
DETA3-7152_Helianthus-angustifolius-1024×768.jpg from: https://mellowmarshfarm.com/catalog/helianthus-angustifolius/
Exploring the Fascinating World of Tylimanthus angustifolius Steph. Moss
Introduction
Mosses are some of the most ancient and resilient plants on Earth, having evolved over 400 million years ago. One particularly interesting species is Tylimanthus angustifolius Steph., a moss in the Acrobolbaceae family, commonly known as Tylimanthus. In this blog post, we’ll take a deep dive into the unique characteristics and ecological importance of this fascinating bryophyte.
Background

48954939821_206696b5de.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/33037982@N04/48954939821/
Tylimanthus angustifolius is a species of leafy liverwort moss classified in the phylum Marchantiophyta and class Jungermanniopsida

helianthus-angustifolius-kt-1.jpg from: https://adkins.donorshops.com/product/Helianthus-angustifolius/helianthus-angustifolius-swamp-sunflower
. The genus Tylimanthus contains around 20 known species found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide. T. angustifolius was first described by German botanist Franz Stephani in 1917.

5202eb292cdd4735109e27bb8bd7a744.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/native–40532465383461901/
Morphology and Identification
Tylimanthus angustifolius forms dense mats of small, delicate plants. The leaves are oblong to lanceolate in shape, 0.5-1.2 mm long, with an acute apex. They attach in an incubous manner (leaf bases overlap like shingles) and lack underleaves. Plants are yellowish-green and slightly glossy.

swamp-sunflower-narrowleaf-sunflower-narrow-leaved-sunflower-helianthus-angustifolius-in-central-virginia-in-late-september-R56KF7.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/helianthus-angustifolius.html
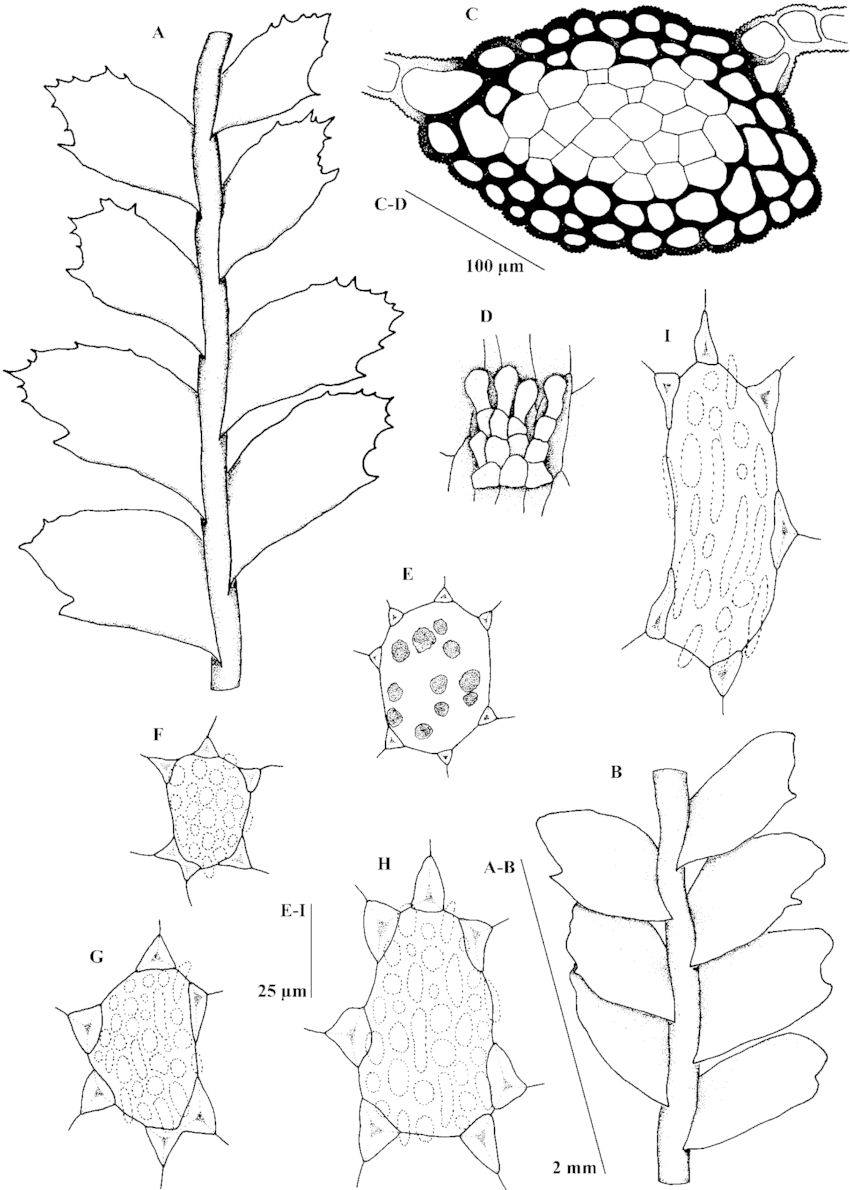
Tylimanthus-laxus-A-B-Part-of-shoot-dorsal-view-C-cross-section-of-stem-D.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Tylimanthus-laxus-A-B-Part-of-shoot-dorsal-view-C-cross-section-of-stem-D_fig1_232660638
The stems are prostrate to ascending, sparsely branched, and 5-20 mm long. Rhizoids are scarce. Gemmae
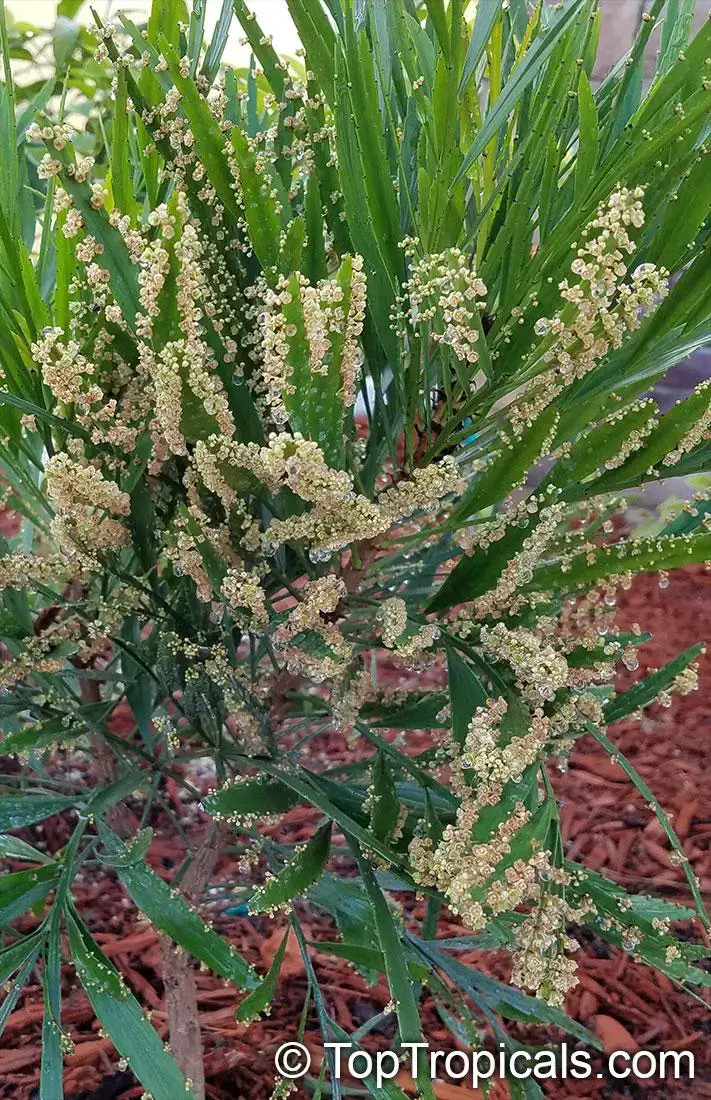

20180718_085416phyllanthus_angustifolius_TA.jpg from: https://toptropicals.com/catalog/uid/phyllanthus_angustifolius.htm
(asexual reproductive structures) are occasionally produced on leaf margins. Perianths are oblong to cylindrical.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Tylimanthus angustifolius has a pantropical distribution, found in tropical regions of Central and South America, Africa, Southeast Asia, and Oceania. It grows as an epiphyte on tree bark and branches in humid montane forests, particularly cloud forests, at elevations of 500-3000 meters. The species prefers shaded, moist microhabitats.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses, T. angustifolius plays important roles in its forest ecosystems:
- Moisture and nutrient retention: The dense mats help capture and retain water and nutrients, regulating humidity and nourishing other plants.
- Microhabitats: The mats provide shelter and microhabitats for various invertebrates and microorganisms.
- Carbon cycling: As a primary producer, it contributes to carbon fixation and enriches forest soils with organic matter.
T. angustifolius has several adaptations for its epiphytic lifestyle:
- Small size and prostrate growth conserve moisture
- Rhizoids anchor it to bark without damaging the tree
- Leaves and shoots efficiently capture water and nutrients from the air and rain
Conclusion
Tylimanthus angustifolius is a small but ecologically mighty moss that thrives in the cloud forests of the tropics worldwide. Its unique morphology and adaptations allow it to play vital roles in moisture retention, habitat provisioning, and nutrient cycling in these biodiverse ecosystems.
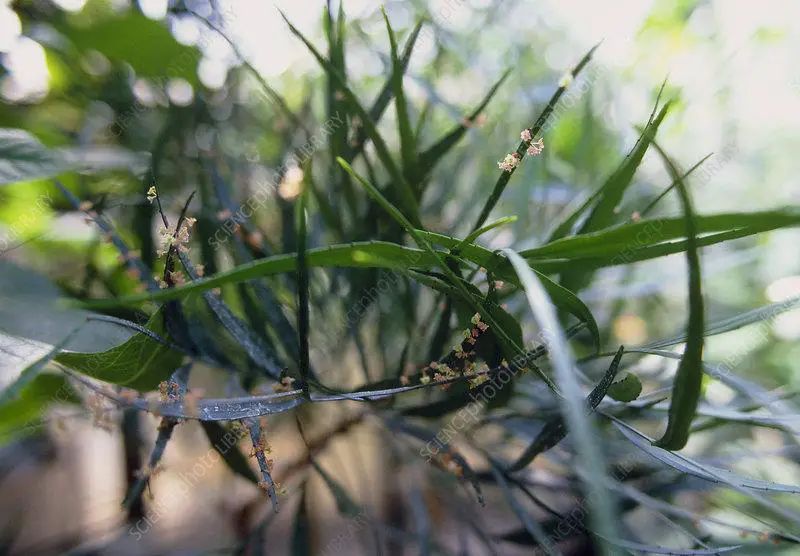

B8303390-Phyllanthus_angustifolius.jpg from: https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/59744/view/phyllanthus-angustifolius
Next time you’re in a tropical montane forest, take a closer look at the trees – you may just spot a patch of Tylimanthus and gain a new appreciation for the complexity of life in the forest canopy! What other secrets might these ancient plants hold?

1605028.jpg from: https://www.forestryimages.org/browse/detail.cfm?imgnum=1605028

153740287137546277.jpeg from: https://www.picturethisai.com/ar/wiki/Centranthus_angustifolius.html