
The-effect-of-methanol-extract-of-liverwort-and-Racomitrium-moss-on-mRNA-expressions-of.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-effect-of-methanol-extract-of-liverwort-and-Racomitrium-moss-on-mRNA-expressions-of_fig1_355318481
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of
m-42a8.jpg from: https://www.irishwildflowers.ie/pages-moss/m-42.html
bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the

maxresdefault.jpg from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bvNLoBxqZCQ
Racomitrium alare (Broth.) Paris moss. Belonging to the Grimmiaceae family, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Background
Bryophytes, often referred to as the “ancient lineage of land plants,” are a diverse group that includes mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. These resilient organisms have played a crucial role in the evolution of terrestrial ecosystems, paving the way for the emergence of more complex plant life.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
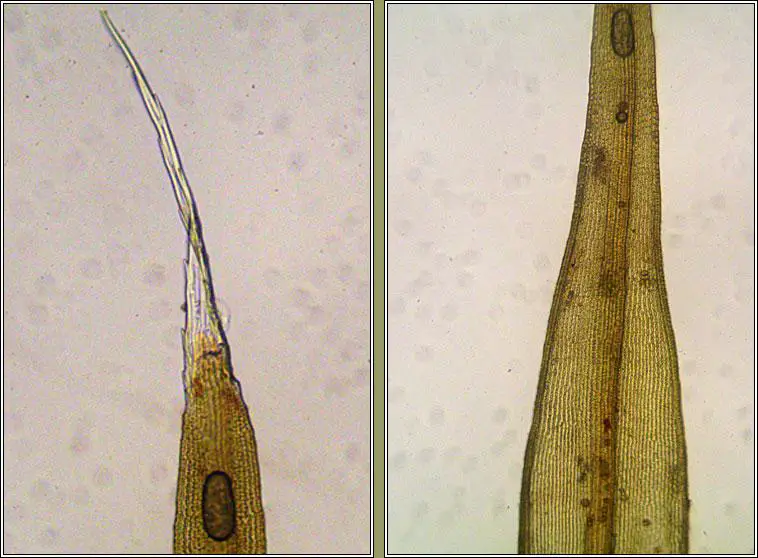
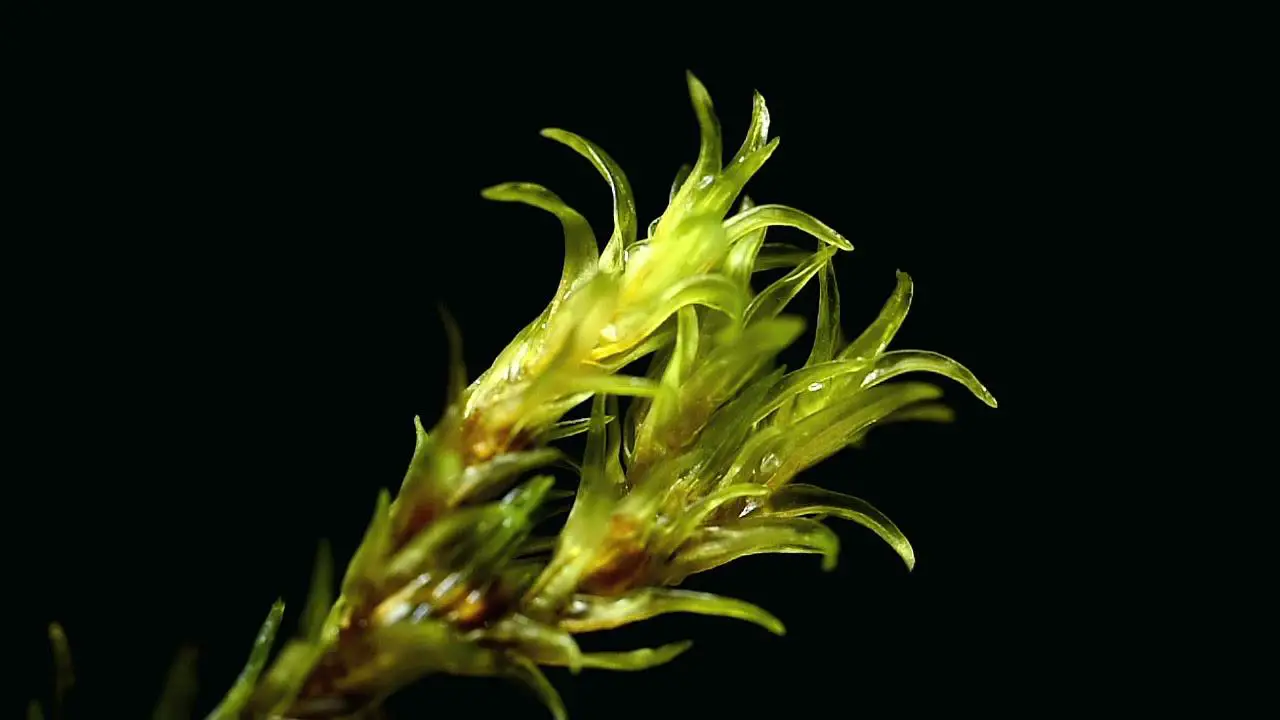
The Racomitrium alare (Broth.) Paris moss is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive hair-point at the apex. The leaf margins are often recurved, and the costa (midrib) is prominent, extending to the leaf tip. This moss is dioicous, meaning that male and female reproductive structures are found on separate plants.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Racomitrium alare is widely distributed across various regions, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in a range of habitats, from rocky outcrops and cliffs to tree bark and soil. This moss is particularly well-adapted to dry and nutrient-poor environments, making it a true survivor in harsh conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Racomitrium alare plays a significant role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and water retention, creating microhabitats for other organisms. Additionally, this moss is known for its remarkable ability to tolerate desiccation, thanks to its specialized adaptations.
One of the key adaptations of Racomitrium alare is its ability to curl its leaves when dry, minimizing water loss. This process, known as poikilohydry, allows the moss to enter a state of dormancy and revive when moisture becomes available again.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Rocky Mountains of North America, researchers found that Racomitrium alare played a crucial role in stabilizing alpine soils and facilitating the establishment of other plant species. Its dense mats helped prevent erosion and provided a suitable microclimate for seedling germination.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Grimmiales |
| Family | Grimmiaceae |
| Genus | Racomitrium |
| Species | alare |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, with a hair-point at the apex |
| Leaf Margin | Often recurved |
| Costa | Prominent, extending to the leaf tip |
| Sexuality | Dioicous |
Conclusion
The Racomitrium alare (Broth.) Paris moss is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. Its ability to thrive in harsh environments and contribute to ecosystem processes makes it a fascinating subject of study. As we continue to explore the intricate world of bryophytes, this unassuming moss may hold the key to unlocking new insights into the evolution and ecology of these ancient lineages. What other secrets might this tiny, yet mighty moss hold, waiting to be discovered?