f02_409.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/cryptogamie-bryologie/volume-35/issue-4/cryb.v35.iss4.2014.409/Sarmentypnum-tundrae-Calliergonaceae-Bryophyta-Espèce-Nouvelle-Pour-la-France-et/10.7872/cryb.v35.iss4.2014.409.full
Introduction
In the vast and fascinating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the Sarmentypnum tundrae (Arnell) Hedenäs. This unassuming yet remarkable moss, belonging to the Calliergonaceae
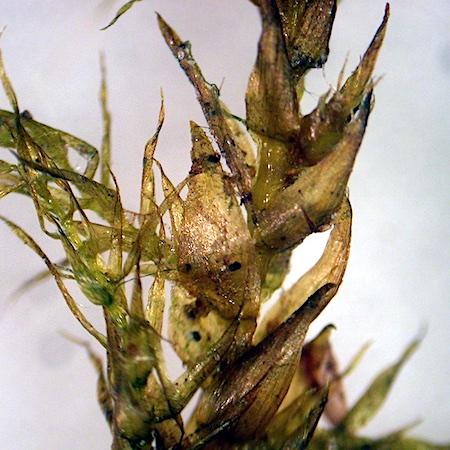

sarmentypnum_tundrae1.jpg from: http://www.luopioistenkasvisto.fi/Sivut/sammalet/pohjansirppisammal.html
family and commonly known as Sarmentypnum, has captured the interest of botanists and nature enthusiasts alike.
Background
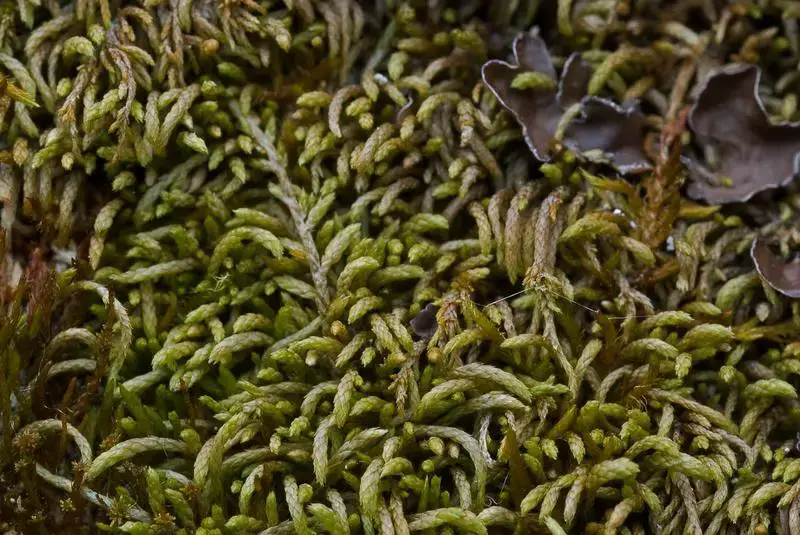

28645_2693_4.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/2693
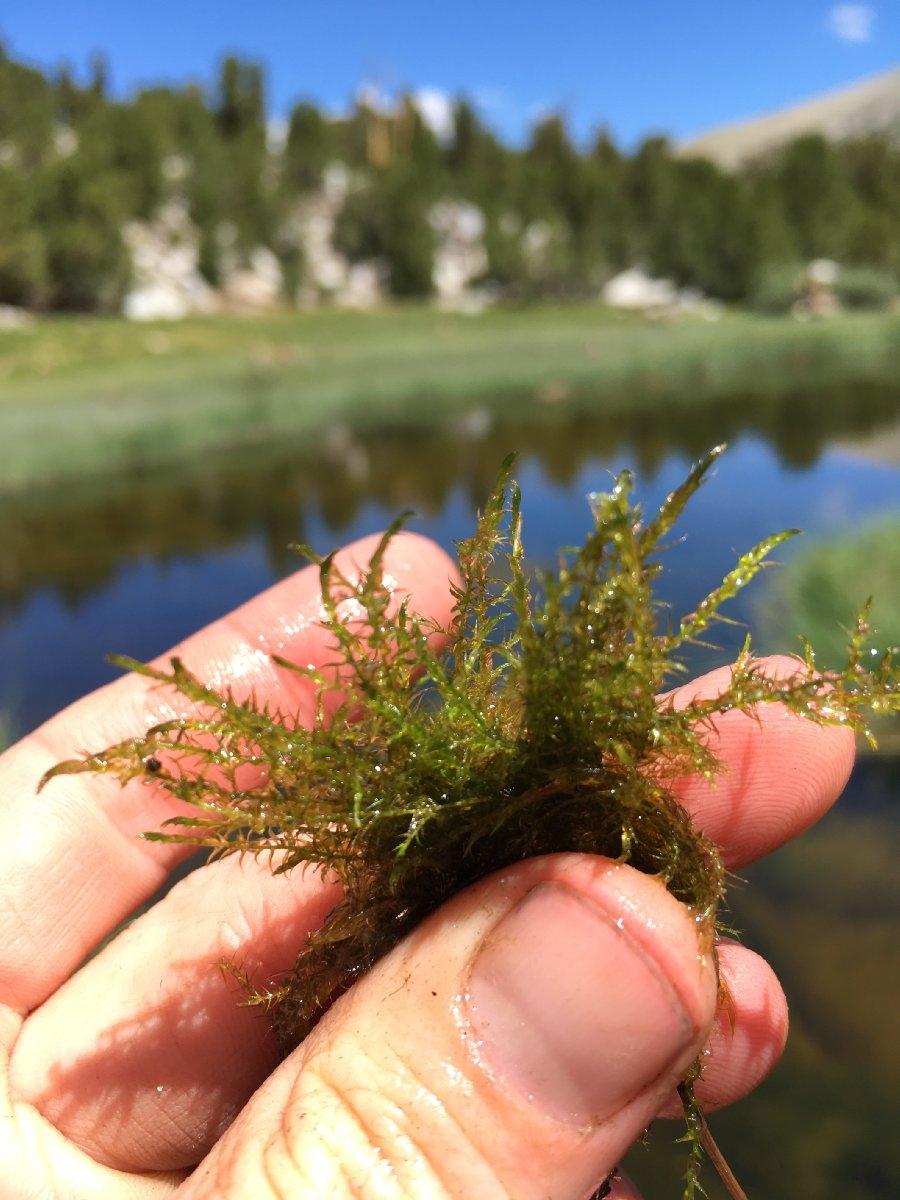

141649.jpg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=14160
Before delving into the intricacies of this moss, it’s essential to understand its taxonomic classification. Sarmentypnum tundrae is a member of the phylum Bryophyta, which encompasses all mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. Within this phylum, it belongs to the class Bryopsida, the true mosses.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
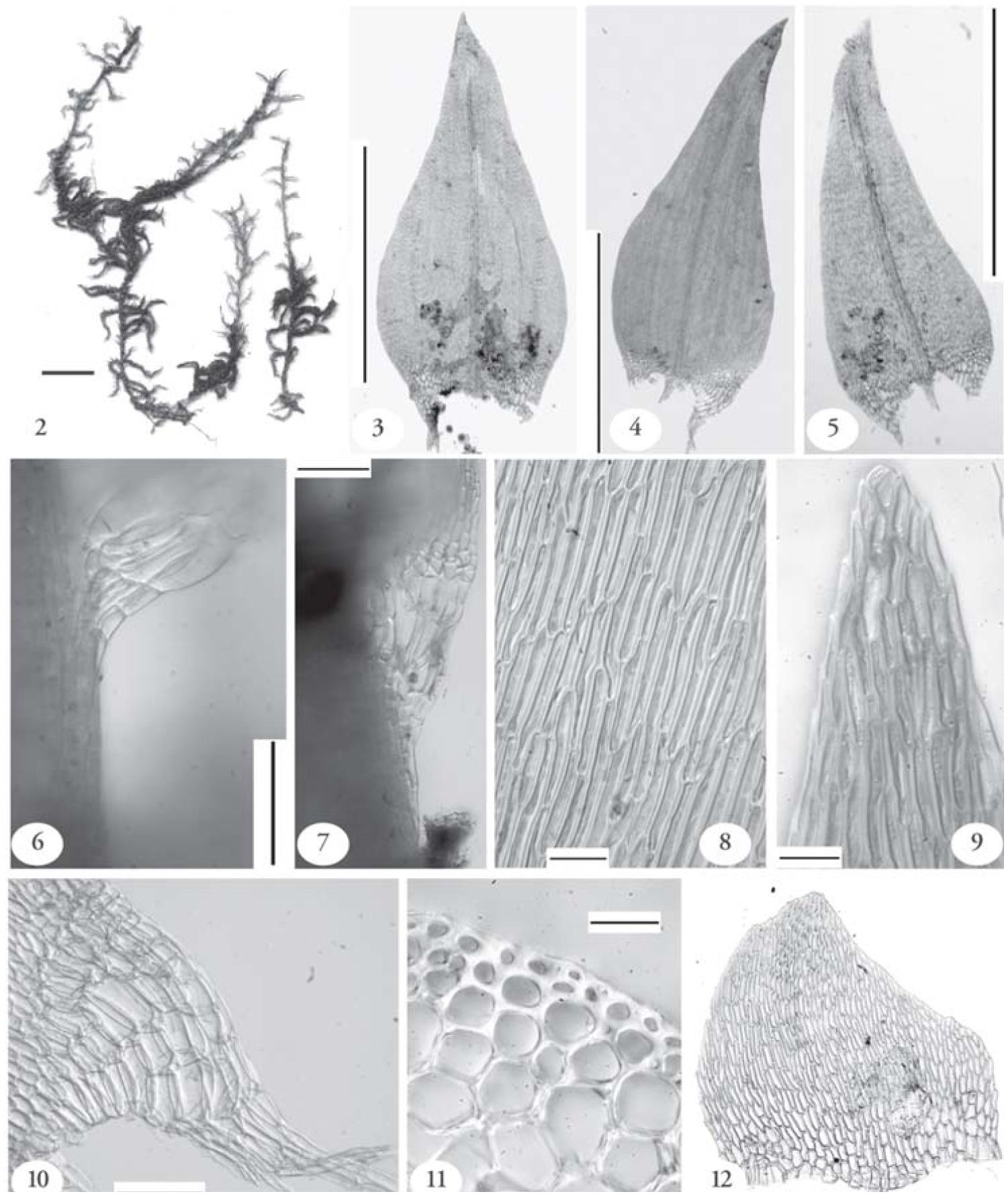
cryptogamie-bryologie2014v35f4a6.jpg from: https://sciencepress.mnhn.fr/en/periodiques/bryologie/35/4/sarmentypnum-tundrae-calliergonaceae-bryophyta-espece-nouvelle-pour-la-france-et-la-chaine-des-alpes
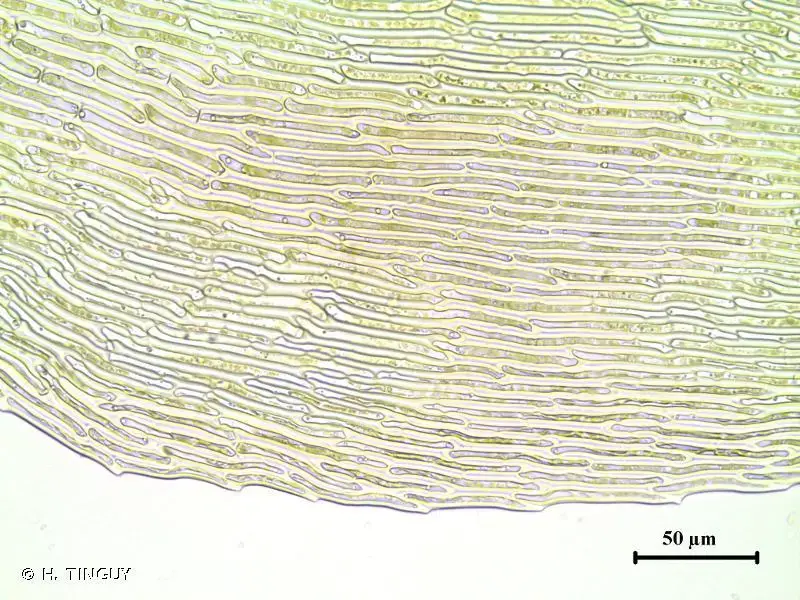
Sarmentypnum tundrae is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or tufts. Its stems are slender and irregularly branched, with leaves that are ovate-lanceolate in shape and typically curved or falcate. The leaves are characterized by a distinct costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a short awn or hair-like projection.
One of the key identifying features of this moss is its distinctive capsule, which is cylindrical in shape and slightly curved or arcuate. The capsules are borne on elongated setae (stalks) and are often found in clusters, making them easily recognizable.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Sarmentypnum tundrae is widely distributed across the Arctic and alpine regions of the Northern Hemisphere, including North America, Europe, and Asia. It thrives in a variety of habitats, such as moist tundra, bogs, fens, and other wetland areas, where it can often be found growing on soil, rocks, or decaying plant matter.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Sarmentypnum tundrae plays a crucial role in the ecosystems it inhabits. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide shelter and nesting material for various invertebrates and small mammals.
This moss is well-adapted to the harsh conditions of the tundra and alpine environments. Its compact growth form and ability to retain moisture help it withstand extreme temperatures, desiccation, and other environmental stresses. Furthermore, its ability to reproduce both sexually (through spores) and asexually (through fragmentation) contributes to its resilience and widespread distribution.
Scapania-tundrae-Arnell-H-Buch-1-habit-dorsal-view-part-of-shoot-ventral-view-3.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Scapania-tundrae-Arnell-H-Buch-1-habit-dorsal-view-part-of-shoot-ventral-view-3_fig20_273492442
210194.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/718804
Case Studies/Examples
In a study conducted in the Canadian Arctic, researchers found that Sarmentypnum tundrae played a significant role in the recovery of disturbed tundra ecosystems. Its ability to rapidly colonize and stabilize soil made it an important contributor to the restoration of vegetation cover and ecosystem functions.
Technical Table

27801_2744_4.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/2744

28678_2812_4.jpg from: https://artfakta.se/naturvard/taxon/rhytidiadelphus-triquetrus-2812

Sarmentypnum%2Bexannulatum.JPG from: https://varietyoflife.com.au/hypnum-exannulatum/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Family | Calliergonaceae |
| Genus | Sarmentypnum |
| Species | tundrae |
| Growth Form | Creeping, forming dense mats or tufts |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate, curved or falcate |
| Leaf Apex | Costa extending beyond the leaf apex, forming a short awn or hair-like projection |
| Capsule Shape | Cylindrical, slightly curved or arcuate |
| Habitat | Moist tundra, bogs, fens, wetlands |
| Distribution | Arctic and alpine regions of the Northern Hemisphere |
Conclusion
The Sarmentypnum tundrae (Arnell) Hedenäs moss, with its unique morphological features, widespread distribution, and ecological significance, is a true marvel of the bryophyte world. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of mosses, this unassuming yet resilient species serves as a reminder of the intricate web of life that exists even in the harshest of environments. Perhaps the next time you find yourself in the tundra or alpine regions, you’ll take a moment to appreciate the beauty and importance of this remarkable moss.