
153979667139788801.jpeg from: https://www.picturethisai.com/wiki/Homalothecium_nuttallii.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the Homalothecium nuttallii (Wilson) A.Jaeger. Belonging to the Brachytheciaceae family, this unassuming yet remarkable moss is commonly referred to as Homalothecium. Let’s delve into the fascinating realm of this diminutive plant and uncover its secrets.

14102434022_52778d1f0f_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/bushman_k/14102434022/in/photostream/
Background
Before we explore the intricacies of Homalothecium nuttallii, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest lineages of land plants. They play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
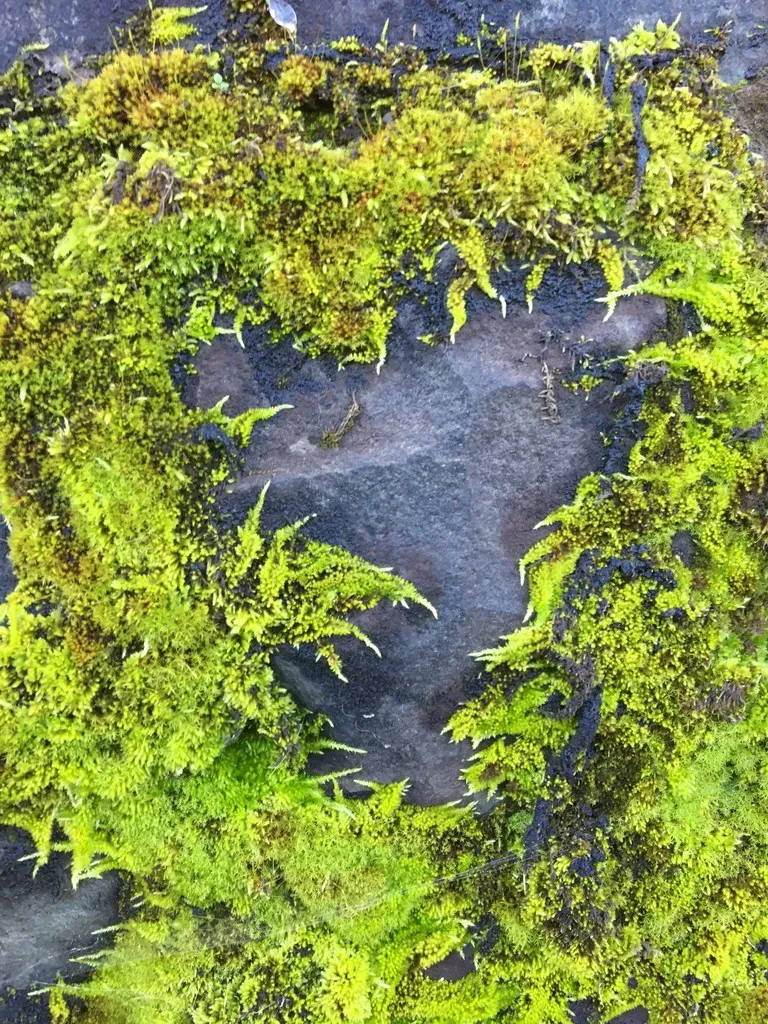
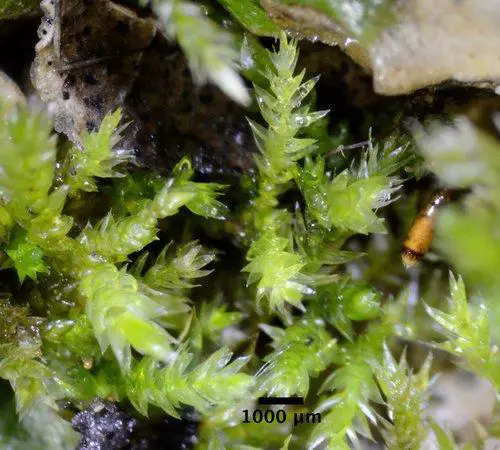
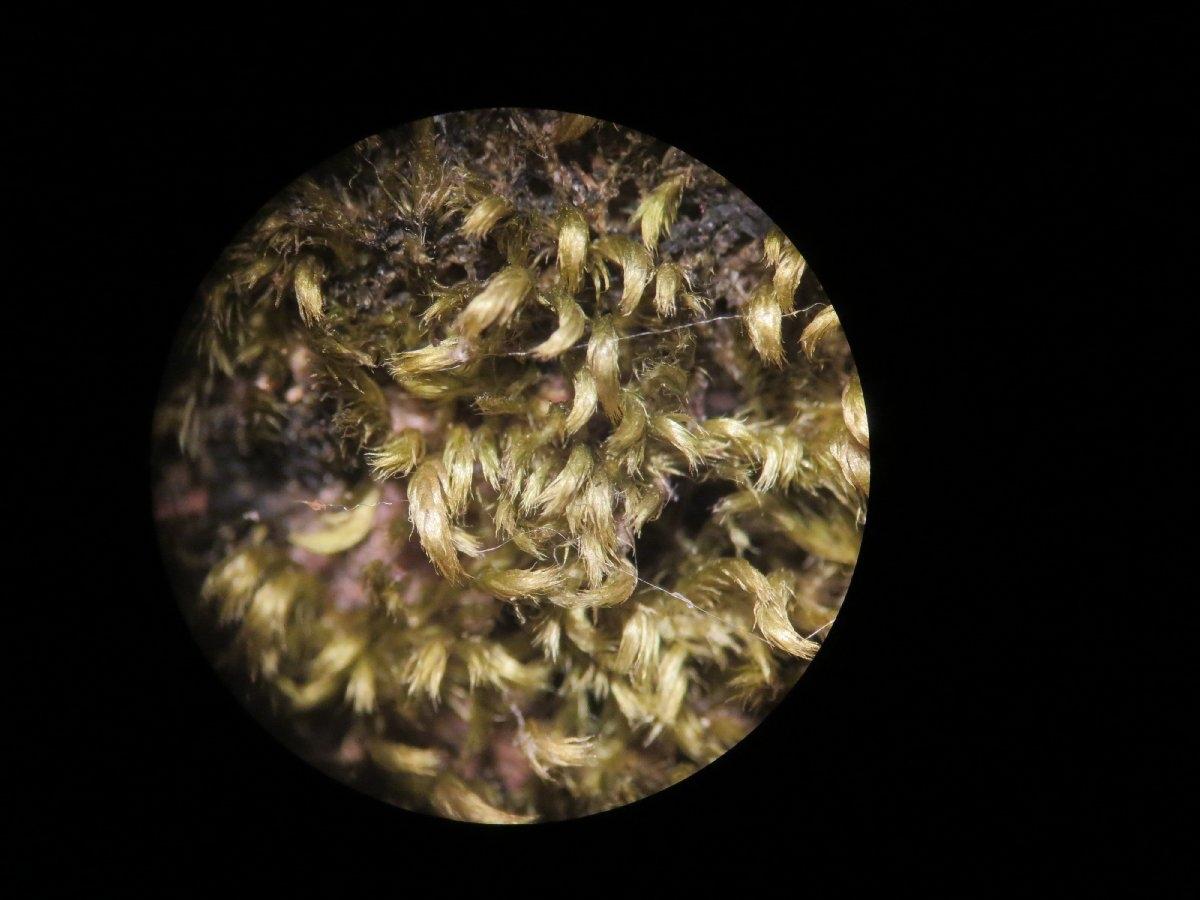
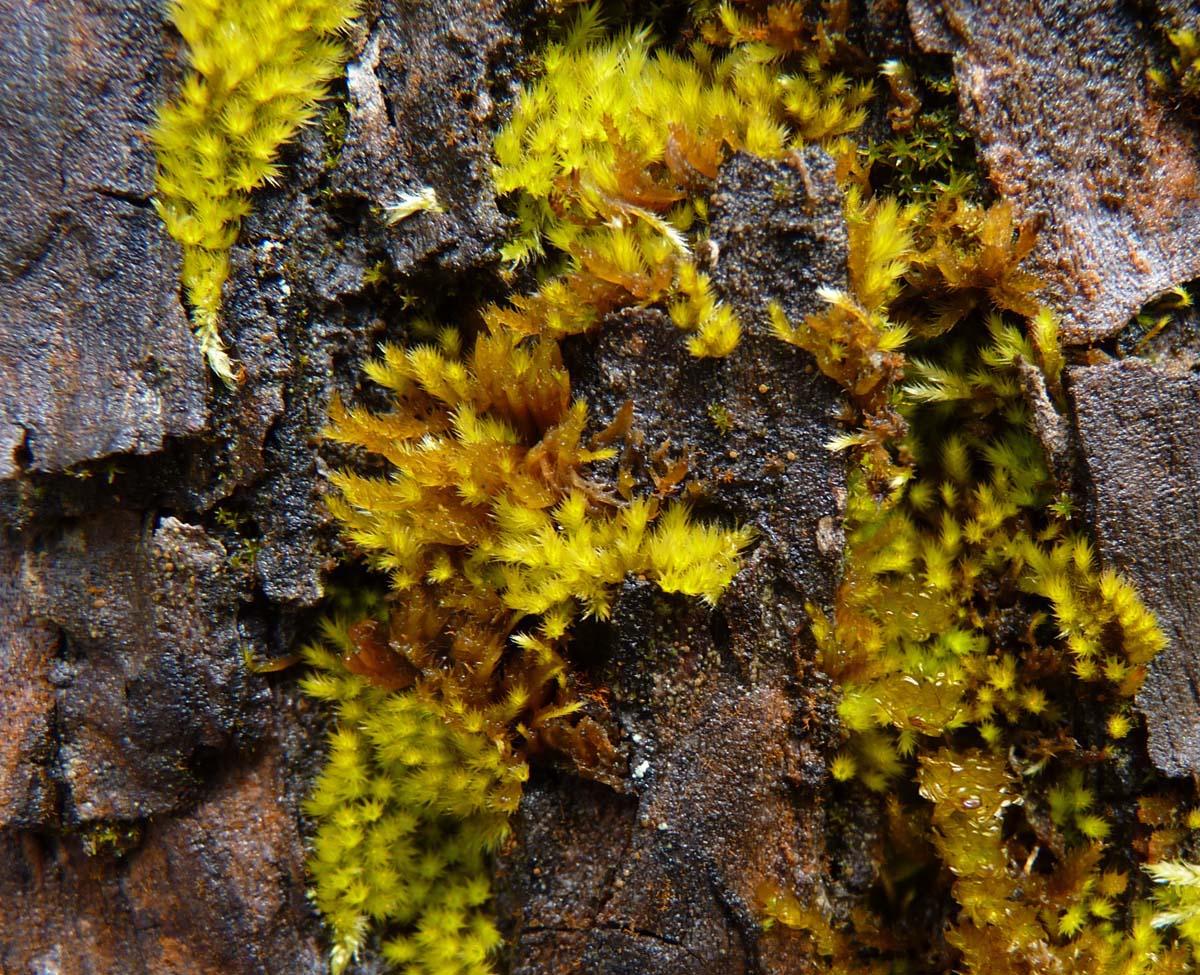
Homalothecium nuttallii is a small, creeping moss that forms dense, green to yellowish-green mats or tufts. Its stems are irregularly branched, and the leaves are ovate to lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive midrib. One of the key identifying features of this moss is the presence of

medium.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/163825-Homalothecium-arenarium
alar cells – specialized cells located at the base of the leaf that are inflated and hyaline (transparent).
Global Distribution and Habitat
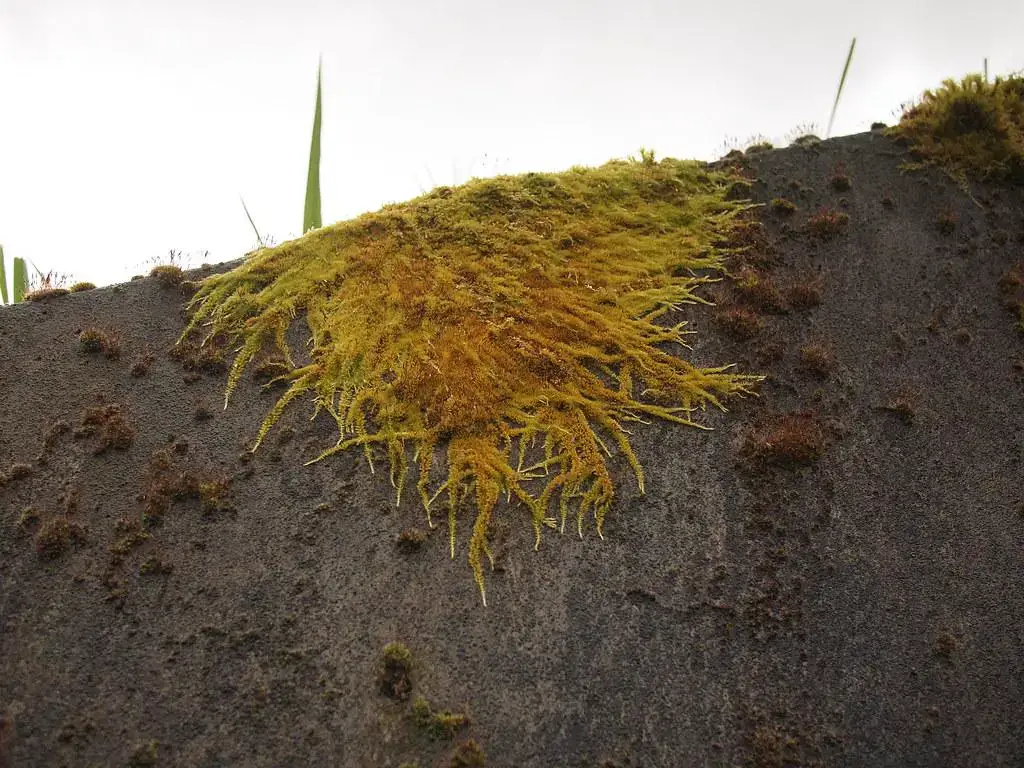
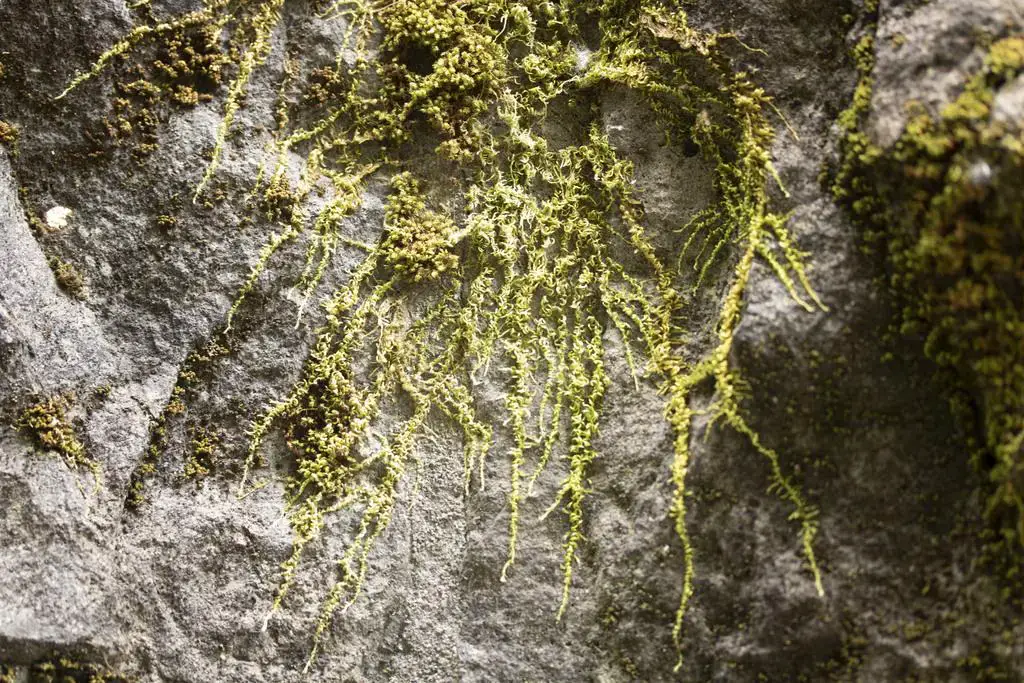
This moss species has a widespread distribution, occurring across various regions of North America, Europe, and Asia. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, including rocks, soil, tree bark, and even man-made structures like walls and roofs.

154143150774943779.jpeg from: https://www.picturethisai.com/ja/wiki/Homalothecium_nuttallii.html
Homalothecium nuttallii is particularly well-adapted to dry and exposed environments, making it a resilient pioneer species.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size,
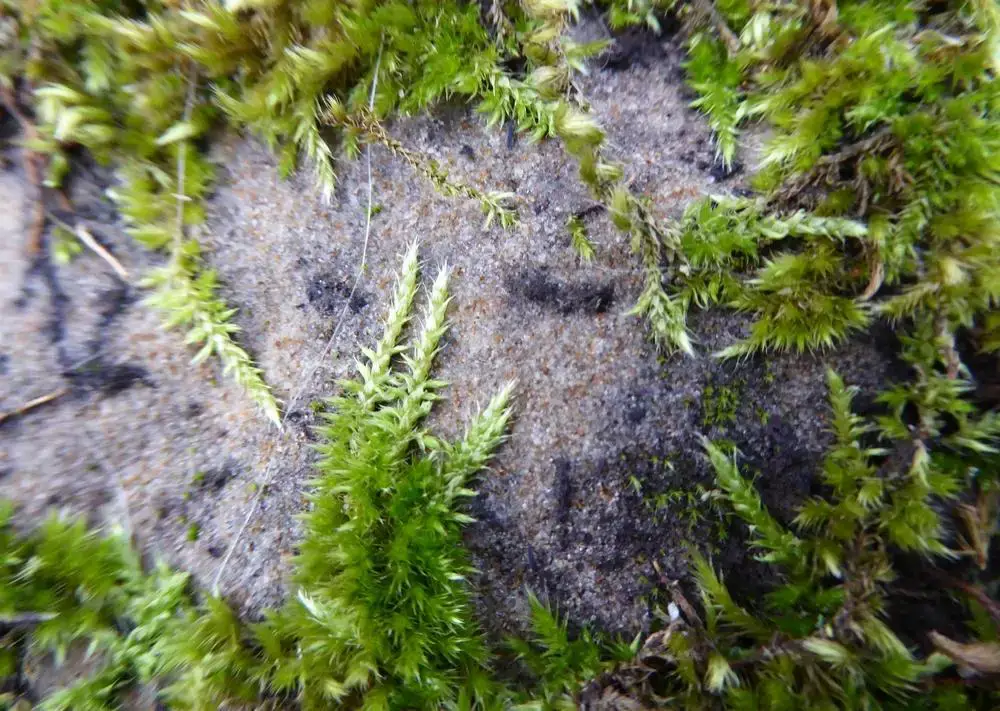

homalothecium-sericeum-shoots.jpg from: https://learningaboutmosses.wordpress.com/2020/01/16/homalothecium-sericeum/homalothecium-sericeum-shoots/
Homalothecium nuttallii plays a vital role in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide microhabitats for various invertebrates and serve as a food source for some herbivores.
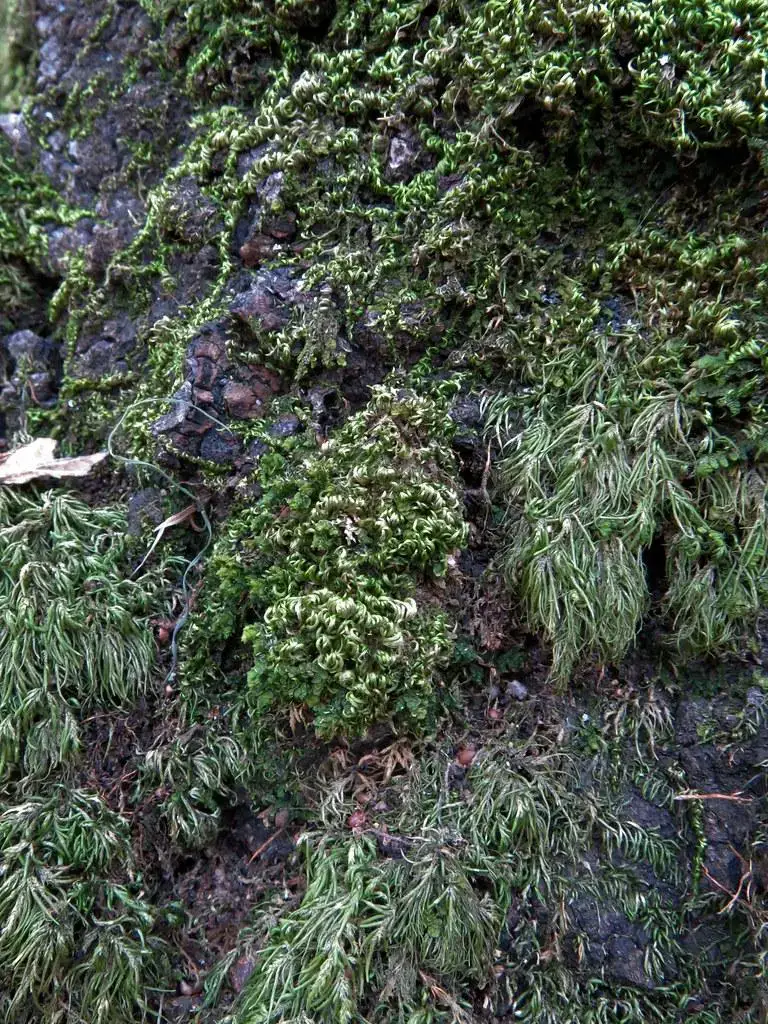

8433274275_02e6d7b784_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/openspacer/8433274275
One of the remarkable adaptations of Homalothecium nuttallii is its ability to withstand desiccation. During dry periods, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, curling its leaves inward to minimize water loss. When moisture becomes available, it quickly revives, demonstrating its resilience in challenging environments.
Case Studies/Examples
In urban areas, Homalothecium nuttallii
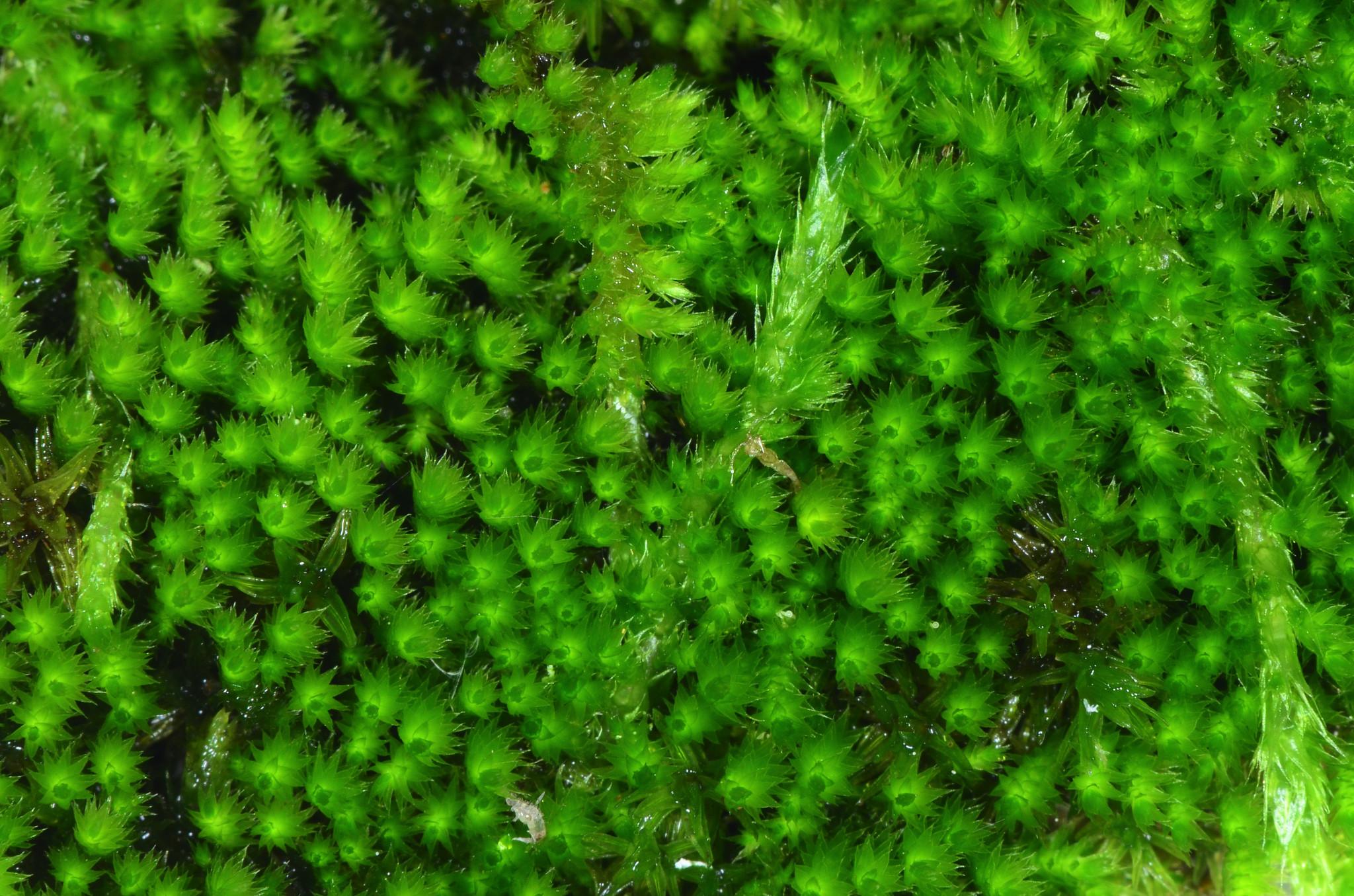

homalothecium_nuttallii.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Brachytheciaceae/homalothecium-nuttallii/en/
has been observed colonizing various man-made structures, such as old buildings, walls, and even gravestones. This ability to thrive in human-modified environments highlights its adaptability and potential for use in green infrastructure projects, such as green roofs and living walls.
Technical Table
169796.jpg from: https://www.calflora.org/app/taxon?crn=13925

48A.jpg from: https://www.fernzenmosses.com/BryoByHabitats/Oaks.html

large.jpg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/123314790
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Family | Brachytheciaceae |
| Genus | Homalothecium |
| Species | Homalothecium nuttallii (Wilson) A.Jaeger |
| Growth Form | Creeping, forming dense mats or tufts |
| Leaf Shape | Ovate to lanceolate |
| Distinctive Feature | Presence of inflated, hyaline alar cells |
Conclusion
Homalothecium nuttallii, a unassuming yet remarkable moss species, serves as a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. Its ability to colonize diverse habitats, stabilize soils, and provide microhabitats for other organisms highlights its ecological significance. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of mosses, we are reminded of the interconnectedness of all life forms, no matter how small. Perhaps the next time you encounter a verdant mat of Homalothecium nuttallii, you’ll pause and ponder the wonders of this diminutive yet extraordinary plant.