
tortula-sand-dune-moss-2DEDT6B.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/tortula-sand-dune-moss-image387537651.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its resilience and adaptability – the Tortula laevinervis Broth. ex Dusén. Belonging to the Pottiaceae family, this unassuming yet remarkable plant has carved out a niche for itself across various habitats, playing a crucial role in the intricate web of life.

153772014060961817.jpeg from: https://www.picturethisai.com/wiki/Tortula_muralis.html
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this moss, let’s set the stage with a brief overview of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but hold immense ecological significance. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have evolved remarkable strategies for survival and reproduction.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
The

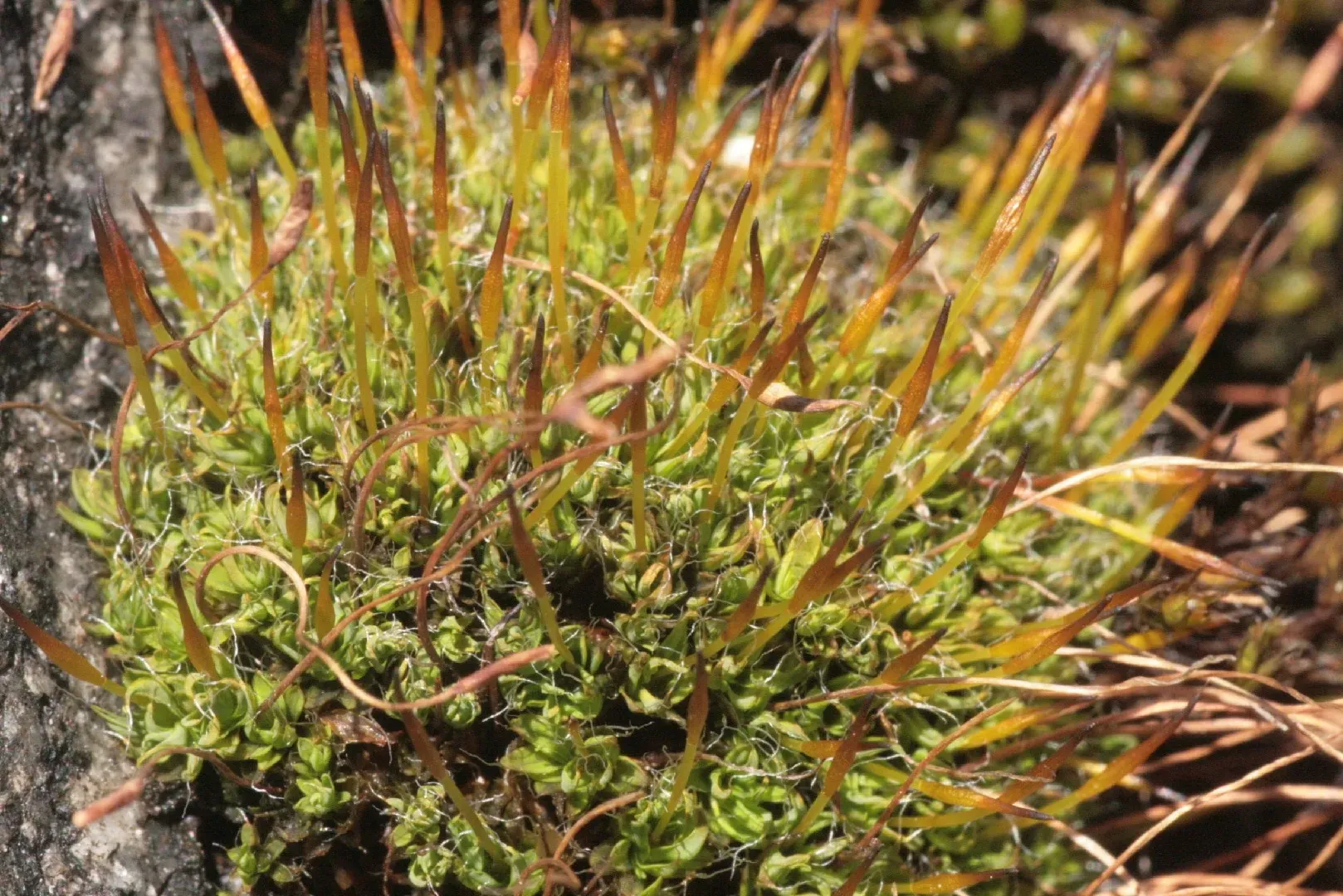
913.78237.jpg from: https://eol.org/pages/853450
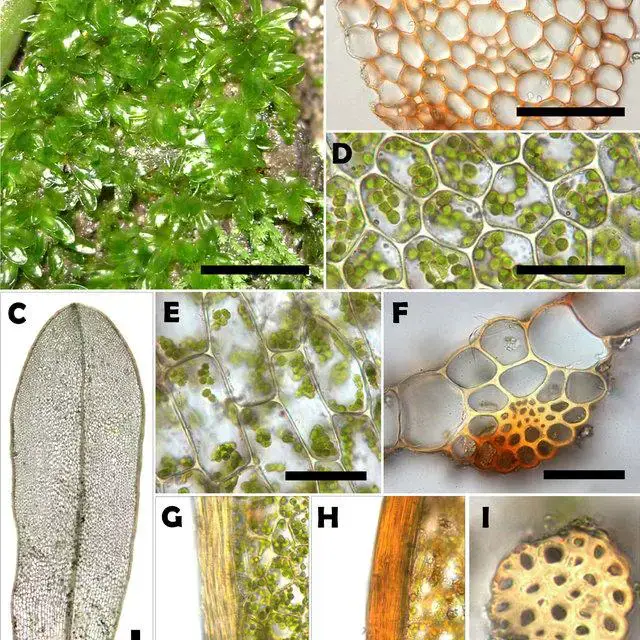
Tortula laevinervis Broth. ex Dusén is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense tufts or cushions. Its leaves are lanceolate

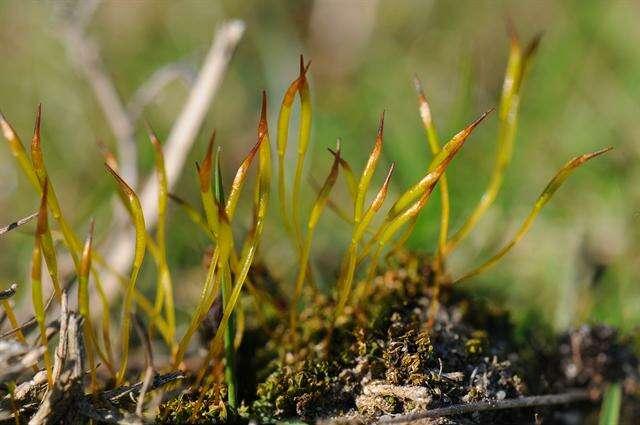
913.33249.jpg from: https://eol.org/pages/53845
to ovate-lanceolate, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a short hair-point. The leaf margins are typically entire or slightly crenulate, and the leaf cells are quadrate to rectangular in shape.
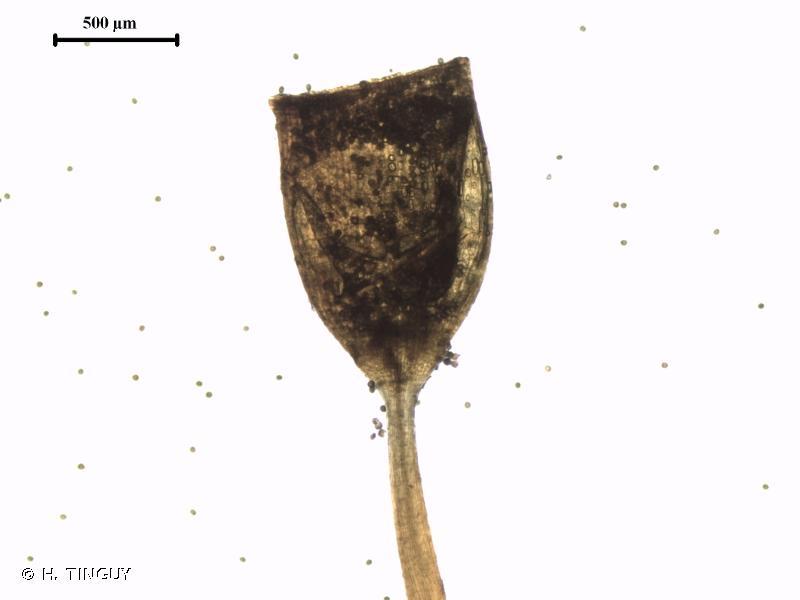
One of the key identifying features of this moss is its twisted and contorted peristome teeth, which are visible under a microscope. The capsules are cylindrical to ovoid in shape and are borne on a reddish-brown seta (stalk).
Global Distribution and Habitat
The Tortula laevinervis Broth. ex Dusén is widely distributed across various regions, including North and South America, Europe, Asia, and Australasia. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from disturbed areas and urban environments to rocky outcrops, soil banks, and tree bases.
This moss’s ability to colonize and persist in such varied environments is a testament to its remarkable adaptability. It can withstand periods of desiccation and rapidly rehydrate when moisture becomes available, making it a true survivor in even the harshest of conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

twisted-oak-moss-tortula-laevipila-syntrichia-laevipila-on-bark-with-DAKFGG.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-twisted-oak-moss-tortula-laevipila-syntrichia-laevipila-on-bark-with-58206976.html
Despite its diminutive size, the Tortula laevinervis Broth. ex Dusén plays a vital role in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, these mosses provide microhabitats for a diverse array of invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of their environments.

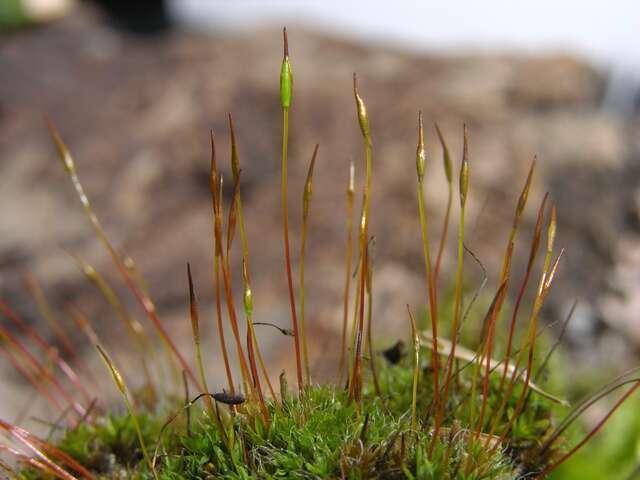
220952.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/786499
One of the key adaptations that enable this moss to thrive is its ability to undergo desiccation tolerance. During periods of drought, the plant can enter a state of dormancy
Dolotortula-mniifolia-Sull-Zander-A-Habito-B-Corte-transversal-del-tallo-C-Hoja_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Trachyphyllum-dusenii-Muell-Hal-ex-Broth-Broth-A-Habito-B-Hoja-C-Celulas-alares_fig3_318583545
, effectively shutting down its metabolic processes until water becomes available again. This remarkable trait allows it to survive in environments where water availability is unpredictable or scarce.
Case Studies/Examples
In urban areas, the Tortula laevinervis Broth. ex Dusén has been observed colonizing various man-made structures, such as concrete walls, pavements, and rooftops. Its ability to establish itself in these environments highlights its resilience and adaptability, making it a valuable subject for studying the impacts of urbanization on plant communities.
Technical Table

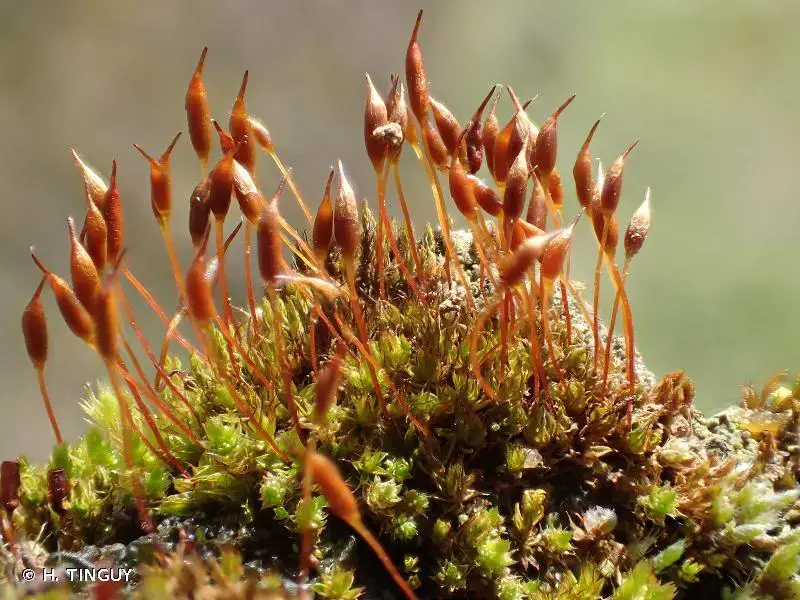
clump-of-tortula-muralis-moss-showing-sporophytes-PFKR58.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/clump-of-tortula-muralis-moss-showing-sporophytes-image216179524.html

304277.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/786497
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Tortula |
| Species | Tortula laevinervis Broth. ex Dusén |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, forming dense tufts or cushions |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate |
| Leaf Margin | Entire or slightly crenulate |
| Leaf Cells | Quadrate to rectangular |
| Costa | Extending beyond leaf apex, forming a short hair-point |
| Peristome | Twisted and contorted teeth |
| Capsule Shape | Cylindrical to ovoid |
| Seta Color | Reddish-brown |
Conclusion
The Tortula laevinervis Broth. ex Dusén is a remarkable example of nature’s resilience and adaptability. Its ability to colonize diverse habitats, withstand harsh conditions, and contribute to ecosystem functioning makes it a true marvel of the bryophyte world. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate tapestry of life on our planet, this unassuming moss serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and complexity that surrounds us, even in the smallest of forms.

twisted-moss-tortula-ruraliformis-germany-EBNF01.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-twisted-moss-tortula-ruraliformis-germany-76075441.html
Ponder this: If a tiny moss can exhibit such remarkable adaptations and play such a vital role in its ecosystems, what other wonders might be hidden in plain sight, waiting to be discovered and appreciated?