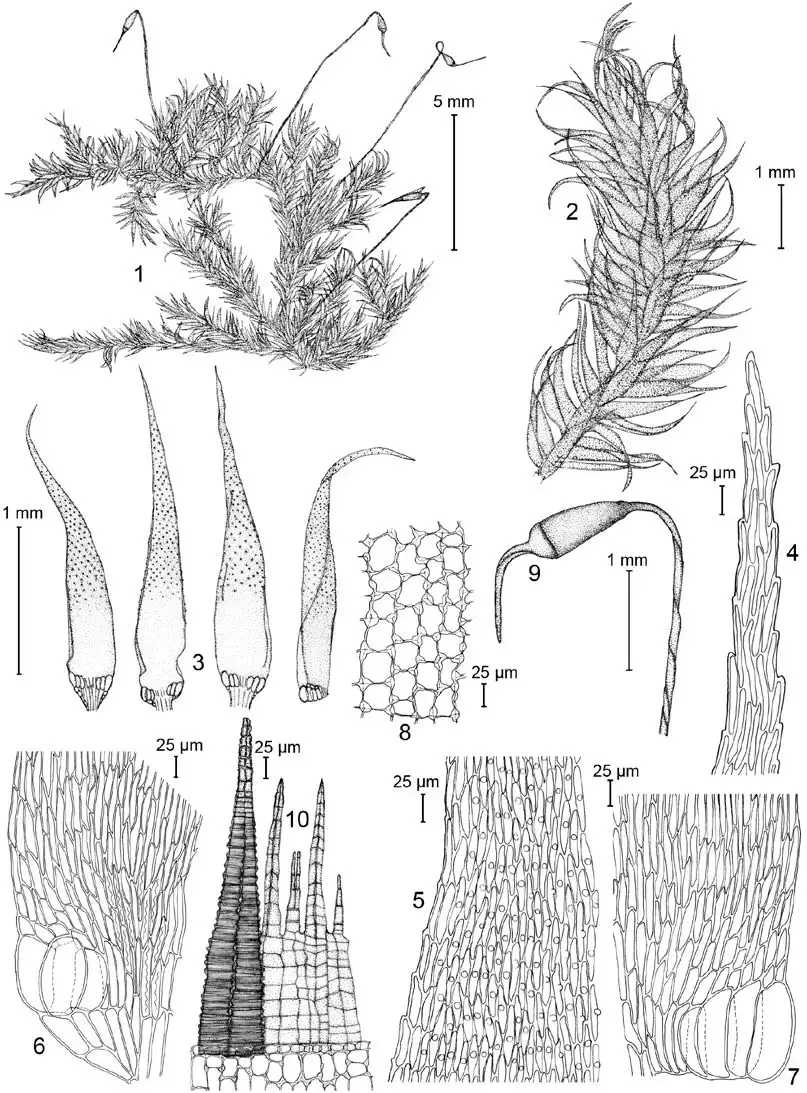
Trichosteleum-stigmosum-Mitt-Sematophyllaceae-1-habit-with-sporophytes-2-branch.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Trichosteleum-stigmosum-Mitt-Sematophyllaceae-1-habit-with-sporophytes-2-branch_fig1_272536394
Exploring the Fascinating World of Trichosteleum Mindanense Broth. Moss
Introduction
Hey moss enthusiasts! Today we’re diving into the captivating realm of
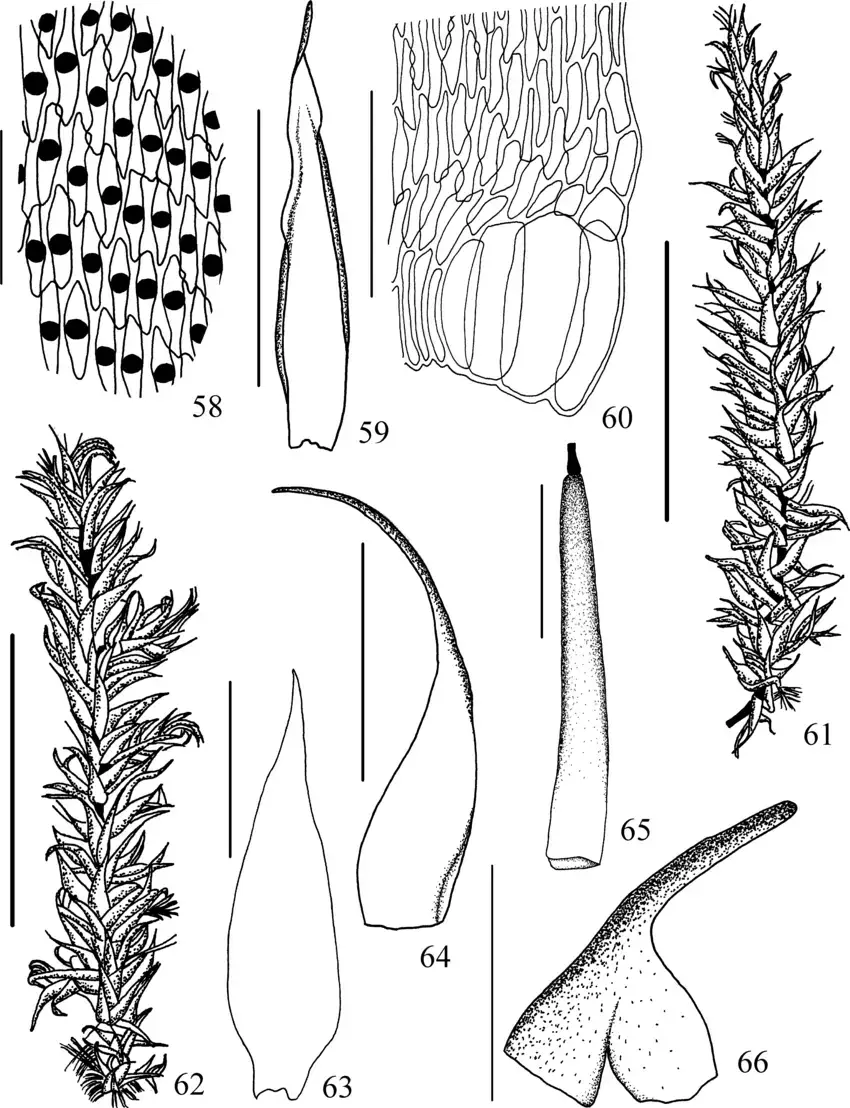
Figuras-58-66-Trichosteleum-papillosum-e-T-sublaevigatum-58-61-Trichosteleum.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figuras-58-66-Trichosteleum-papillosum-e-T-sublaevigatum-58-61-Trichosteleum_fig3_264879602
Trichosteleum mindanense Broth., a unique species of moss from the Sematophyllaceae family. This tiny but mighty plant is sure to pique your curiosity, so let’s explore what makes it so special!
Background
Trichosteleum mindanense Broth., commonly known as just Trichosteleum, is a type of moss classified under the Bryophyta division and Bryopsida class. It was first described by German botanist Viktor Ferdinand Brotherus
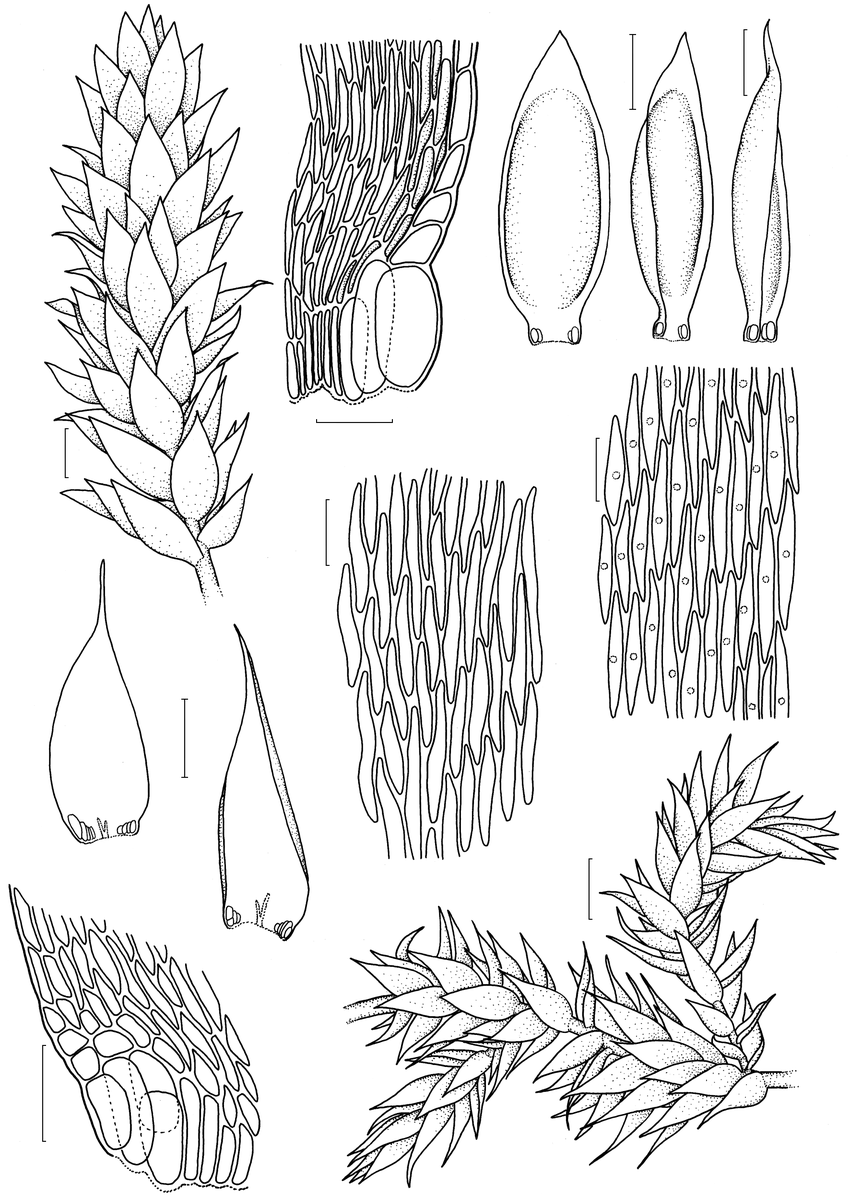
a-d-Trichosteleum-subdemissum-a-habit-b-leaf-base-c-leaves-d-median-cells-e-h.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-d-Trichosteleum-subdemissum-a-habit-b-leaf-base-c-leaves-d-median-cells-e-h_fig3_327378013
in 1913 based on specimens collected from the island of Mindanao in the Philippines, which is where its species name “mindanense” comes from.
Morphology and Identification
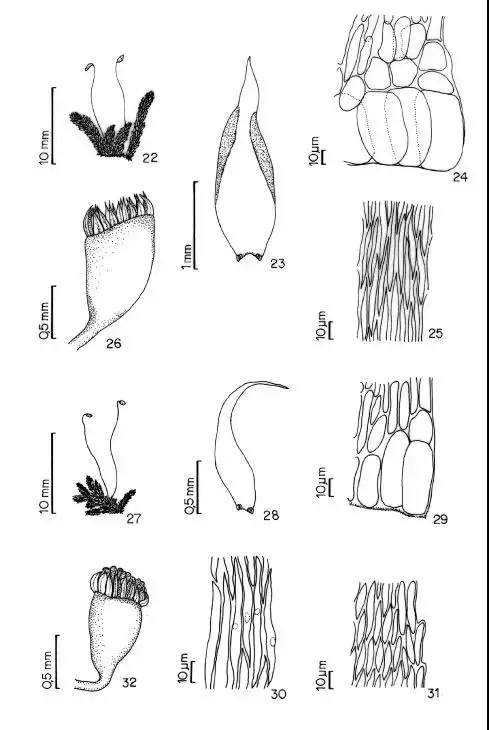
Figuras-22-26-Sematophyllum-galipense-C-Muell-Mitt-22-habito-23-filidio-24.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figuras-22-26-Sematophyllum-galipense-C-Muell-Mitt-22-habito-23-filidio-24_fig3_26360403
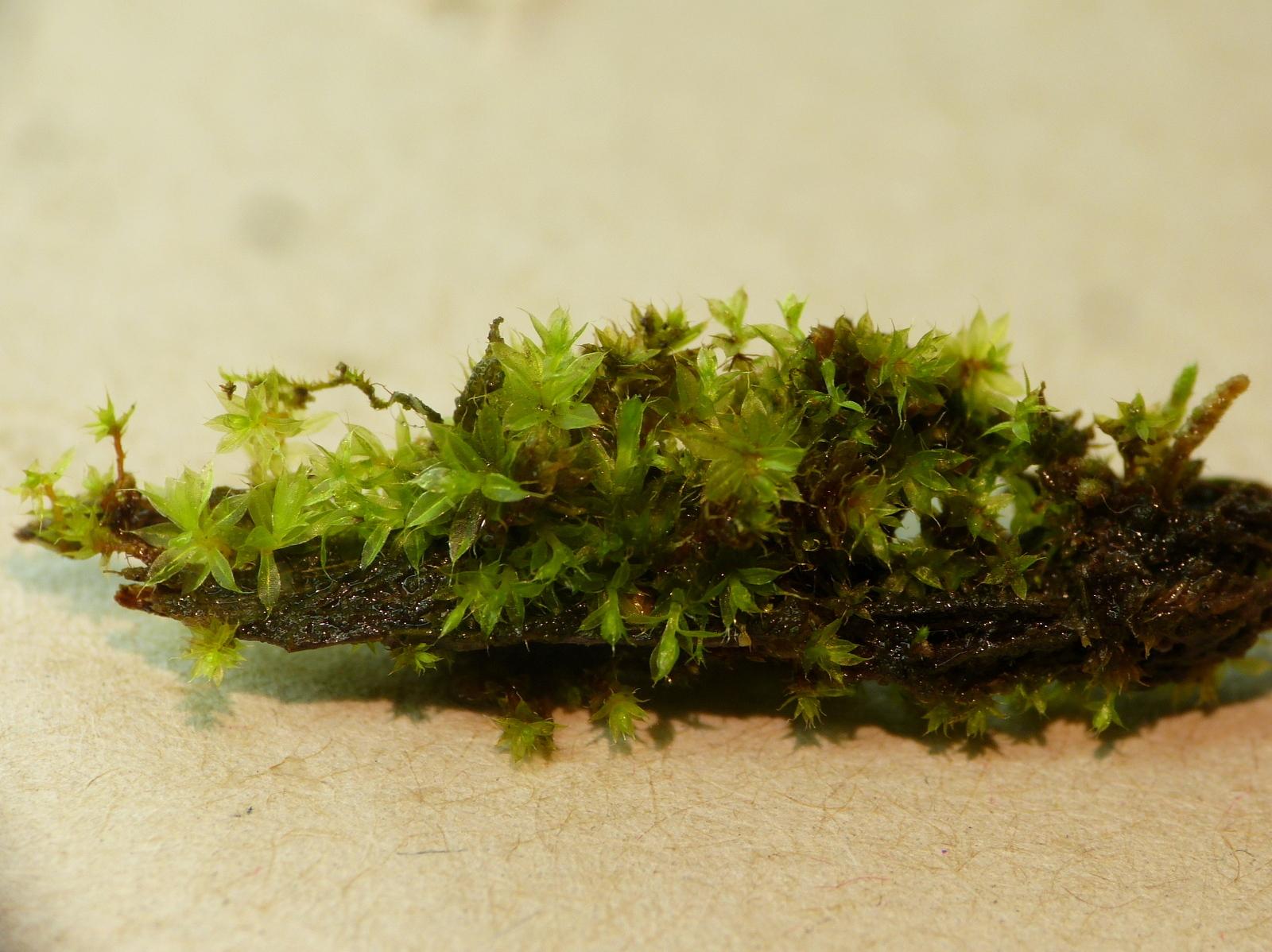

P1120623.JPG from: https://southwalesbryos.blogspot.com/2016/11/a-thatch-moss.html

2021-09-14-12-06-27.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/hylocomiastrum-umbratum/
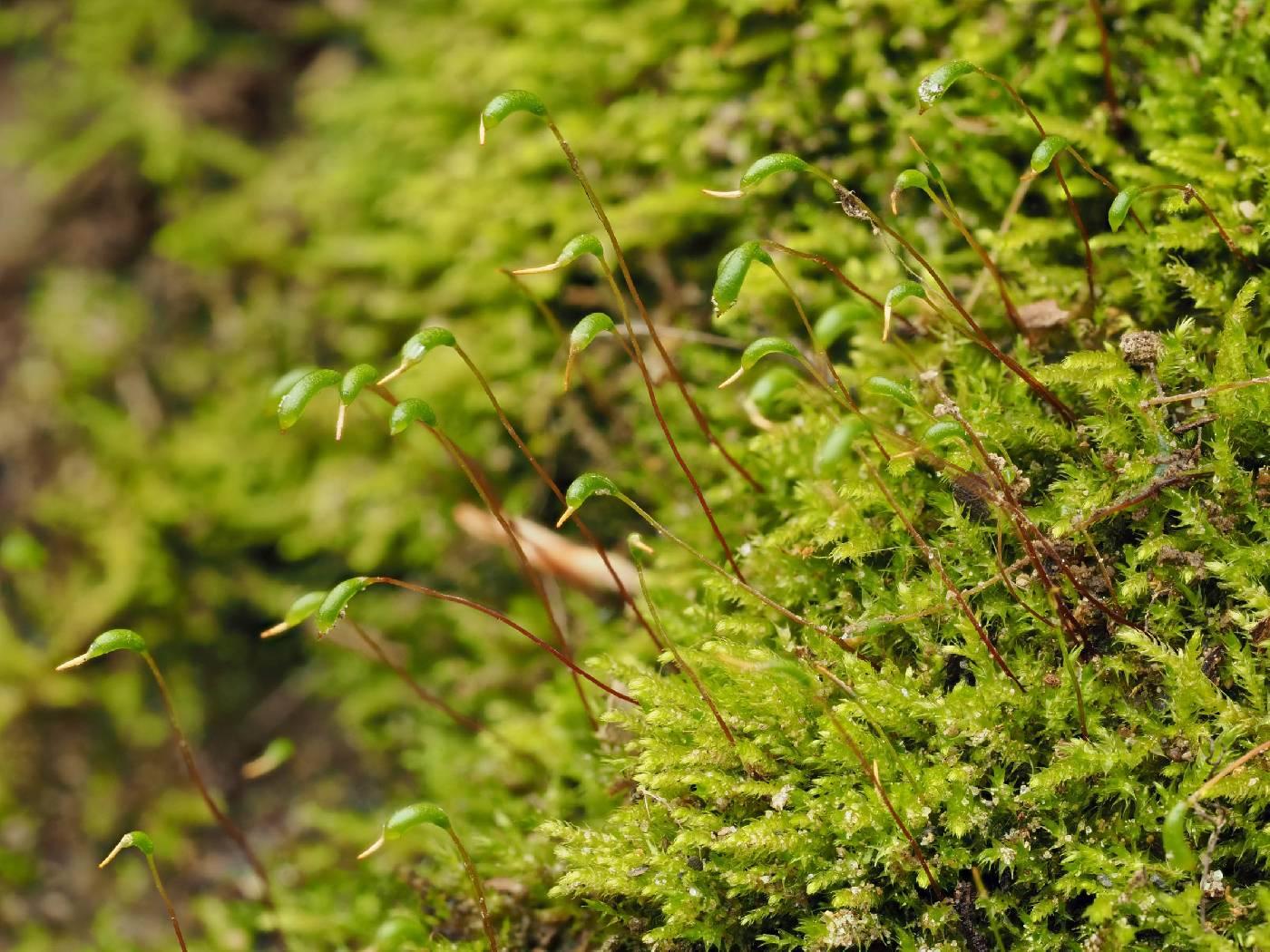
One of the most distinctive features of T. mindanense

OS0149365_1577822715.jpg from: https://bryophyteportal.org/portal/taxa/index.php?taxauthid=1&taxon=158184&clid=210
is its delicate, feather-like appearance. The moss forms small, dense mats with branching stems that are covered in tiny, overlapping leaves. Each individual leaf is only about 0.5-1 mm long and has a pointed tip and finely serrated edges when viewed under magnification.
The leaves are arranged in a characteristic pattern known as “complanate”, meaning they lie flat in a single plane on either side of the stem. This gives the moss a compressed, two-dimensional look. Trichosteleum is named for the presence of rhizoids, root-like filaments, on its stems that help it attach to substrates.
Global Distribution and Habitat
T. mindanense has a relatively limited distribution, being found primarily in tropical and subtropical regions of Southeast Asia and Oceania. In addition to the Philippines, it has been recorded in Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, and some Pacific islands.

waterplant-taxiphyllum-alternans-taiwan-moss-in-vi.jpg from: https://www.aquastorexl.nl/taxiphyllum-alternans-taiwan-moss-in-vitro-bakje.html
This moss is typically found growing as an epiphyte on the bark and leaves of trees and shrubs in humid forests. It prefers shaded, moist microhabitats and is often associated with other epiphytic plants like liverworts and lichens.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like many bryophytes, Trichosteleum plays important ecological roles despite its small size. It helps retain moisture and nutrients in forest ecosystems, provides shelter for micro-organisms, and serves as a pioneer species in plant succession.
T. mindanense has several adaptations that allow it to thrive in its epiphytic lifestyle:
- Its flattened growth form maximizes surface area for photosynthesis and moisture absorption
- Dense mats help prevent desiccation and buffer against temperature fluctuations
- Rhizoids anchor the moss to tree bark and other substrates

taxiphyllum-alternans-taiwan-moss-in-vitro.jpg from: https://www.aquasabi.de/Taxiphyllum-alternans-Taiwan-Moss-in-Vitro-XL

DT_Warburgiella_leucocytus_1.jpg from: https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/01_Semat_images.html
Conclusion
From its intricate leaf arrangement to its ecological significance, Trichosteleum mindanense Broth. is a prime example of how even the tiniest organisms can be endlessly fascinating. The next time you find yourself in a tropical forest, take a closer look – you might just spot this marvelous moss! What other secrets do you think bryophytes like Trichosteleum hold?