
16914889880_c6ccdd99c4.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/61217591@N07/16914889880/
Introduction
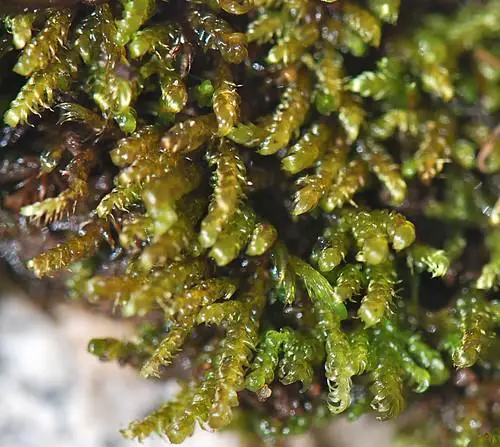
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the

h_ochraceum2.jpg from: https://soe.wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/hygrohypnum_ochraceum.html
Hygrohypnum ochraceum (Turner ex Wilson) Loeske. This unassuming yet remarkable moss, belonging to the Scorpidiaceae family and commonly known as Hygrohypnum, has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this fascinating moss, let’s set the stage with some essential background information. Bryophytes, a group that includes mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest and most primitive land plants on Earth. These resilient organisms have played a crucial role in the colonization of terrestrial environments, paving the way for the evolution of more complex plant life.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
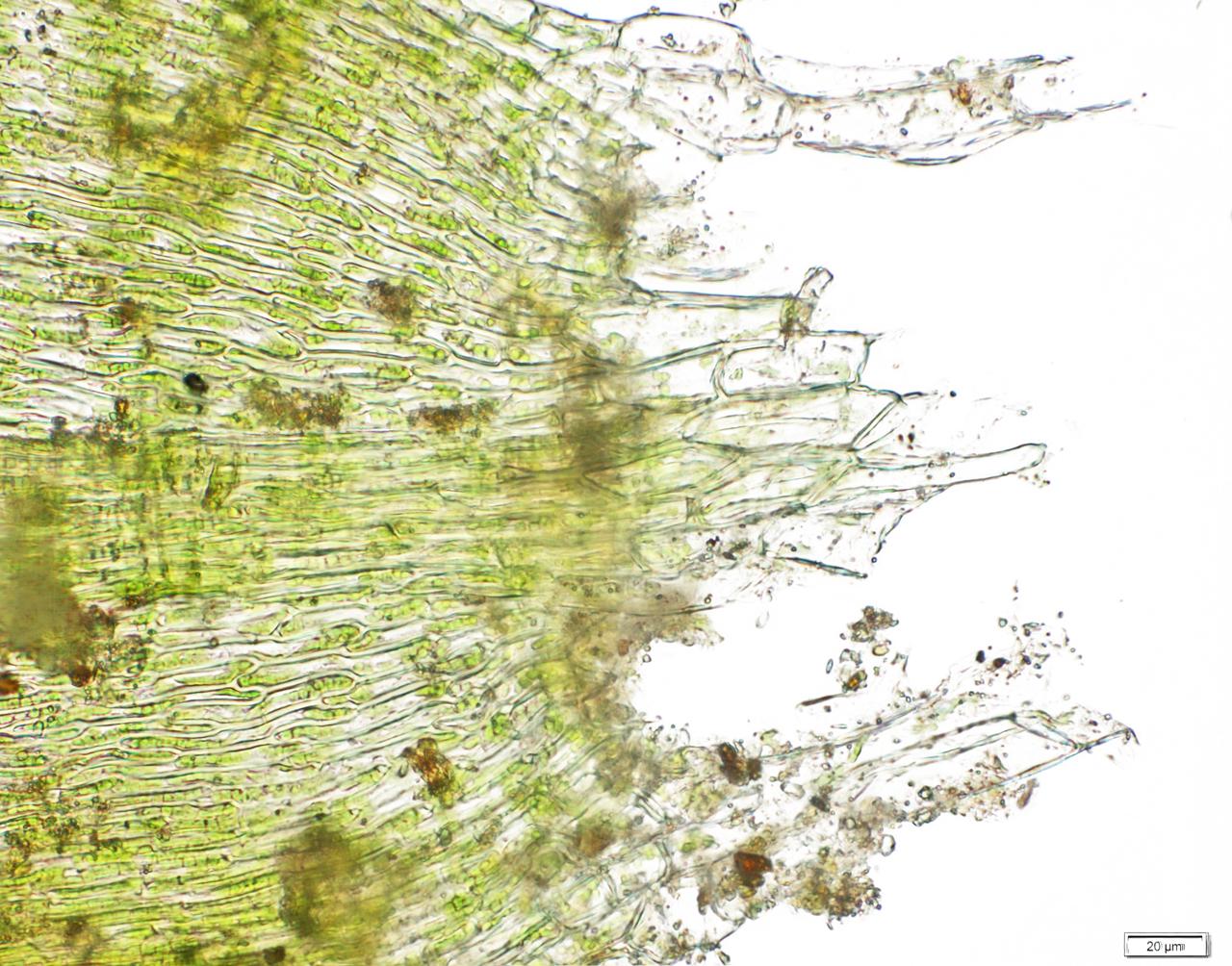
The Hygrohypnum ochraceum is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems and branches grow horizontally along the substrate. Its vibrant ochre-yellow color, derived from the presence of pigments called carotenoids, is one of its most distinctive features. This moss forms dense, cushion-like mats or tufts, with stems that can reach up to 10 centimeters in length.
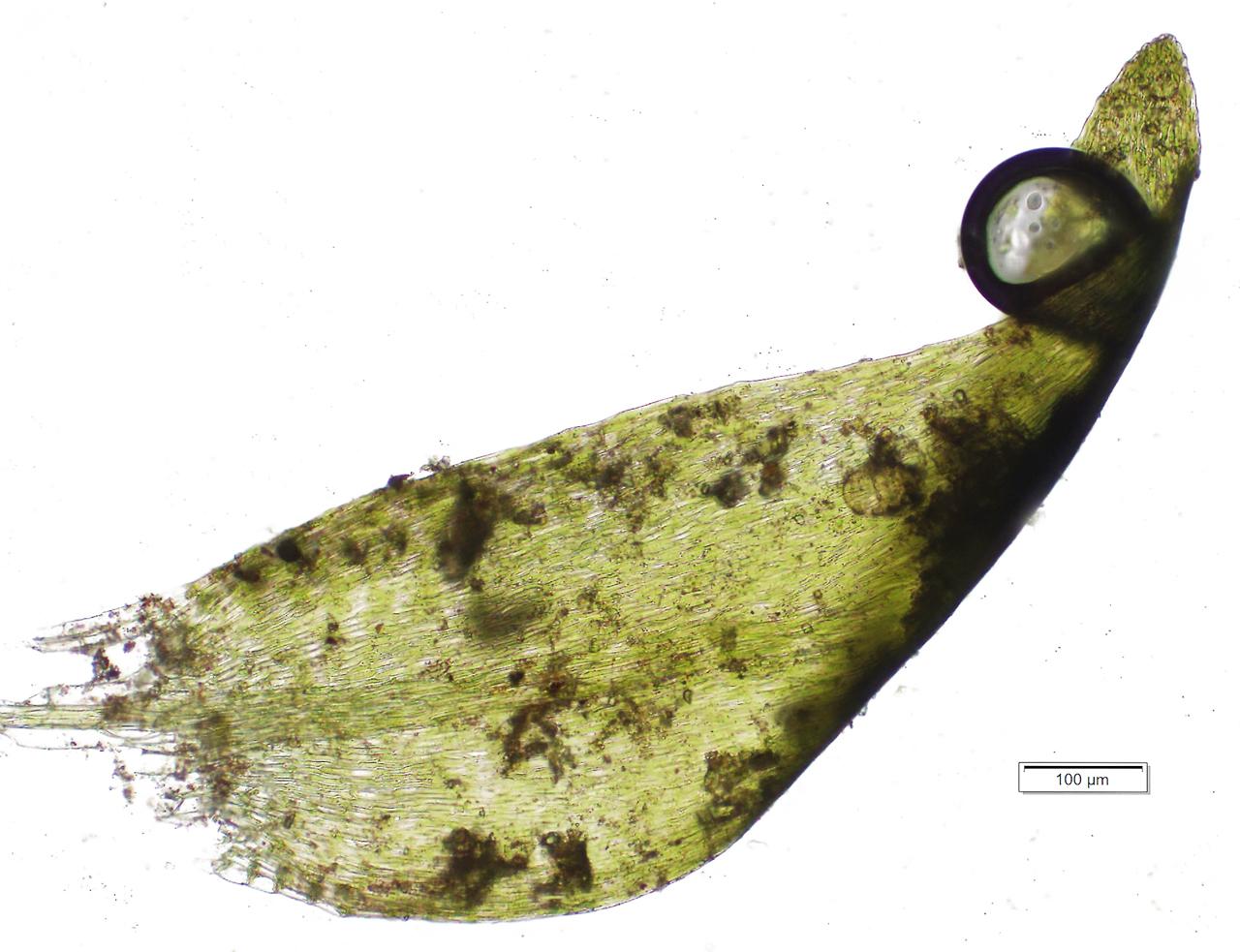
The leaves of Hygrohypnum ochraceum are ovate-lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive midrib that extends nearly to the leaf apex. The leaf margins are entire (smooth), and the leaf cells are elongated and relatively thick-walled, contributing to the moss’s overall robustness.
Global Distribution and Habitat
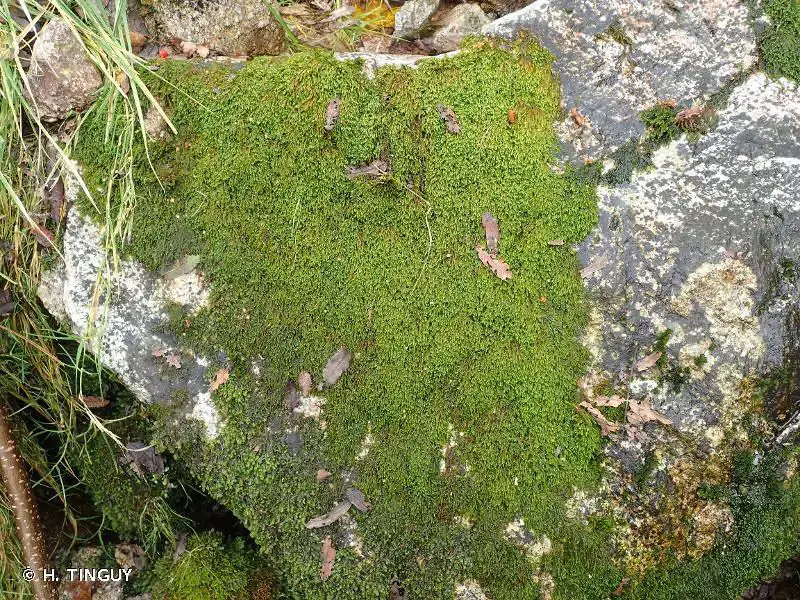
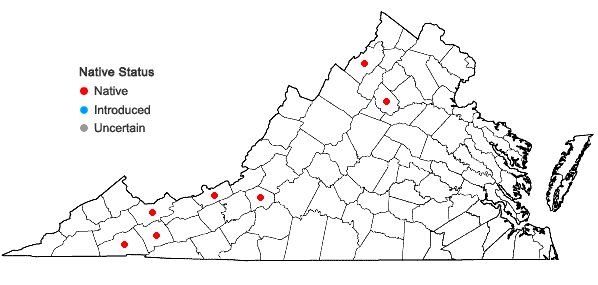
Hygrohypnum ochraceum is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from moist and shaded areas in forests to the banks of streams, rivers, and other freshwater bodies.
This moss is particularly well-adapted to aquatic environments, where it can grow submerged or partially submerged. Its ability to tolerate fluctuating water levels and periods of desiccation makes it a resilient and versatile species.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Hygrohypnum ochraceum plays a vital role in its ecosystem, serving as a habitat and food source for various invertebrates and microorganisms. Its dense mats provide shelter and nesting sites for insects, spiders, and other small creatures, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
One of the remarkable adaptations of this moss is its ability to regulate water flow and prevent soil erosion. Its dense growth pattern and extensive rhizoid system help stabilize stream banks and retain moisture, making it an invaluable ally in riparian ecosystems.
Additionally, Hygrohypnum ochraceum is known for its ability to accumulate heavy metals and other pollutants from the environment, making it a potential bioindicator for monitoring water quality and environmental health.
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers found that Hygrohypnum ochraceum

239277.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5798
played a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of stream ecosystems. Its presence helped stabilize stream banks, reduce erosion, and provide habitat for various aquatic invertebrates, contributing to the overall health and biodiversity of the ecosystem.
h_ochraceum5.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/hygrohypnum_ochraceum.html
Another interesting example comes from a research project in Europe, where Hygrohypnum ochraceum was used as a bioindicator to assess the levels of heavy metal pollution in freshwater systems. The moss’s ability to accumulate these contaminants made it a valuable tool for monitoring environmental quality and identifying potential sources of pollution.
Technical Table
Hygrohypnum_ochraceum_4085.png from: https://vaplantatlas.org/index.php?do=plant&plant=4085&search=equisetum
239275.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/436120
239280.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/436120/tab/fiche
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Hygrohypnum ochraceum (Turner ex Wilson) Loeske |
| Family | Scorpidiaceae |
| Common Name | Hygrohypnum |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss, forming dense cushions or tufts |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Margin | Entire (smooth) |
| Leaf Cells | Elongated, relatively thick-walled |
| Color | Vibrant ochre-yellow |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas, stream banks, freshwater bodies |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North America, parts of South America |
| Ecological Roles | Habitat provision, soil stabilization, bioindicator |
Conclusion
The Hygrohypnum ochraceum (Turner ex Wilson) Loeske moss, with its vibrant ochre-yellow hue and remarkable adaptations, is a true marvel of the bryophyte world. From its role in stabilizing stream banks and preventing erosion to its potential as a bioindicator for environmental monitoring, this unassuming moss has proven its worth time and time again.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, the Hygrohypnum ochraceum serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and resilience of nature’s smallest inhabitants. Perhaps the next time you encounter a vibrant yellow-green mat along a stream or in a shaded forest, you’ll pause to appreciate the wonders of this remarkable Bryopsida species.