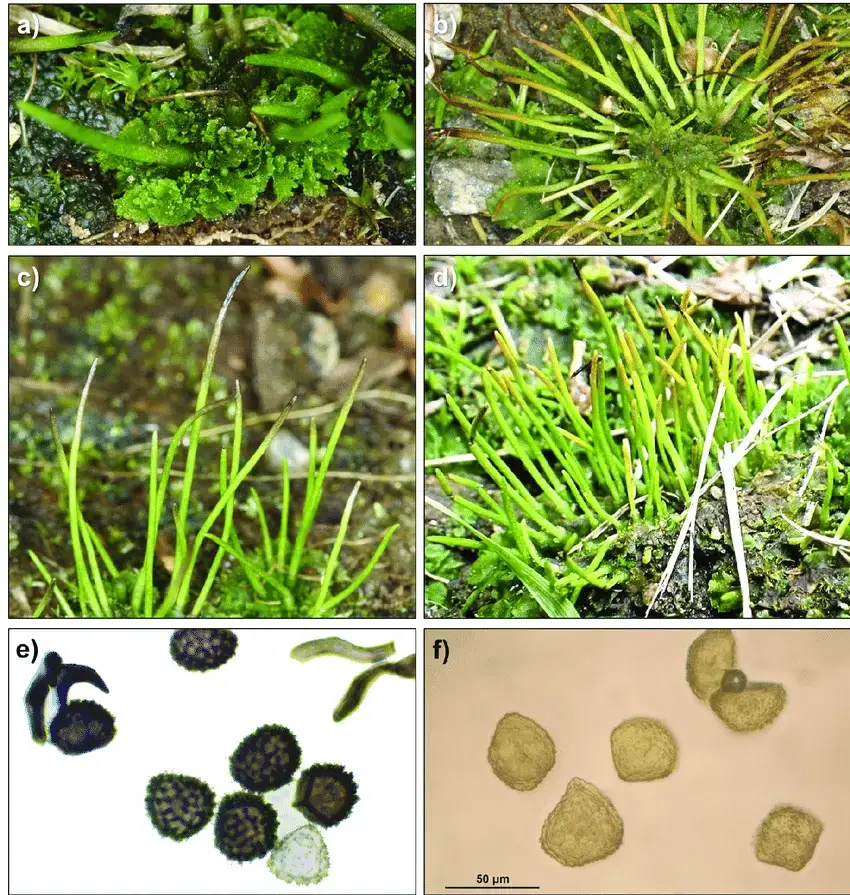

Comparaison-entre-lAnthoceros-agrestis-colonne-de-gauche-et-le-Phaeoceros.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Comparaison-entre-lAnthoceros-agrestis-colonne-de-gauche-et-le-Phaeoceros_fig2_327534593
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in a temperate forest ecosystem, researchers found that Anthoceros agrestis Paton played a crucial role in maintaining soil moisture levels and facilitating the germination of various plant species. The moss’s ability to retain water and create a microclimate suitable for seedling establishment was highlighted as a key factor in promoting biodiversity within the forest understory.
Technical Table

Anthoceros-agrestis-A-with-maturing-sporophytes-Phaeoceros-carolinianus-B-with.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Anthoceros-agrestis-A-with-maturing-sporophytes-Phaeoceros-carolinianus-B-with_fig2_352355944

783157.jpg from: https://waarnemingen.be/species/17683/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Anthoceros agrestis Paton |
| Family | Anthocerotaceae |
| Division | Anthocerotophyta |
| Class | Anthocerotopsida |
| Growth Form | Thallose liverwort |
| Sporophyte | Hornlike structures |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded environments |
| Distribution | Europe, North America, Asia |
Conclusion
The Anthoceros agrestis Paton

18.193582bc7eef158ad31cc53da2d9daa7.jpg from: https://eol.org/pages/399515
moss, a member of the Anthocerotaceae family, is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. Its unique morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of bryophytes, we are left with a thought-provoking question: What other wonders lie hidden within the microscopic realms of these ancient and resilient plants?