
04-19-Grimmia-tergestina-St-Marys-churchyard-Tetbury-ST890929.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/grimmia-tergestina/
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Grimmia tergestina Tomm. ex B.S.G. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Grimmiaceae family. This unassuming yet resilient plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ability to thrive in seemingly inhospitable environments.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this fascinating moss, let’s set the stage with some essential background information. Bryophytes, often referred to as the “ancient lineage of land plants,” are a diverse group that includes mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. These diminutive yet mighty organisms have played a crucial role in the evolution of terrestrial ecosystems, paving the way for more complex plant life to flourish.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
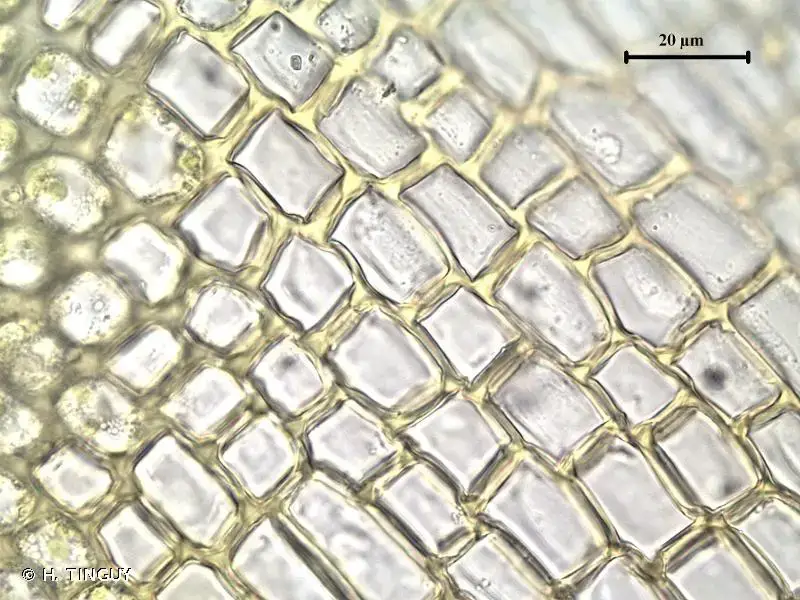
The Grimmia tergestina moss is a true marvel of nature, boasting a unique morphology that sets it apart from its bryophyte brethren. This acrocarpous moss forms dense, cushion-like tufts that cling tenaciously to rocks, walls, and tree bark. Its leaves are lanceolate, with a distinctive hair-like tip (hyaline hair point) that aids in water absorption and retention.
One of the most striking features of this moss is its ability to change color. When dry, the leaves appear grayish-green, but upon hydration, they transform into a vibrant emerald hue, showcasing their remarkable resilience and adaptability.
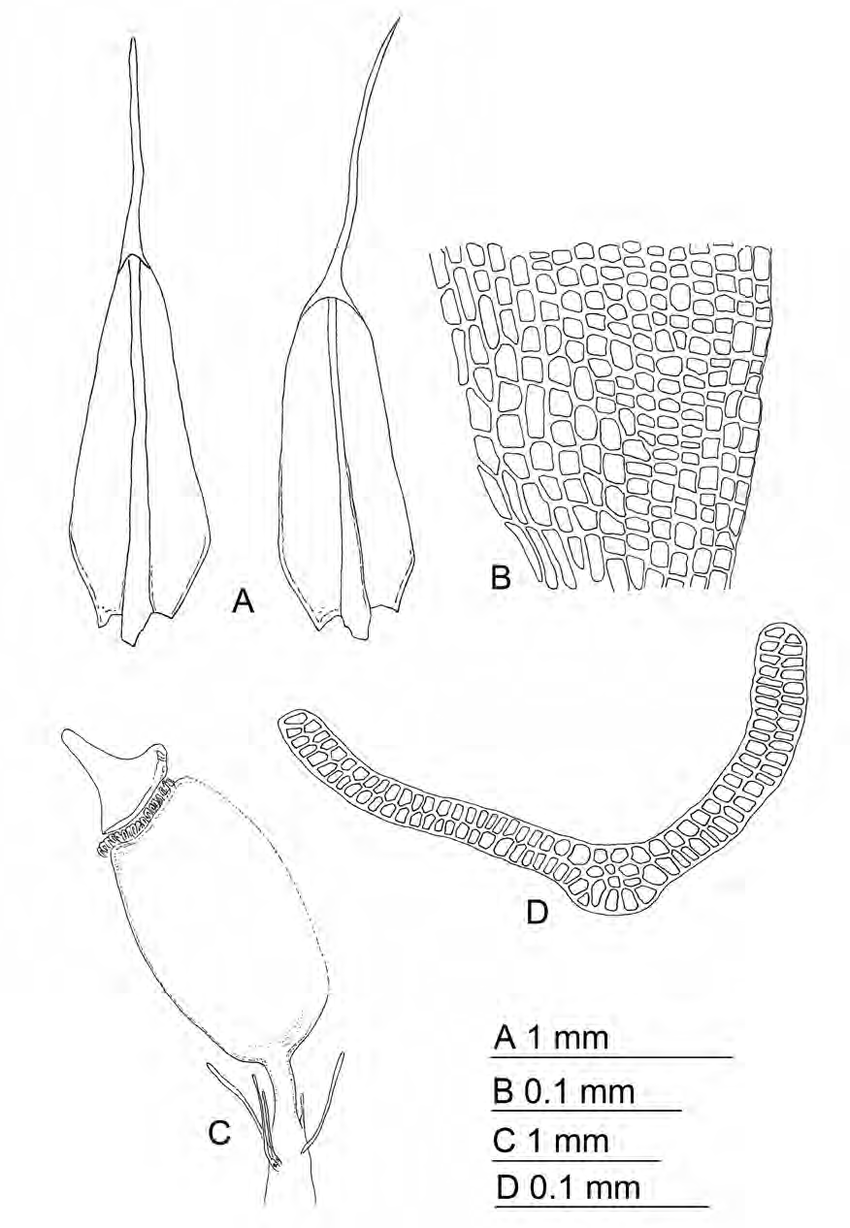
Grimmia-tergestina-A-Leaves-B-Proximal-leaf-cells-C-Sporophyte-D-Mid-leaf.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Grimmia-tergestina-A-Leaves-B-Proximal-leaf-cells-C-Sporophyte-D-Mid-leaf_fig24_283461562
Global Distribution and Habitat
The Grimmia tergestina moss is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, North America, and parts of Asia. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from coastal areas to mountainous regions, demonstrating its remarkable adaptability to different climatic conditions.
This moss is particularly well-suited to thrive in dry, exposed environments, such as rock outcrops, old walls, and even urban areas. Its ability to withstand desiccation and rapidly rehydrate when moisture becomes available is a testament to its evolutionary success.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, the Grimmia tergestina

f01_137.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/herzogia/volume-27/issue-1/heia.27.1.2014.137/Grimmia-crassiuscula-sp-nov-Grimmiaceae-from-China-and-Its-Separation/10.13158/heia.27.1.2014.137.full
moss plays a vital role in various ecosystems. It serves as a pioneer species, colonizing bare surfaces and paving the way for other organisms to establish themselves. Additionally, this moss provides a microhabitat for a diverse array of invertebrates, fungi, and other microorganisms, contributing to the overall biodiversity of its environment.

Grimmia-anomala-3-0712.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/grimmia-anomala/

Grimmia%2Bpulvinata.jpg from: https://varietyoflife.com.au/grimmia/
234806.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5557
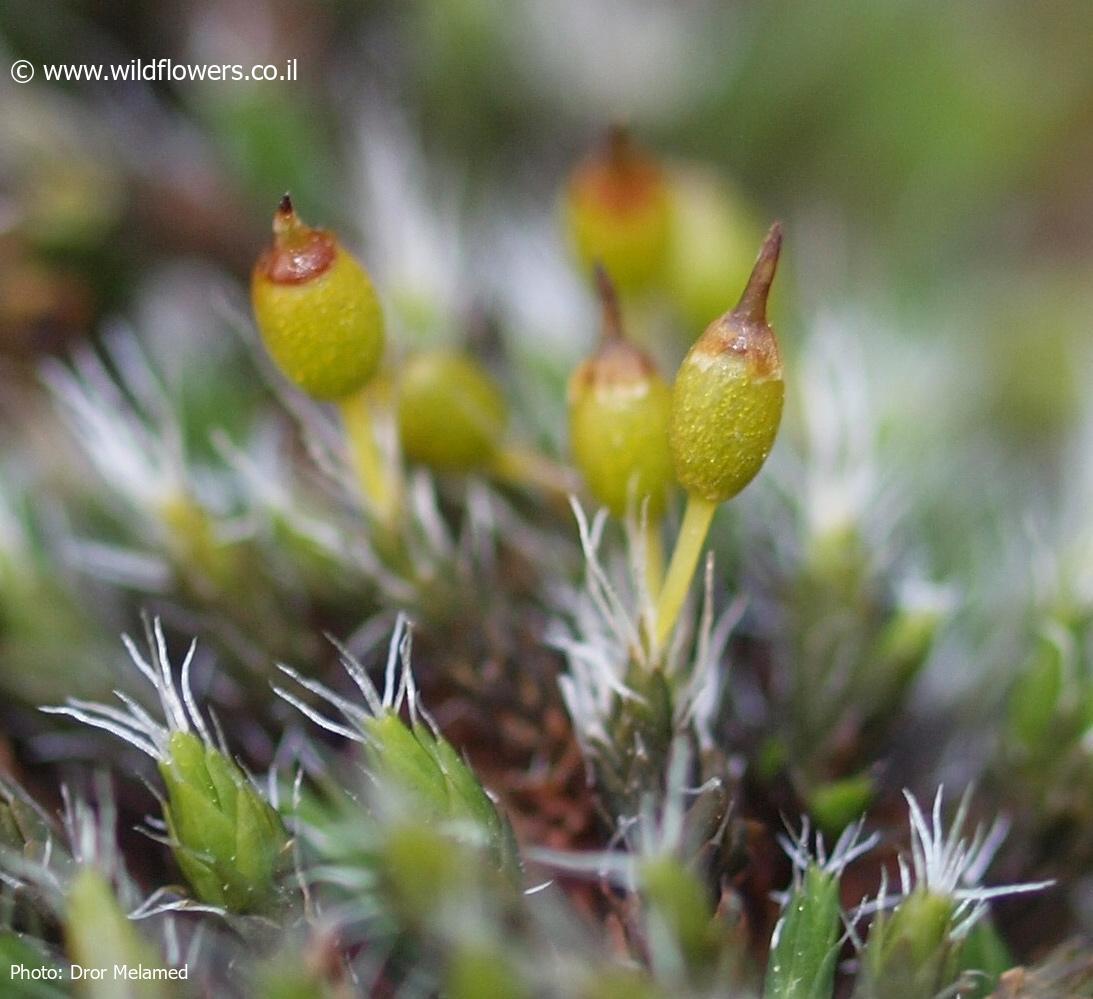

3276-l-5.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=19485
One of the most fascinating adaptations of this moss is its ability to undergo desiccation tolerance, a process that allows it to survive prolonged periods of drought by entering a state of dormancy. During this time, the moss’s metabolic processes slow down significantly, enabling it to conserve energy and resources until favorable conditions return.
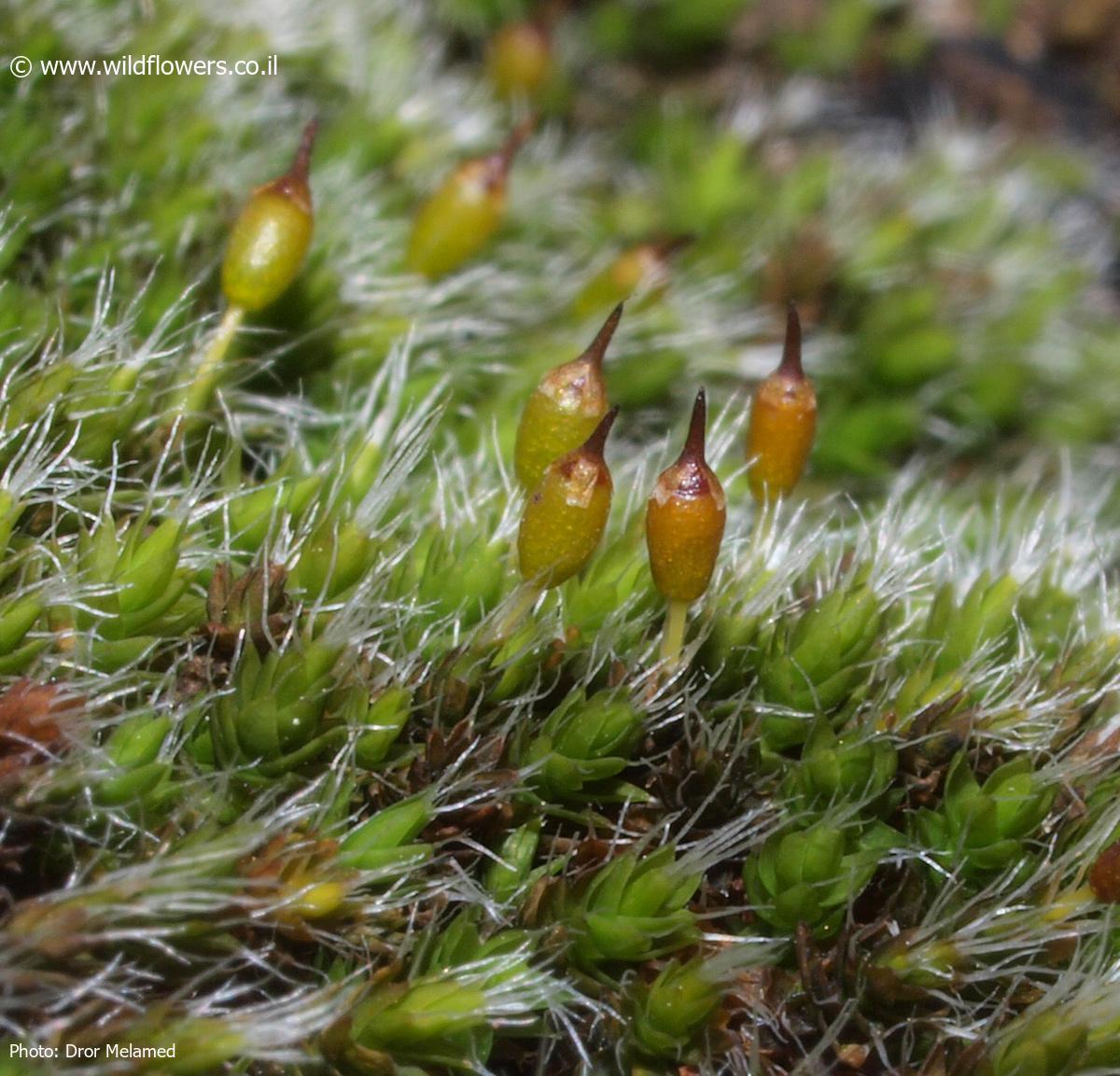

3276-l-3.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=19483
Case Studies/Examples
The Grimmia tergestina moss has been the subject of numerous scientific studies, shedding light on its remarkable adaptations and ecological significance. For instance, researchers have investigated the moss’s ability to accumulate heavy metals, making it a potential biomonitor for environmental pollution.
In urban areas, this moss has been observed thriving on concrete structures, demonstrating its resilience and ability to colonize man-made environments. Its presence on historic buildings and monuments has also sparked interest among conservationists, as it can serve as an indicator of air quality and environmental conditions.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Scientific Name
 5.jpg from: https://nathistoc.bio.uci.edu/Mosses/Grimmia laevigata/index.html |
Grimmia tergestina Tomm. ex B.S.G. |
| Family | Grimmiaceae |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss, forming dense cushions |
| Leaf Morphology | Lanceolate, with hyaline hair point |
| Color | Grayish-green (dry), emerald green (hydrated) |
| Habitat | Rock outcrops, walls, tree bark, urban areas |
| Distribution | Europe, North America, Asia |
| Adaptations | Desiccation tolerance, rapid rehydration |
| Ecological Roles | Pioneer species, microhabitat provider, biomonitor |
Conclusion
The Grimmia tergestina moss is a true testament to the resilience and adaptability of bryophytes. Its ability to thrive in harsh environments, undergo desiccation tolerance, and rapidly rehydrate when moisture becomes available is nothing short of remarkable. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, this unassuming moss serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and complexity that exists within even the smallest of organisms.
Before we part ways, let’s ponder this thought-provoking question: In a world where urbanization and environmental changes are rapidly altering landscapes, how can we ensure the preservation of species like the Grimmia tergestina moss, which play vital roles in maintaining ecosystem balance and biodiversity?