
carex-albicans-willd-ex-spreng-carex-albicans-willd-ex-spreng-2BXERXM.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/carex-albicans-willd-ex-spreng-carex-albicans-willd-ex-spreng-image360514524.html
Introduction
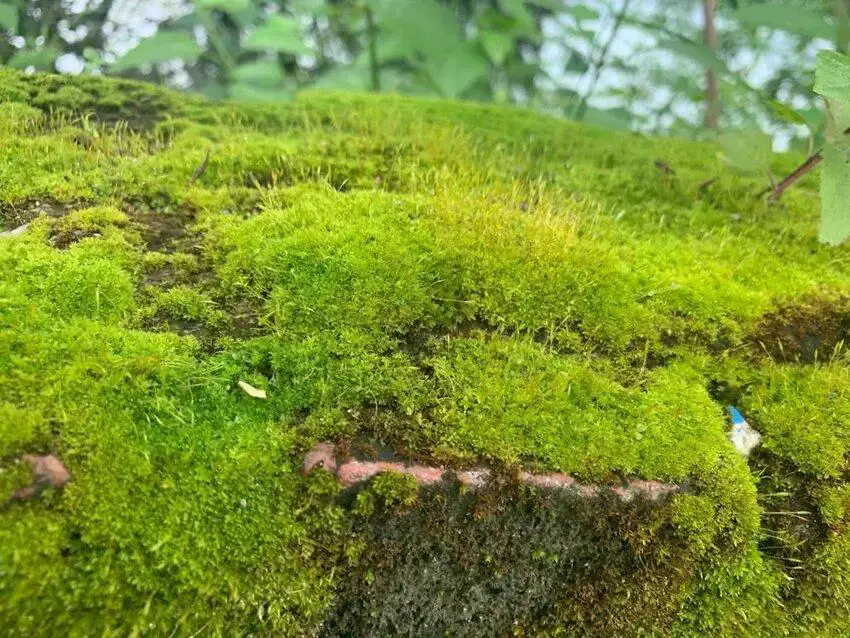
The world of bryophytes, or non-vascular plants, is a fascinating realm that often goes unnoticed by many. Among these diminutive yet remarkable organisms is the Barbula indica (Willd. ex Schrad.) Spreng., a moss species belonging to the Ptychomitriaceae family, commonly known as Barbula. This unassuming plant has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a glimpse into the intricate workings of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Barbula indica, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These ancient plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, have been around for over 400 million years, predating even the earliest vascular plants. Despite their diminutive size, they play crucial roles in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.

Barbula-indica-population-in-the-wild.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Barbula-indica-population-in-the-wild_fig1_368722783
Main Content
6b60e6256f18be3158254ad3f8659b1ed9bb45d9 from: https://identify.plantnet.org/fr/weurope/observations/1017172078
Morphology and Identification

carex-albicans-willd-ex-spreng-2BTP86X.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/carex-albicans-willd-ex-spreng-image359448514.html
Barbula indica is a small, acrocarpous moss, meaning its sporophytes (spore-bearing structures) grow at the tips of the stems. Its leaves are narrow, lance-shaped, and often twisted when dry, a characteristic that aids in water conservation. The sporophytes are borne on short, reddish-brown setae (stalks), and the capsules are cylindrical in shape, with a conical operculum (lid) that detaches to release the spores.
One of the key identifying features of Barbula indica is its distinctive peristome, a fringe-like structure surrounding the mouth of the capsule. This peristome is composed of 16 teeth, which twist and untwist in response to changes in humidity, facilitating the gradual release of spores.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Barbula indica is a cosmopolitan species, meaning it can be found across various regions of the world. It thrives in a wide range of habitats, from urban areas to natural environments, and is particularly abundant in disturbed or degraded sites. This moss is often found growing on soil, rocks, walls, and even tree bark, showcasing its remarkable adaptability.

artemisia-ludoviciana-subsp-mexicana-willd-ex-spreng-dd-keck-artemisia-ludoviciana-subsp-mexicana-willd-ex-spreng-dd-keck-2C1FFHJ.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/artemisia-ludoviciana-subsp-mexicana-willd-ex-spreng-dd-keck-artemisia-ludoviciana-subsp-mexicana-willd-ex-spreng-dd-keck-image362373918.html
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite their small size, mosses like Barbula indica play vital roles in their ecosystems. They contribute to soil formation and stabilization, acting as pioneers in colonizing bare or disturbed areas. Additionally, they serve as important microhabitats for various invertebrates and provide nesting materials for some bird species.
Barbula indica exhibits several adaptations that enable its survival in diverse environments. Its ability to tolerate desiccation (drying out) and rapidly rehydrate when moisture becomes available is a remarkable feat. This trait is facilitated by the presence of specialized cells called
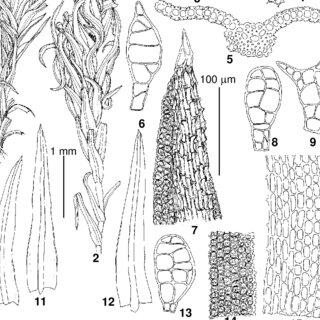
Barbula-indica-Hook-Spreng-ex-Steud-var-kurilensis-Ignatova-Ignatov-from-Kuril_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Barbula-indica-Hook-Spreng-ex-Steud-var-kurilensis-Ignatova-Ignatov-from-Kuril_fig1_274301518
hyaline cells, which act as water reservoirs, allowing the moss to quickly resume metabolic activities after a period of dormancy.
Case Studies/Examples
One notable example of Barbula indica’s ecological significance can be found in urban environments. This moss is often among the first colonizers of disturbed or degraded areas, such as construction sites or abandoned lots. Its presence helps stabilize the soil, preventing erosion and creating a suitable environment for other plant species to establish themselves, ultimately contributing to the regeneration of urban green spaces.
Technical Table

24676309898_5971ed0c83_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/138955704@N02/24676309898/

Rotala-indica_Meruvambayi-River_Kerala2_NKhardina.jpg from: https://biotopeaquariumproject.com/plant/rotala-indica-anjarakandy/

0192438-1-scaled.jpg from: https://makinodatabase.jp/plantsdatabase/artemisia_indica_willd_x_a_myriantha_wall_ex_besser/

artemisia-ludoviciana-subsp-mexicana-willd-ex-spreng-dd-keck-artemisia-ludoviciana-subsp-mexicana-willd-ex-spreng-dd-keck-2BXATP3.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/artemisia-ludoviciana-subsp-mexicana-willd-ex-spreng-dd-keck-artemisia-ludoviciana-subsp-mexicana-willd-ex-spreng-dd-keck-image360427371.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Family | Ptychomitriaceae |
| Genus | Barbula |
| Species | Barbula indica (Willd. ex Schrad.) Spreng. |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Narrow, lance-shaped |
| Sporophyte | Cylindrical capsule with conical operculum |
| Peristome | 16 twisted teeth |
| Habitat | Soil, rocks, walls, tree bark |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan |
| Adaptations | Desiccation tolerance, hyaline cells for water storage |
Conclusion
The Barbula indica (Willd. ex Schrad.) Spreng., or Barbula moss, may be small in stature, but its impact on the natural world is undeniably significant. From its remarkable adaptations to its vital ecological roles, this unassuming bryophyte serves as a testament to the resilience and importance of even the smallest organisms in our ecosystems. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of nature, perhaps we can find inspiration in the humble Barbula indica, a tiny moss with a mighty presence.
Ponder this: In a world where we often overlook the smallest beings, what other hidden marvels might we be missing, and how can we cultivate a deeper appreciation for the intricate tapestry of life that surrounds us?