
medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/169800-Tortella-fragilis
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Tortella fragilis (Drumm.) Limpr. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Pottiaceae family. Often referred to simply as Tortella, this unassuming yet resilient moss has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Tortella fragilis, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
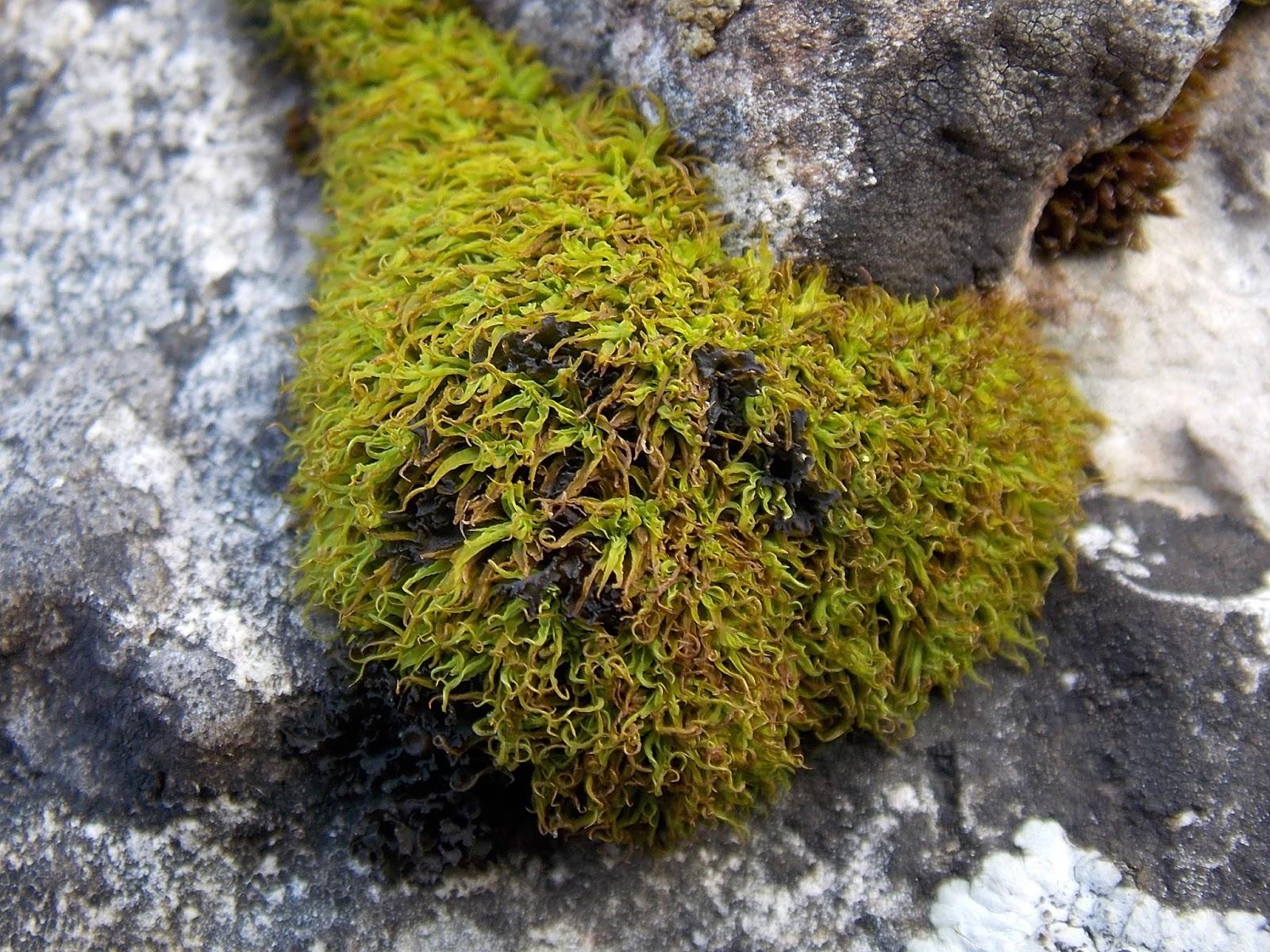
Tortella fragilis is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its stems are typically unbranched, and the leaves are arranged in a spiral pattern. The leaves themselves are lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive hair-point at the apex. This hair-point, or hyaline awn, is a characteristic feature that aids in identifying this species.
One of the most striking aspects of Tortella fragilis is its fragile nature, as implied by its specific epithet. The leaves are easily detached from the stem, a trait that has earned it the nickname “the fragile moss.” This fragility is thought to be an adaptation to dry conditions, allowing the moss to conserve moisture by shedding leaves during periods of drought.

0056.jpeg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=12940
Global Distribution and Habitat
Tortella fragilis is a cosmopolitan species, meaning it can be found on multiple continents. It has a wide distribution range, occurring in various regions across Europe, Asia, Africa, North America, and parts of South America. This moss thrives in a variety of habitats, including dry and exposed areas such as rock outcrops, sandy or gravelly soils, and even disturbed urban environments.
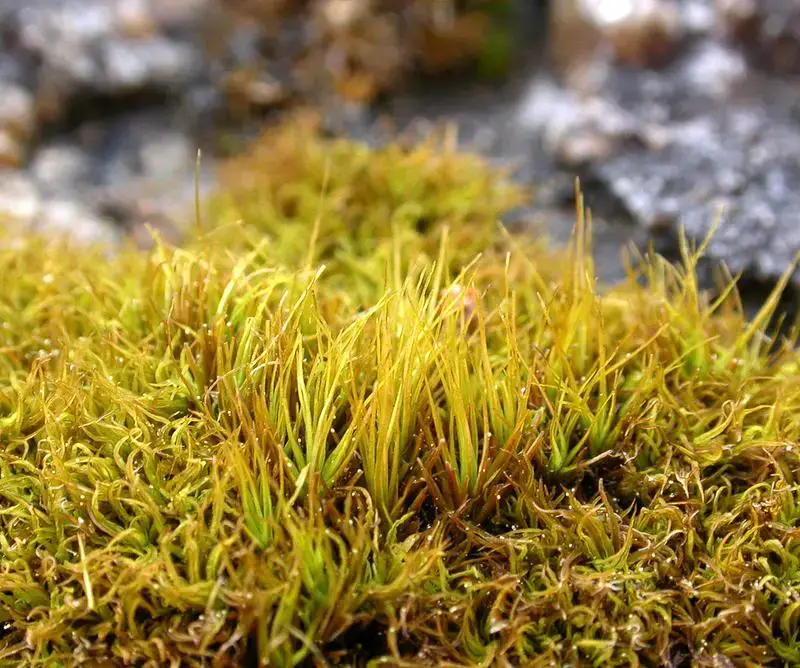

21393_2243_4.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/artbestamning/taxon/tortella-fragilis-2243
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its delicate appearance,
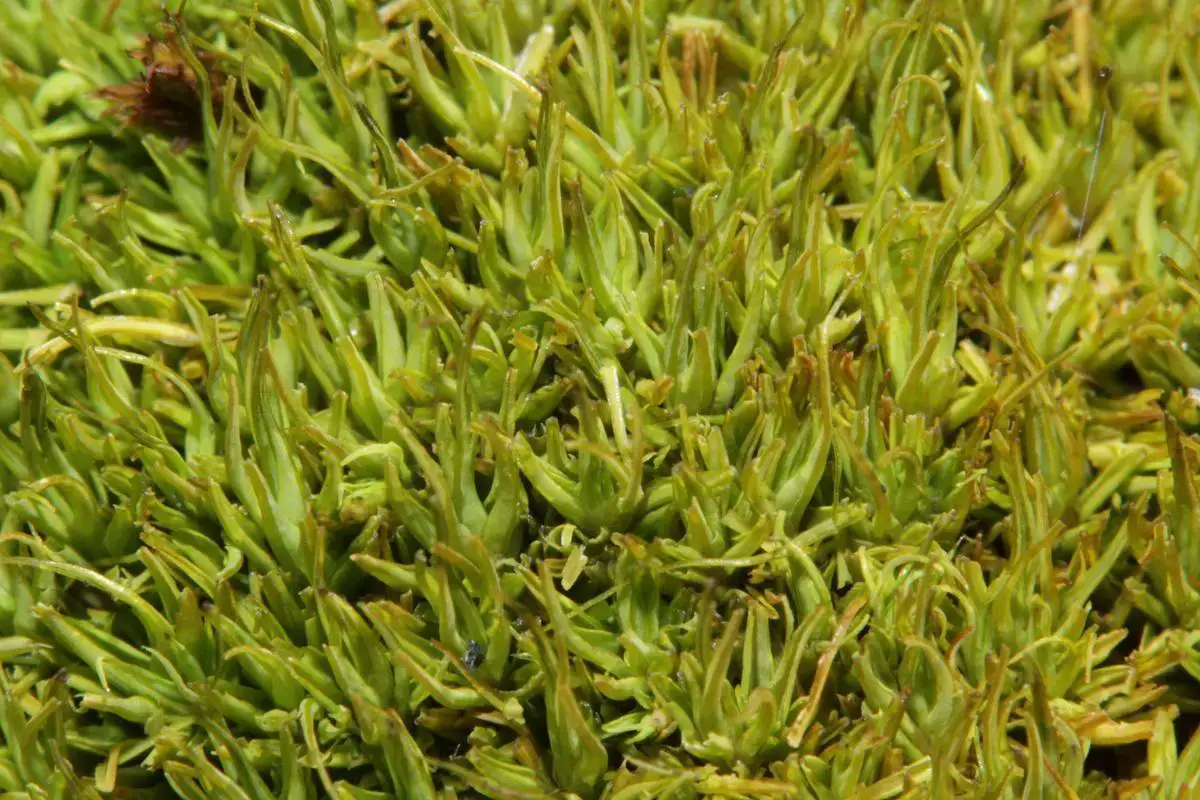

a0a0d31e61c7bc262094a8d71a892e203568456f.jpg from: https://atlas.roslin.pl/plant/9230
Tortella fragilis is a hardy and resilient moss, well-adapted to survive in harsh conditions. Its ability to tolerate desiccation and rapidly rehydrate after periods of drought makes it a pioneer species, capable of colonizing newly exposed or disturbed areas.
This moss plays a vital role in stabilizing soil and preventing erosion, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions. Its dense mats help retain moisture and create microhabitats for other organisms, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.
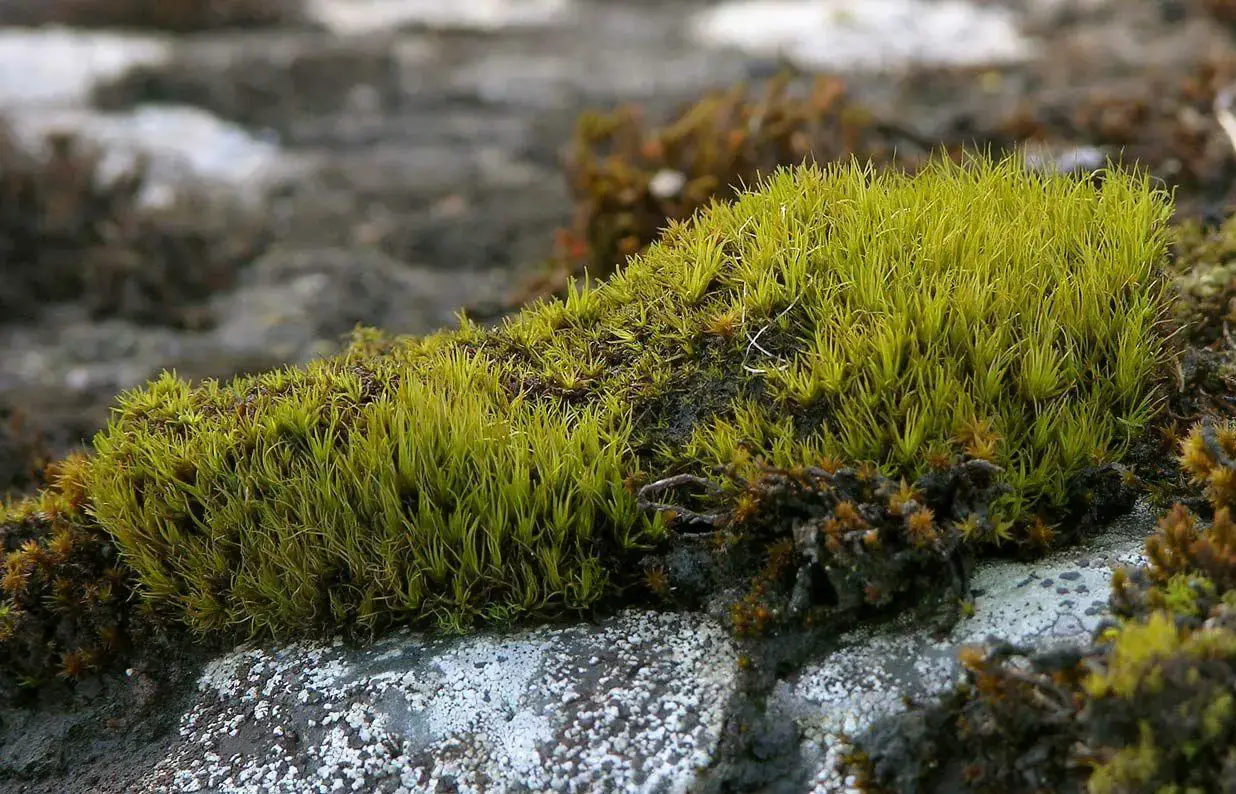

705135f47ae1dc04ec44716e039b0caa.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.fr/pin/777152479423470192/
Case Studies/Examples
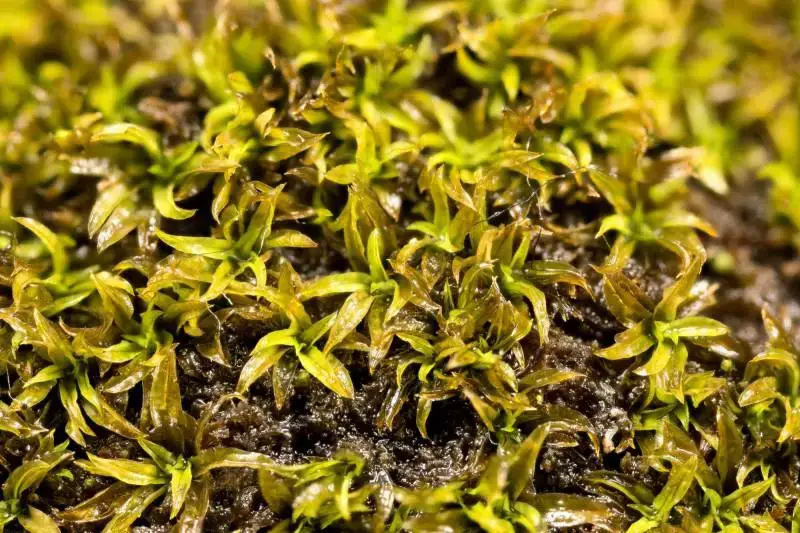

Tortella-humilis-6-800×533.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-tortella-humilis/
One notable example of the ecological significance of Tortella fragilis can be found in the Mediterranean region. In areas affected by desertification, this moss has been observed to play a crucial role in soil stabilization and the establishment of plant communities, acting as a facilitator for the growth of other plant species.
Technical Table

DSCN8450.JPG from: https://briofitedelmatese.blogspot.com/2018/03/tortella-tortuosa-hedw-limpr.html
428290.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5344

large.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/guide_taxa/225528
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Tortella |
| Species | fragilis |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss, forming dense tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, with a distinctive hair-point (hyaline awn) |
| Habitat | Dry and exposed areas, rock outcrops, sandy or gravelly soils, disturbed urban environments |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan, found on multiple continents |
Conclusion
The Tortella fragilis (Drumm.) Limpr. moss, a member of the Pottiaceae family, is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. Its fragile appearance belies its hardy nature, allowing it to thrive in harsh environments and play crucial ecological roles. From stabilizing soil to facilitating plant communities, this unassuming moss reminds us of the intricate web of life that exists even in the most seemingly barren landscapes. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, the Tortella fragilis stands as a testament to the wonders that can be found in the smallest and most unassuming of organisms.
Ponder this: In a world where fragility is often perceived as a weakness, how can we learn from the resilience and adaptability of the Tortella fragilis moss?