
medium.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/167145-Pohlia-proligera
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Pohlia proligera (Kindb.) Lindb. ex Broth. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Mniaceae family. Often referred to simply as Pohlia, this unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this diminutive marvel and uncover its secrets.
Background
Before we explore the intricate details of Pohlia proligera, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
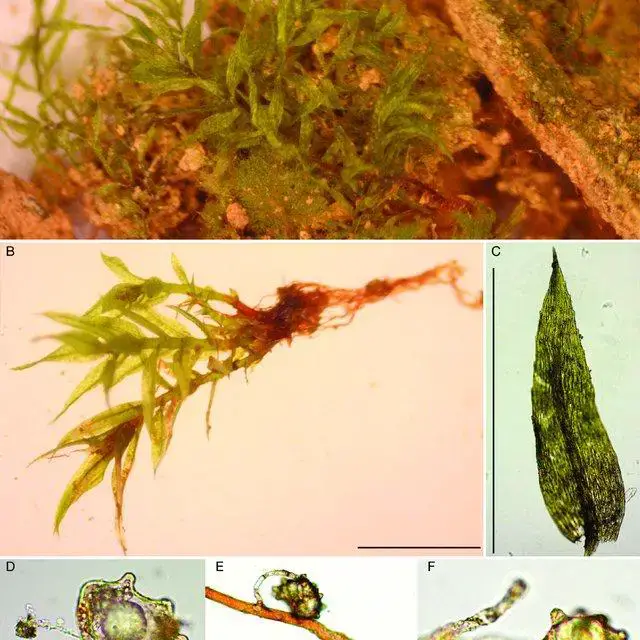
Pohlia proligera is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, green to yellowish-green tufts or cushions. Its slender stems can reach up to 5 centimeters in height, and the leaves are narrowly lanceolate, with a distinctive midrib extending to the leaf apex. One of the key identifying features of this moss is its

Pohlia-lutescens-Limpr-H-Lindb-KTUB-1608-A-habit-B-shoot-wet-C-leaf-D-F_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Pohlia-lutescens-Limpr-H-Lindb-KTUB-1608-A-habit-B-shoot-wet-C-leaf-D-F_fig2_348909786
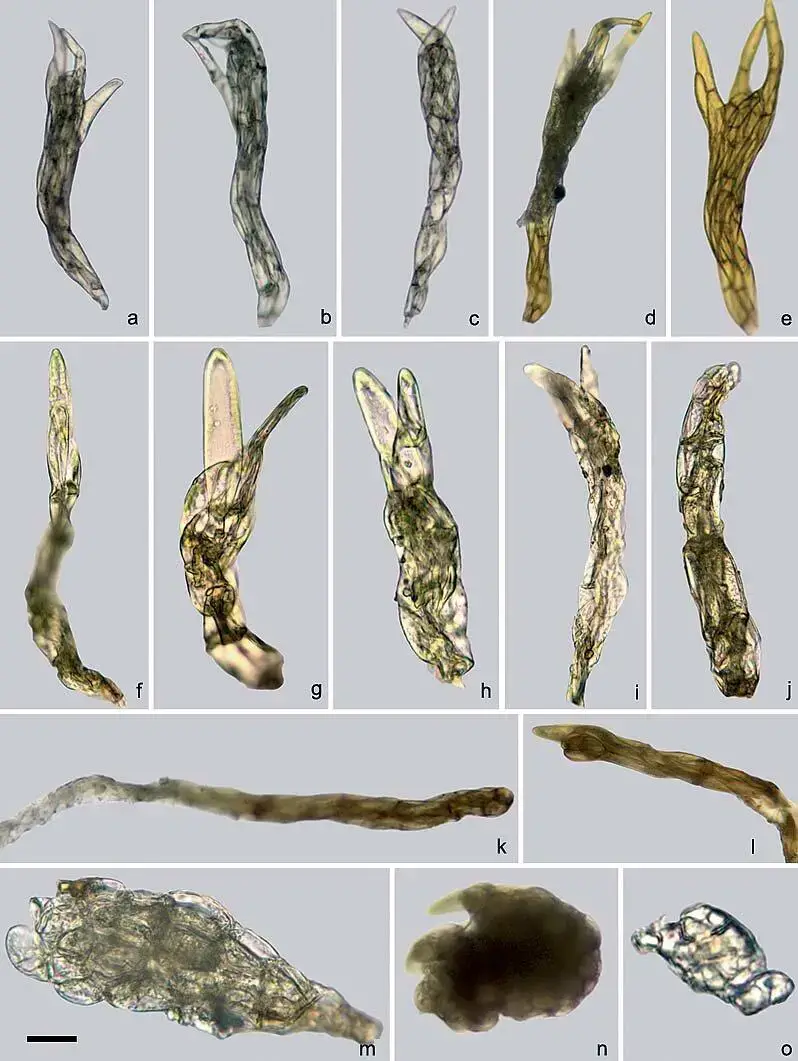
prolific production of gemmae – small, specialized reproductive structures that aid in its propagation.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss has a widespread distribution, found across various regions of the Northern Hemisphere, including North America, Europe, and Asia. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from moist soil and disturbed areas to the edges of streams and ponds. Pohlia proligera is particularly fond of acidic substrates, making it a common sight in coniferous forests and bogs.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Pohlia proligera plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating a nurturing environment for other plants to thrive. Additionally, this moss serves as a valuable food source and habitat for various invertebrates, further enhancing biodiversity.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Pohlia proligera is its ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. While sexual reproduction involves the production of spores, the asexual reproduction through gemmae allows for rapid colonization and dispersal, ensuring the moss’s survival in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that Pohlia proligera played a crucial role in the recovery of disturbed forest ecosystems. Its ability to rapidly colonize and stabilize soil surfaces facilitated the establishment of other plant species, contributing to the overall restoration of the ecosystem.

Pohlia-annotina-MA-7549-a-e-bulbils-P-proligera-MUB-1584-f-i-bulbils-P.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Pohlia-annotina-MA-7549-a-e-bulbils-P-proligera-MUB-1584-f-i-bulbils-P_fig2_28162547
Technical Table
Pohlia_proligera_4482.png from: https://vaplantatlas.org/index.php?do=plant&plant=4482&search=equisetum
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Bryales |
| Family | Mniaceae |
| Genus | Pohlia |
| Species | Pohlia proligera (Kindb.) Lindb. ex Broth. |
| Common Name | Prolific Thread Moss |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous |
| Leaf Shape | Narrowly lanceolate |
| Reproduction | Sexual (spores) and asexual (gemmae) |
Conclusion
The Pohlia proligera (Kindb.) Lindb. ex Broth. moss, a member of the Mniaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its unassuming appearance belies its remarkable adaptations, ecological significance, and global distribution. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these often-overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems?