203951.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5151
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/1248803-Lescuraea-mutabilis
bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its remarkable adaptability and resilience – the Lescuraea mutabilis (Brid.) Lindb., commonly known as

3507535914_f46ff68d31_z.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/12639178@N07/3507535914/
Lescuraea. This unassuming yet fascinating member of the Pseudoleskeaceae family has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide, offering a unique glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background

120px-Lescuraea_mutabilis_(a%2C_143358-474515)_8167.JPG from: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Lescuraea_mutabilis
Before delving into the intricacies of Lescuraea mutabilis, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with fossil records dating back over 400 million years, making them true survivors of evolutionary history.
Main Content
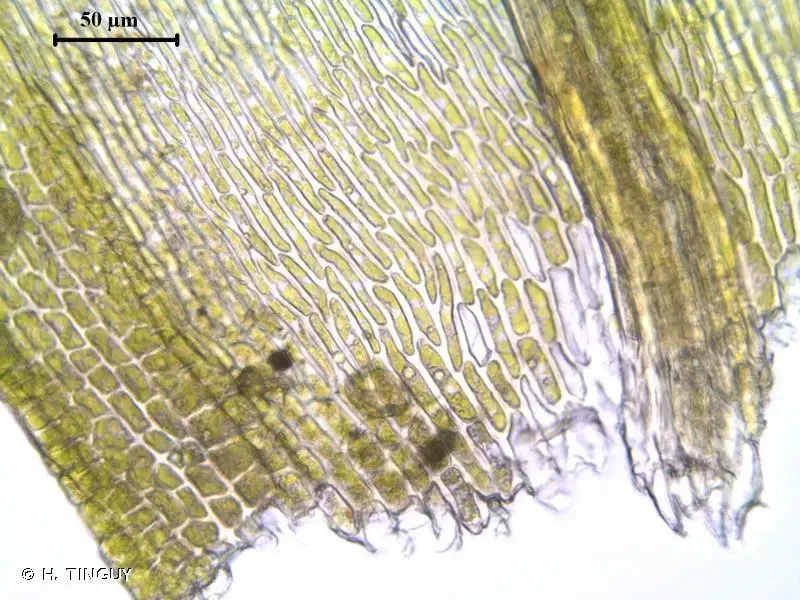
Morphology and Identification
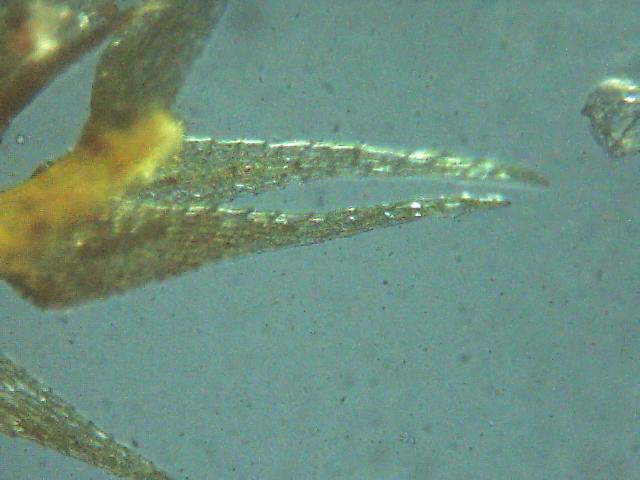
Lescuraea mutabilis is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its slender stems are typically unbranched, reaching heights of up to 2-3 centimeters. The leaves are ovate-lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a short awn or hair-like projection. This characteristic feature aids in the identification of this species.
Global Distribution and Habitat
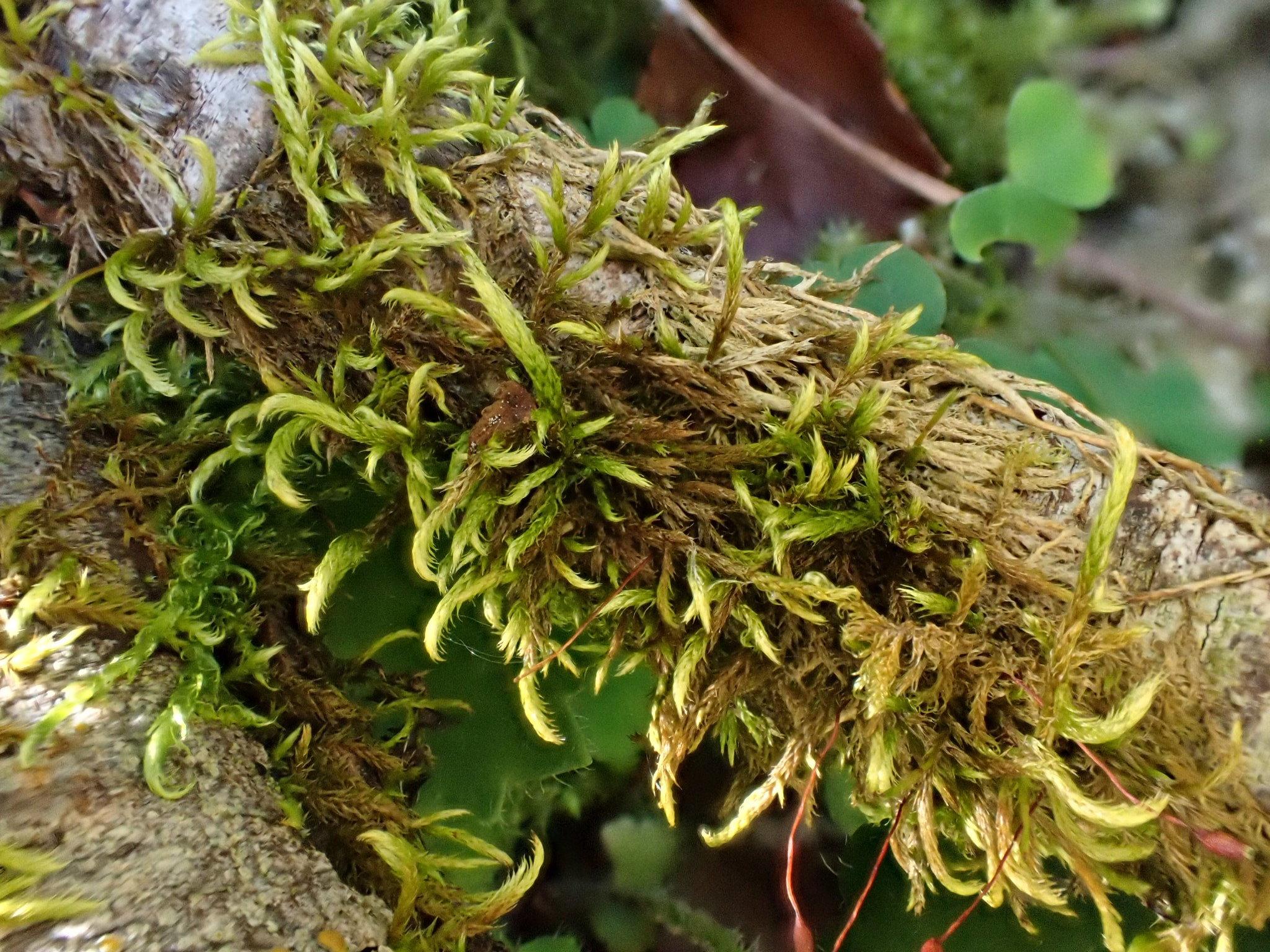
Lescuraea mutabilis is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, thriving in various habitats such as rock crevices, cliffs, boulders, and even tree bark. It is particularly abundant in mountainous regions, where it can be found growing on acidic substrates like granite or sandstone. This moss is known for its tolerance to desiccation, allowing it to survive in dry and exposed environments.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

original.jpeg from: https://www.gbif.org/pt/species/2681255
Despite its diminutive size, Lescuraea mutabilis plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It acts as a pioneer species, colonizing bare rock surfaces and facilitating the establishment of other plant species. Additionally, its dense mats help retain moisture and prevent soil erosion, contributing to the stability of the environment.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Lescuraea mutabilis is its ability to undergo desiccation and revive upon rehydration. This process, known as poikilohydry, allows the moss to survive prolonged periods of drought by entering a dormant state and resuming its metabolic activities when water becomes available again.
Case Study: Lescuraea mutabilis in Alpine Environments
In the harsh and unforgiving alpine environments, Lescuraea mutabilis thrives, showcasing its resilience and adaptability. A study conducted in the Rocky Mountains of North America revealed that this moss species plays a crucial role in stabilizing soil and facilitating the establishment of other plant communities in these extreme conditions.
Pleurochaete+squarrosa+(Brid.)+Lindb+(1).JPG from: https://floranelsalento.blogspot.com/2014/02/pleurochaete-squarrosa-brid-lindb.html
209765.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/436151
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Pseudoleskeaceae |
| Genus | Lescuraea |
| Species | mutabilis |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate, with a costa extending beyond the leaf apex |
| Habitat | Rock crevices, cliffs, boulders, tree bark |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere, particularly in mountainous regions |
Conclusion
Lescuraea mutabilis, a true marvel of the bryophyte world, serves as a testament to the incredible resilience and adaptability of these often-overlooked organisms. From its unique morphological features to its remarkable ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions, this moss species continues to captivate and inspire moss enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we delve deeper into the intricate world of bryophytes, what other fascinating secrets await us, hidden within the folds of these ancient and resilient life forms?