
medium.jpeg from: https://enciclovida.mx/especies/136760-brachymenium
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the Brachymenium condensatum R.S.Williams. Belonging to the Bryaceae family, this unassuming yet remarkable plant is commonly referred to as Brachymenium. Let’s embark on an engaging journey to unravel the secrets of this fascinating moss.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Brachymenium condensatum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
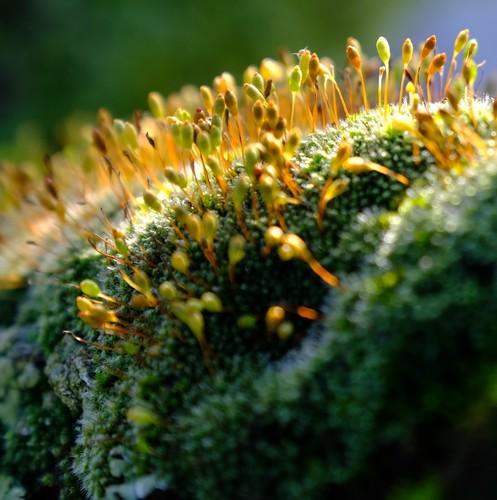
Brachymenium condensatum is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are ovate-lanceolate

22797985264_25700975e5_z.jpg from: https://www.flickriver.com/photos/adaduitokla/22797985264/
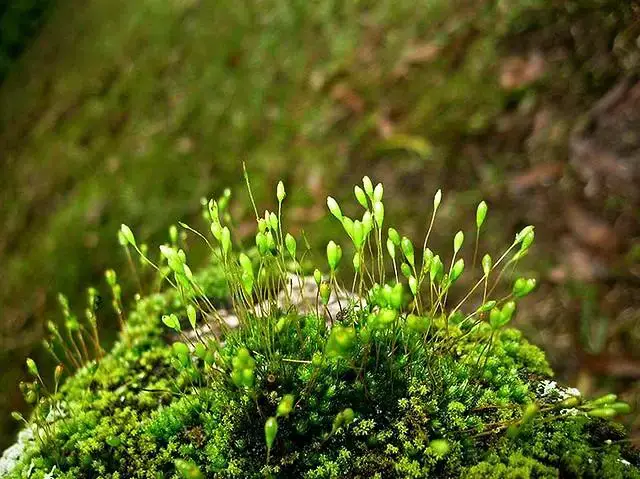
, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a short awn or hair-like projection. The

38265039624_d20b28ef68_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/gails_pictures/38265039624
capsules, which contain the spores, are erect and cylindrical, borne on a short seta (stalk).
Global Distribution and Habitat
This moss species has a widespread distribution, occurring on various continents, including North America, Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. It thrives in a range of habitats, from moist and shaded areas to exposed rock surfaces and soil. Brachymenium condensatum is often found growing on rocks, tree bark, and even concrete surfaces in urban environments, showcasing its remarkable adaptability.

large.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/guide_taxa/495189
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Brachymenium condensatum plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It contributes to soil formation and moisture retention, creating microhabitats for other organisms. Additionally, this moss serves as a food source for various invertebrates and provides nesting material for some bird species.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Brachymenium condensatum is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling up its leaves to minimize water loss. When moisture returns, it quickly revives, demonstrating its resilience and ability to thrive in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In urban areas, Brachymenium condensatum has been observed growing on concrete surfaces, such as retaining walls and sidewalks. This moss’s ability to colonize these man-made structures highlights its adaptability and potential for use in green infrastructure projects, contributing to the beautification and ecological enhancement of urban landscapes.
Technical Table

52081166666_f749dec350_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/133688054@N03/52081166666
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta
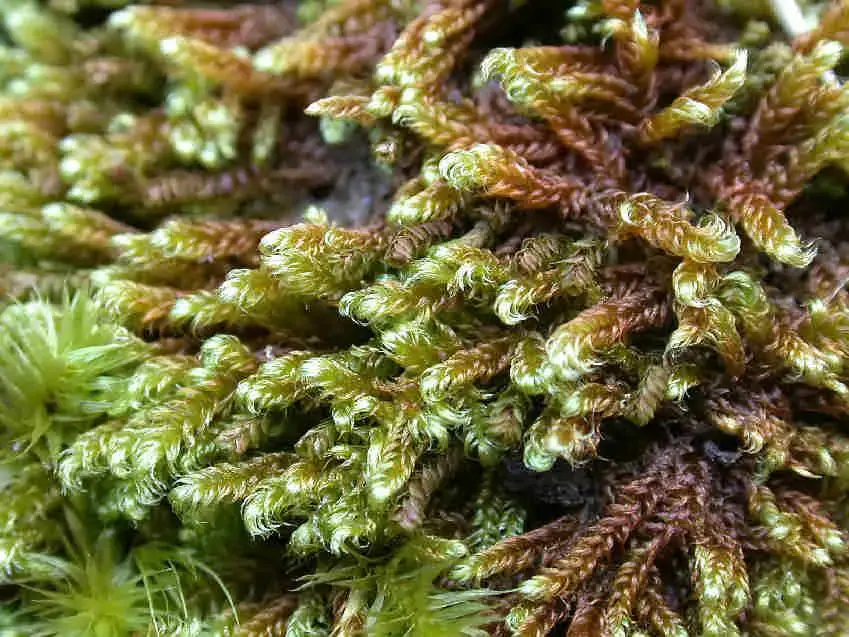 Ctenidium_molluscum-cond_011.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Ctenidium_molluscum_var_condensatum.html |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Bryales |
| Family | Bryaceae |
| Genus | Brachymenium
 24248200050_f005724790_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/starr-environmental/24248200050/ |
| Species | Brachymenium condensatum R.S.Williams |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate-lanceolate, with a costa extending beyond the leaf apex |
| Capsule | Erect, cylindrical |
| Habitat | Moist and shaded areas, exposed rock surfaces, soil, tree bark, concrete surfaces |
| Distribution | Widespread across North America, Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa |
Conclusion
The Brachymenium condensatum R.S.Williams moss, a member of the Bryaceae family, may be small in stature, but its impact on the natural world is profound. From its unique morphology and adaptations to its ecological roles and ability to thrive in diverse habitats, this unassuming plant deserves our appreciation and admiration. As we continue to explore the wonders of the bryophyte world, let us ponder: What other hidden gems await discovery, and how can we better protect and preserve these vital components of our ecosystems?

50348718833_347c3220d4_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/rensehaveman/50348718833/
A-B-Schizachyrium-condensatum-A-habito-B-par-de-espiguetas-C-D-S-tenerum-C.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-B-Schizachyrium-condensatum-A-habito-B-par-de-espiguetas-C-D-S-tenerum-C_fig3_270550793

leptostomopsis_systylia.jpg from: https://wnmu.edu/academic/nspages/gilaflora/leptostomopsis_systylia.html