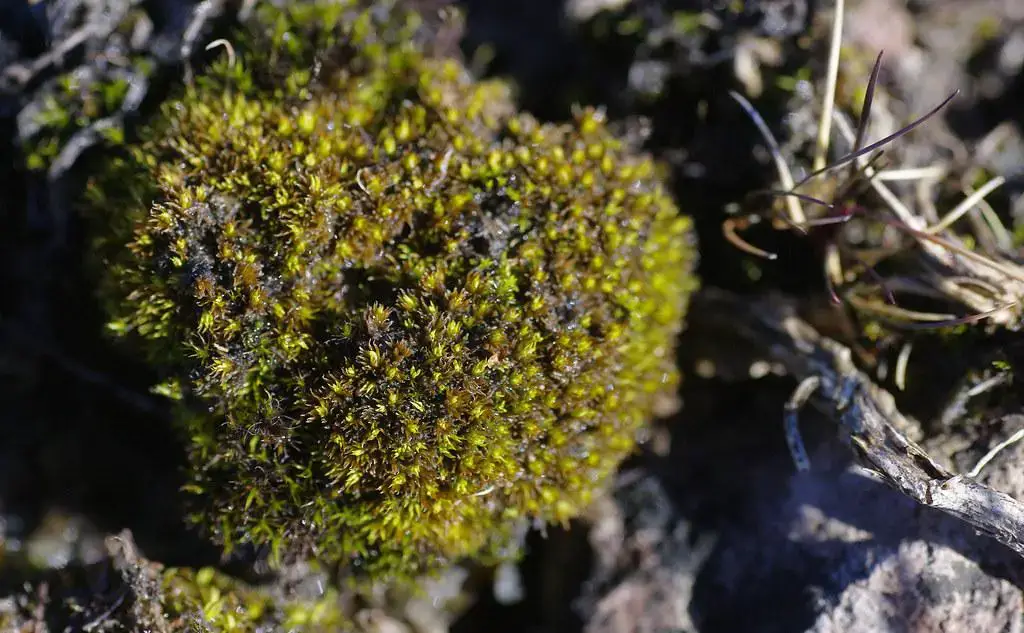

32990576682_8ab6222aaf_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/126598284@N05/32990576682
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes
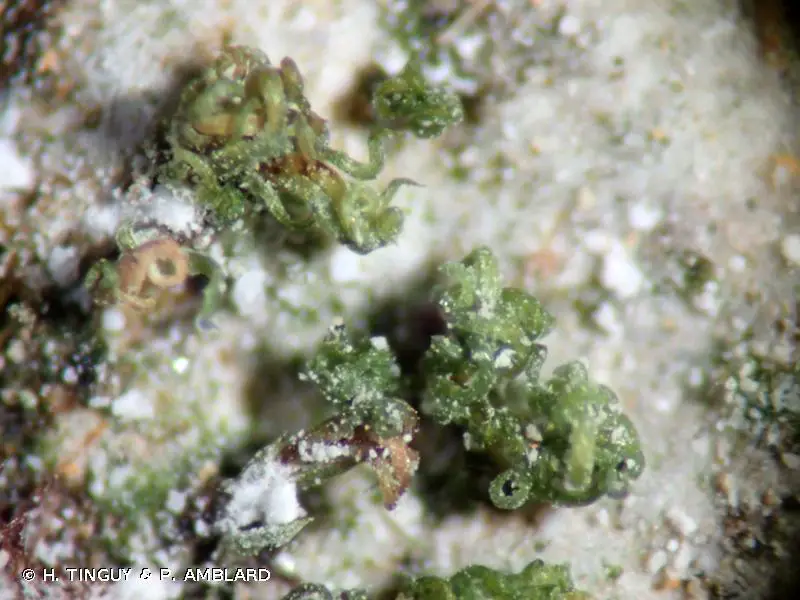

397480.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5347?lg=en
, one tiny moss stands out as a true marvel – the Tortella inclinata (R.Hedw.) Limpr., a member of the Pottiaceae family. Often referred to simply as
304261.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5347/tab/sources
Tortella, this unassuming plant has captured the hearts and minds of moss enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Tortella inclinata, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These remarkable organisms, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest land plants on Earth. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.
Main Content
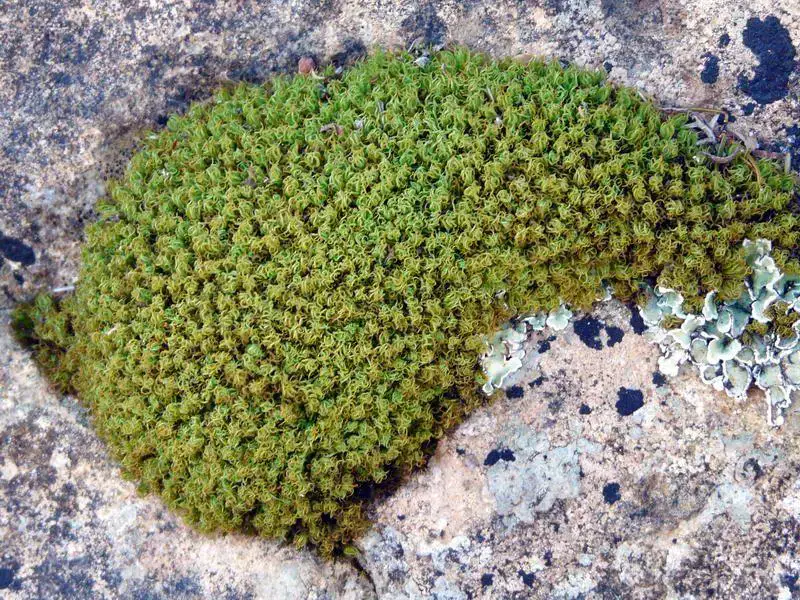

Tortella-tortuosa-(Hedw.)-Limpr.-133910.jpg from: https://www.biodiversidadvirtual.org/herbarium/Tortella-tortuosa-(Hedw.)-Limpr.-img133910.html

397482.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5347
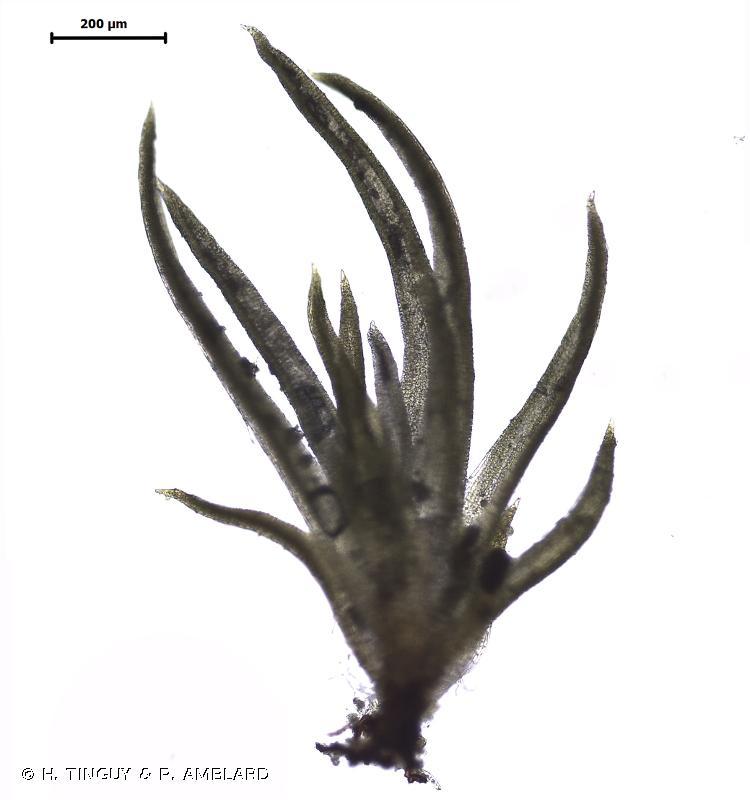
Morphology and Identification
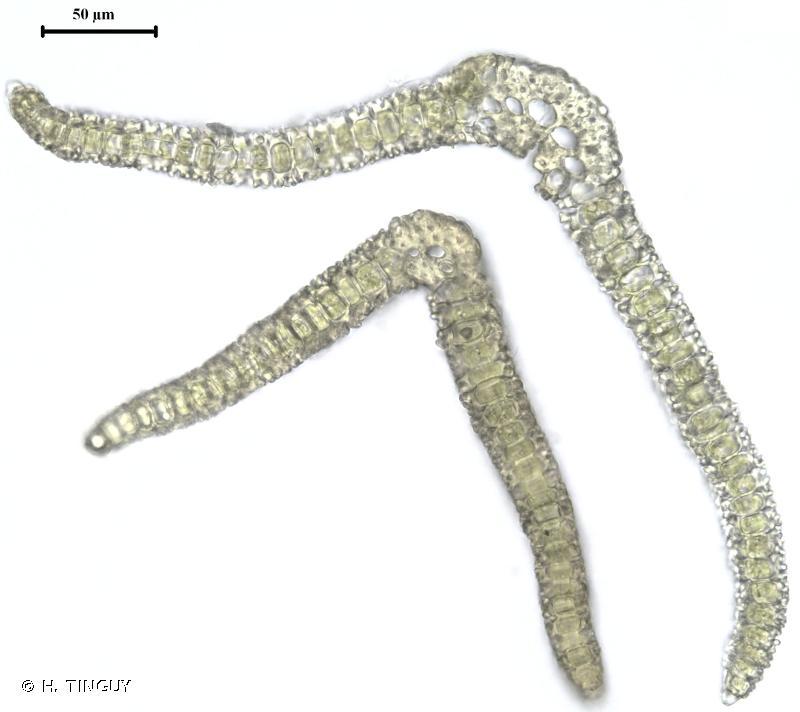
Tortella inclinata is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its leaves are inclined (hence the specific epithet “inclinata”), giving the plant a distinctive appearance. The leaves are lanceolate in shape, with a pointed apex and a single costa (midrib) that extends to the leaf tip. The capsules, which contain the spores, are erect and cylindrical, often with a reddish-brown

Tortella-inclinata-2-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/tortella-inclinata/
color when mature.
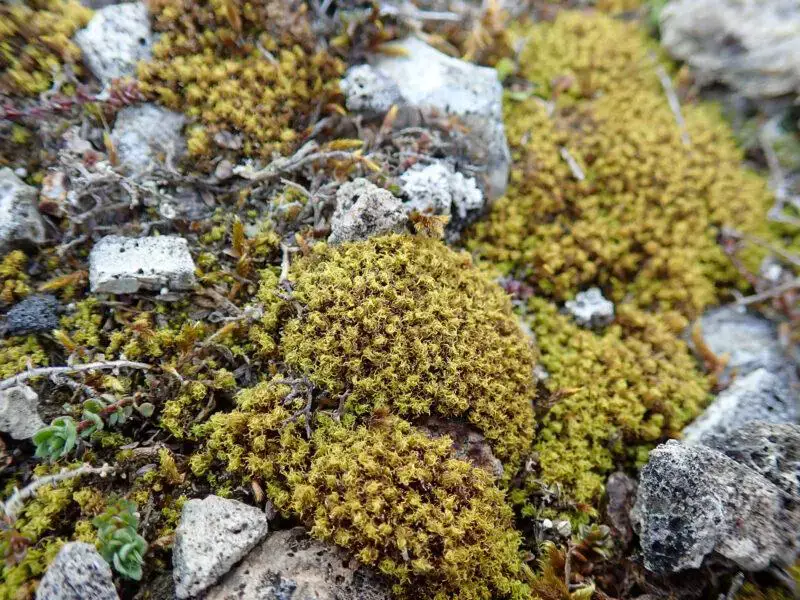
Global Distribution and Habitat

52198373094_139abd73d2_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/herbier/52198373094/
This remarkable moss has a widespread distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. It thrives in a variety of habitats, including disturbed areas, rocky outcrops, soil banks, and even urban environments. Tortella inclinata is known for its ability to colonize and persist in harsh, dry conditions, making it a true survivor in the plant kingdom.
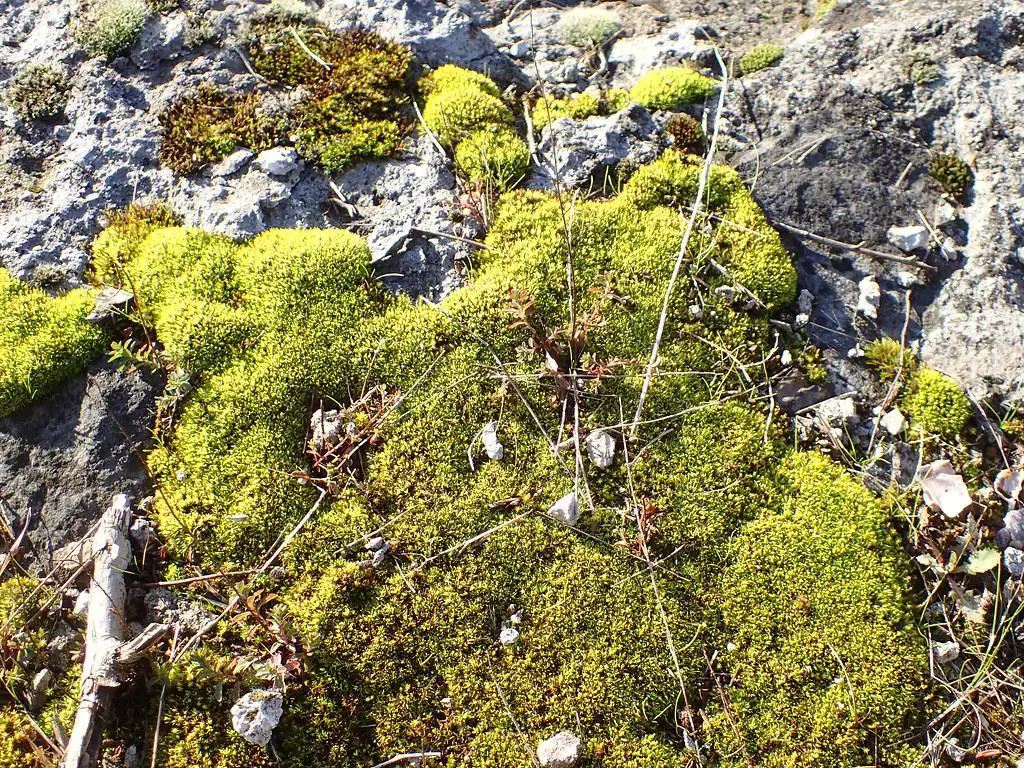
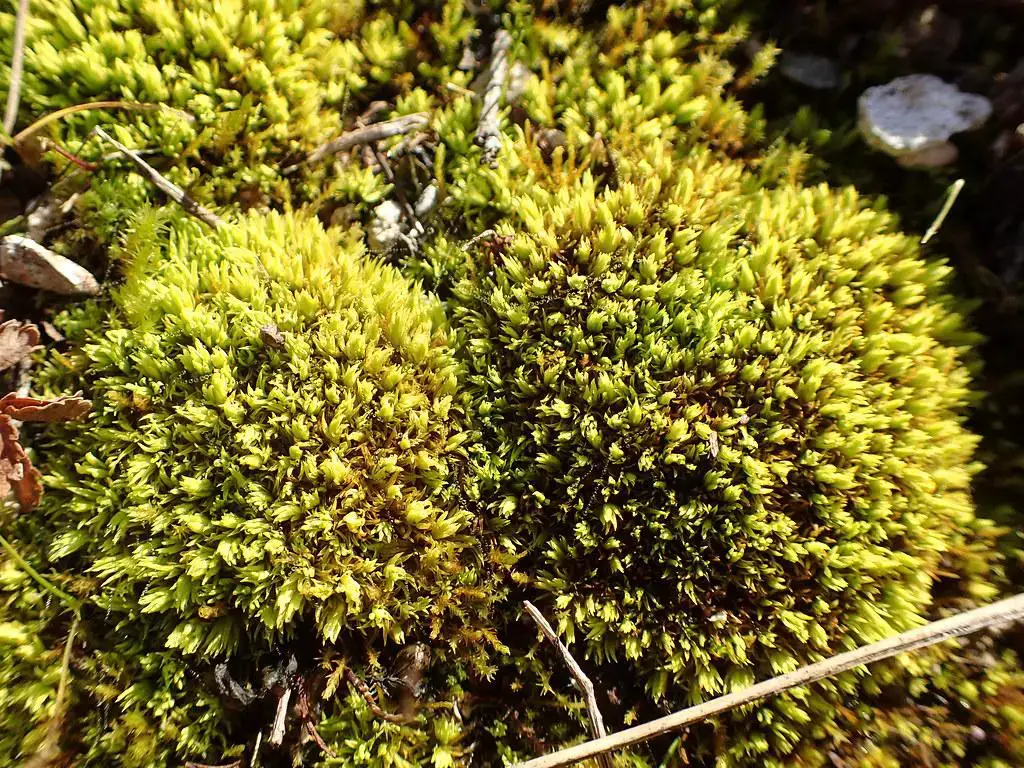
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

52197102167_1b33c79c8b_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/herbier/52197102167/
Despite its diminutive size, Tortella inclinata plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It acts as a pioneer species, helping to stabilize and enrich soils, and providing a suitable environment for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of its surroundings.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Tortella inclinata is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving itself when moisture becomes available again. This remarkable trait allows it to thrive in environments where water is scarce or unpredictable.

43218314.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/226232743?_popup=1
Case Studies/Examples
In urban areas, Tortella inclinata
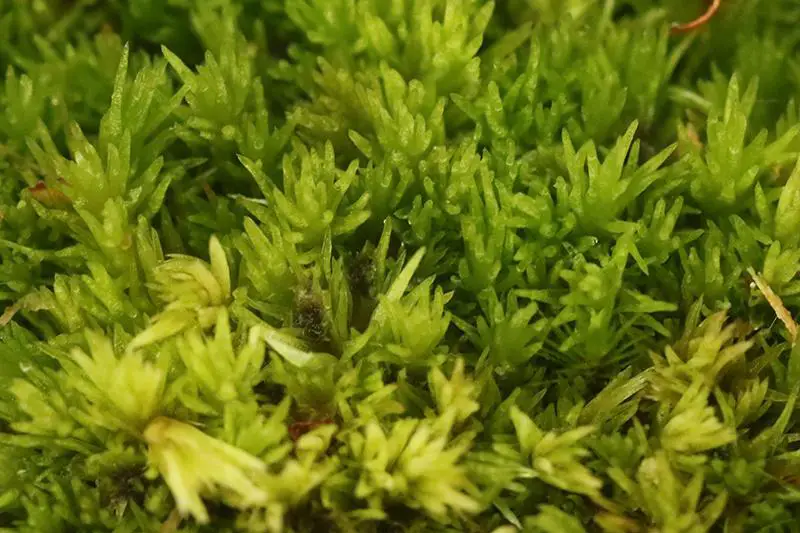

32209219.jpg from: https://waarneming.nl/waarneming/view/203239702?_popup=1
has proven to be a resilient colonizer, often found growing on concrete and brick surfaces. Its presence in these environments serves as an indicator of air quality, as mosses are sensitive to atmospheric pollutants. Researchers have used Tortella inclinata as a biomonitor to assess the levels of heavy metals and other contaminants in urban settings.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Tortella |
| Species | inclinata |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, inclined |
| Leaf Apex | Pointed |
| Costa | Single, extending to leaf tip |
| Capsule | Erect, cylindrical, reddish-brown when mature |
Conclusion
Tortella inclinata (R.Hedw.) Limpr., a true marvel of the Bryophyta world, has captured the hearts and minds of moss enthusiasts with its resilience, adaptability, and ecological significance. From its ability to colonize harsh environments to its role as a biomonitor, this unassuming moss continues to inspire awe and curiosity. As we delve deeper into the intricate world of bryophytes, what other wonders await our discovery? Perhaps the answer lies in the tiny, unassuming mosses that surround us, reminding us of the incredible diversity and resilience of life on our planet.