
lepexc_pgd10015web1.jpg from: https://www.southernappalachianbryophytes.org/leptodontiumexcelsum.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one remarkable species stands out – the Leptodontium excelsum (Sull.) E.Britton moss. This unassuming yet fascinating plant belongs to the Pottiaceae family and is commonly referred to as Leptodontium. Prepare to embark on a journey through the intricate details of this extraordinary moss, where we’ll unravel its secrets and appreciate its unique place in the natural world.

leptodontium_flexifolium.jpg from: https://www.earth.com/plant-encyclopedia/Bryophytes/Pottiaceae/leptodontium-flexifolium/en/
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Leptodontium excelsum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification

leptodontium_sp01.jpg from: https://www.chilebosque.cl/moss/leptodontium_sp.html
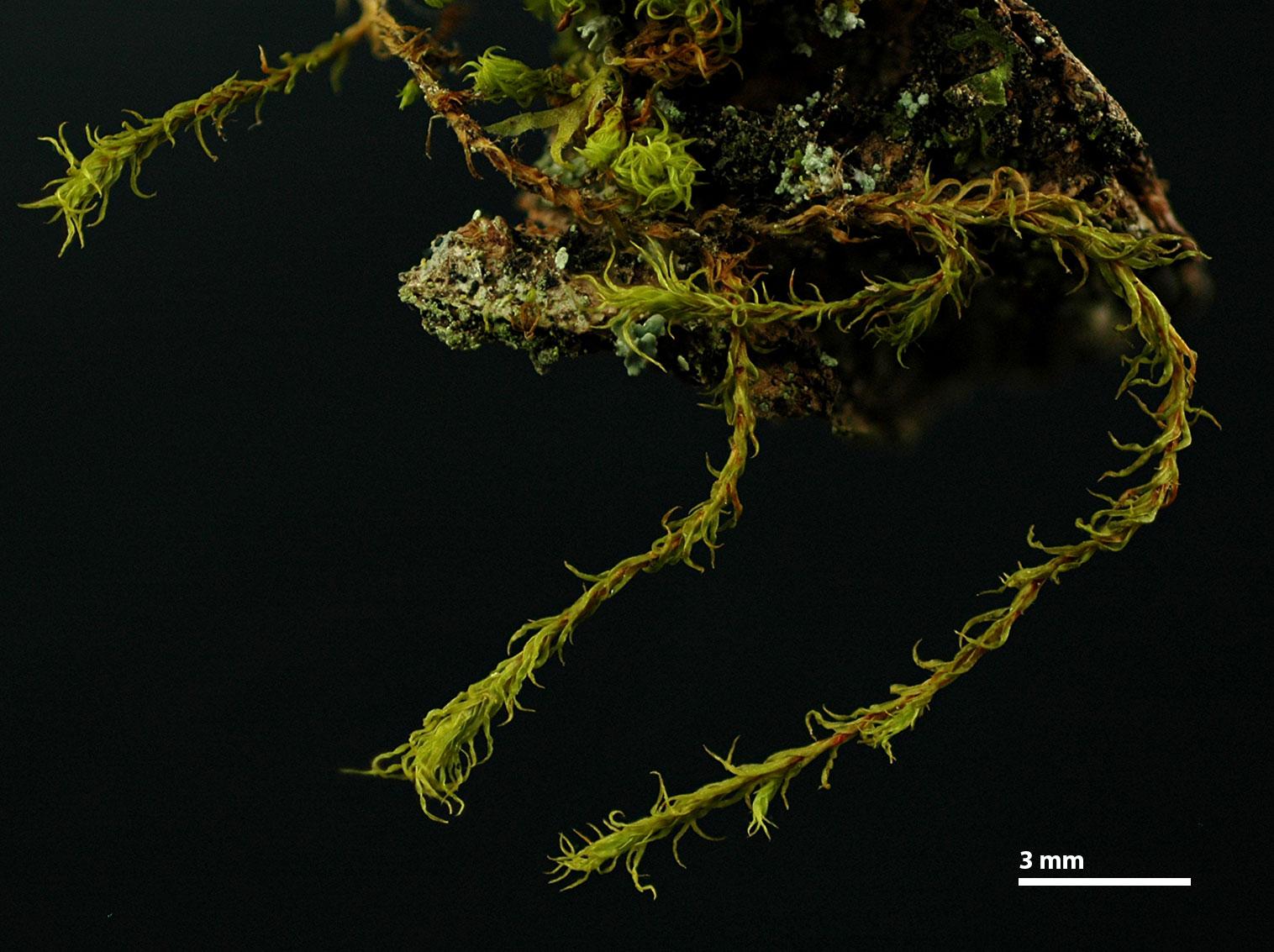
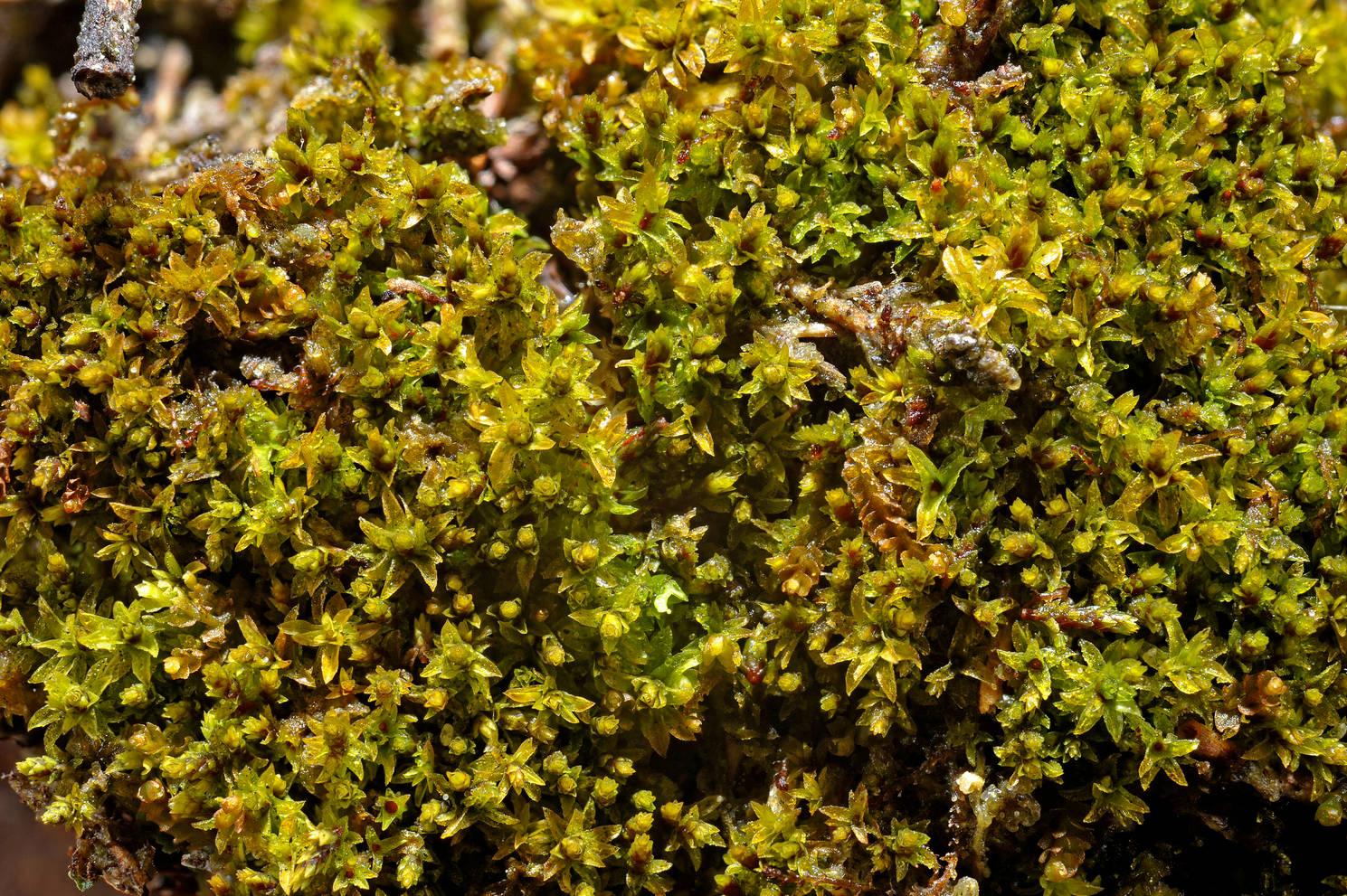
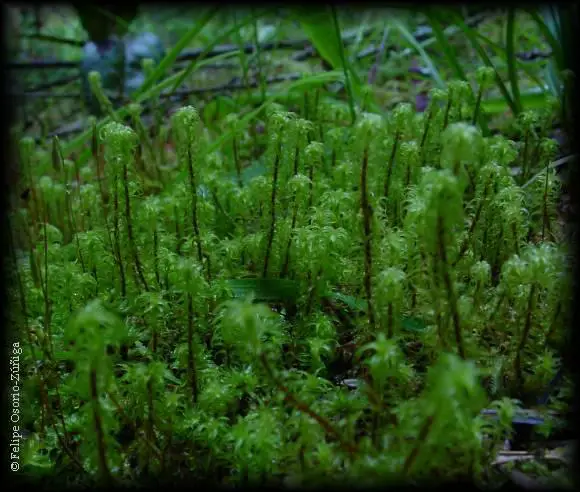
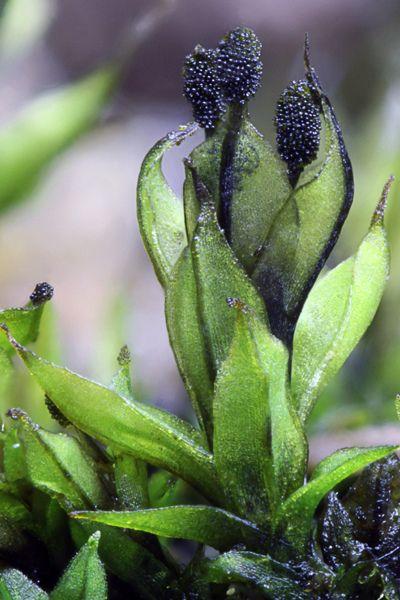
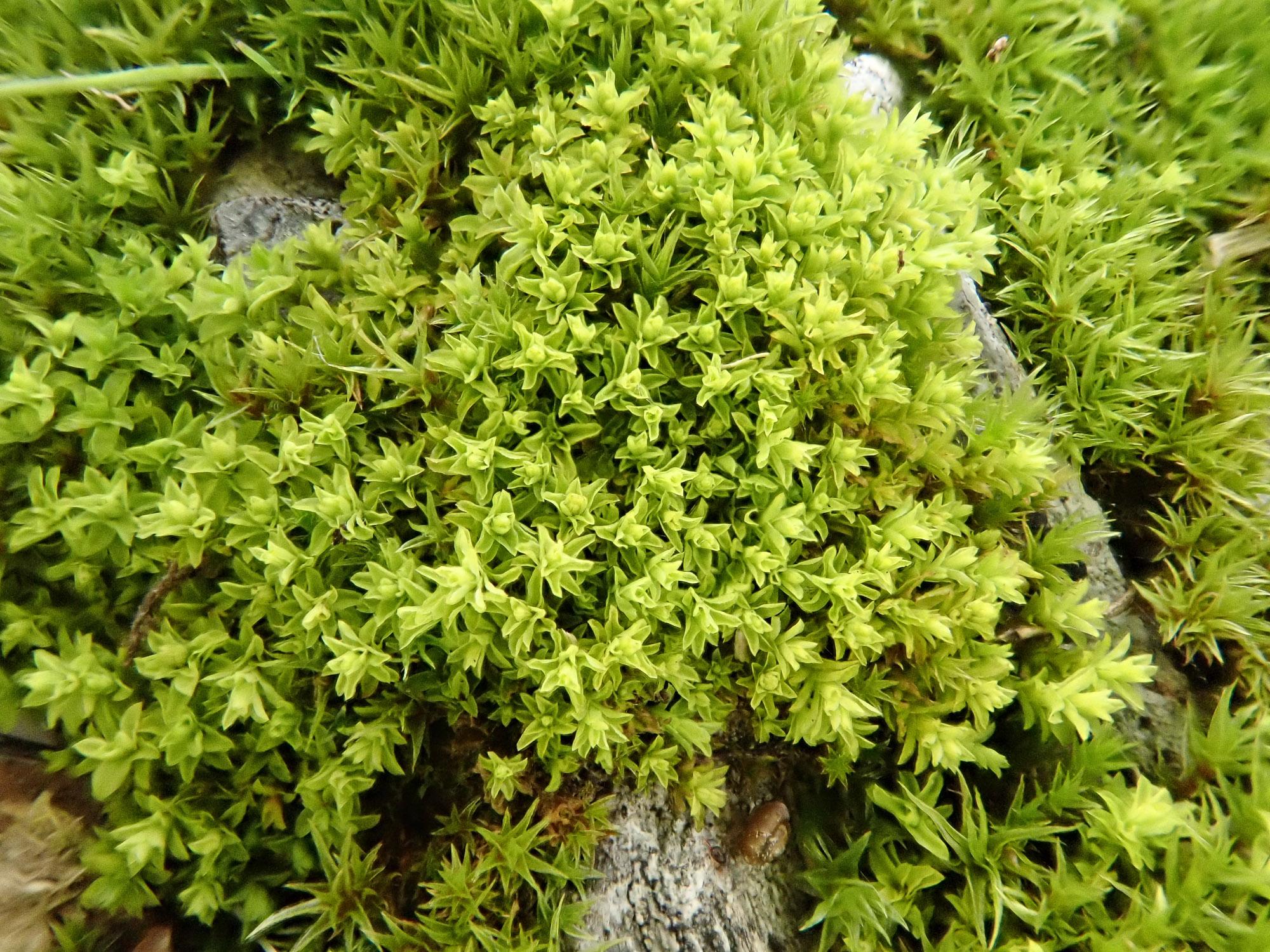
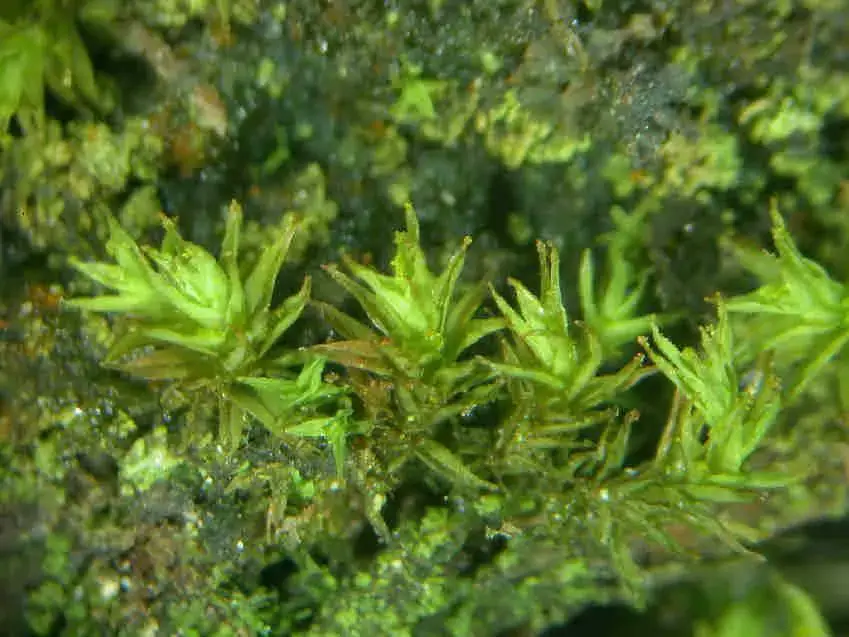
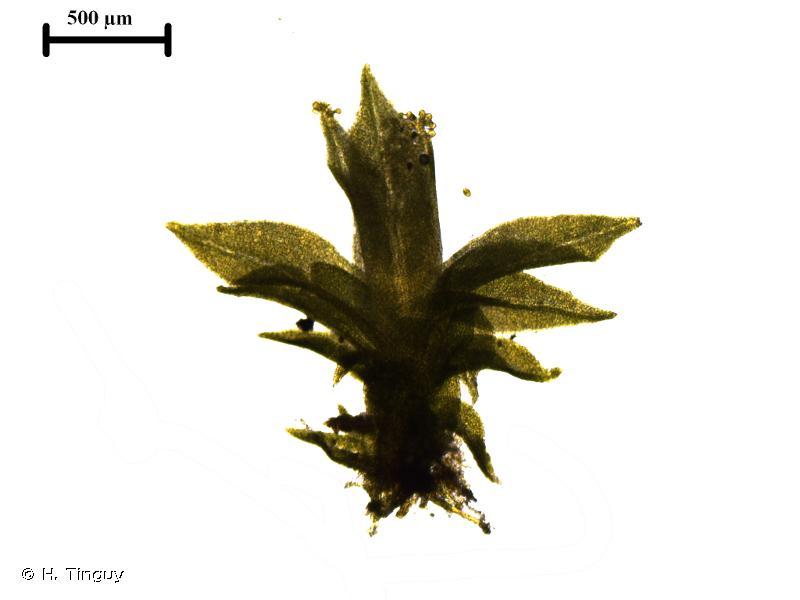
Leptodontium excelsum is a striking moss species that can be identified by its distinctive features. It forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats, with slender stems that can reach up to several centimeters in height. The leaves are narrow, lance-shaped, and often curved or twisted, giving the plant a unique and eye-catching appearance.
One of the most remarkable characteristics of Leptodontium excelsum is its ability to produce specialized structures called gemmae. These tiny, bud-like structures are capable of detaching from the parent plant and developing into new individuals, allowing for efficient propagation and dispersal.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Leptodontium excelsum is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa. It thrives in a diverse range of habitats, from rocky outcrops and cliffs to soil banks and even tree bark. This adaptability is a testament to the resilience and versatility of this remarkable moss species.
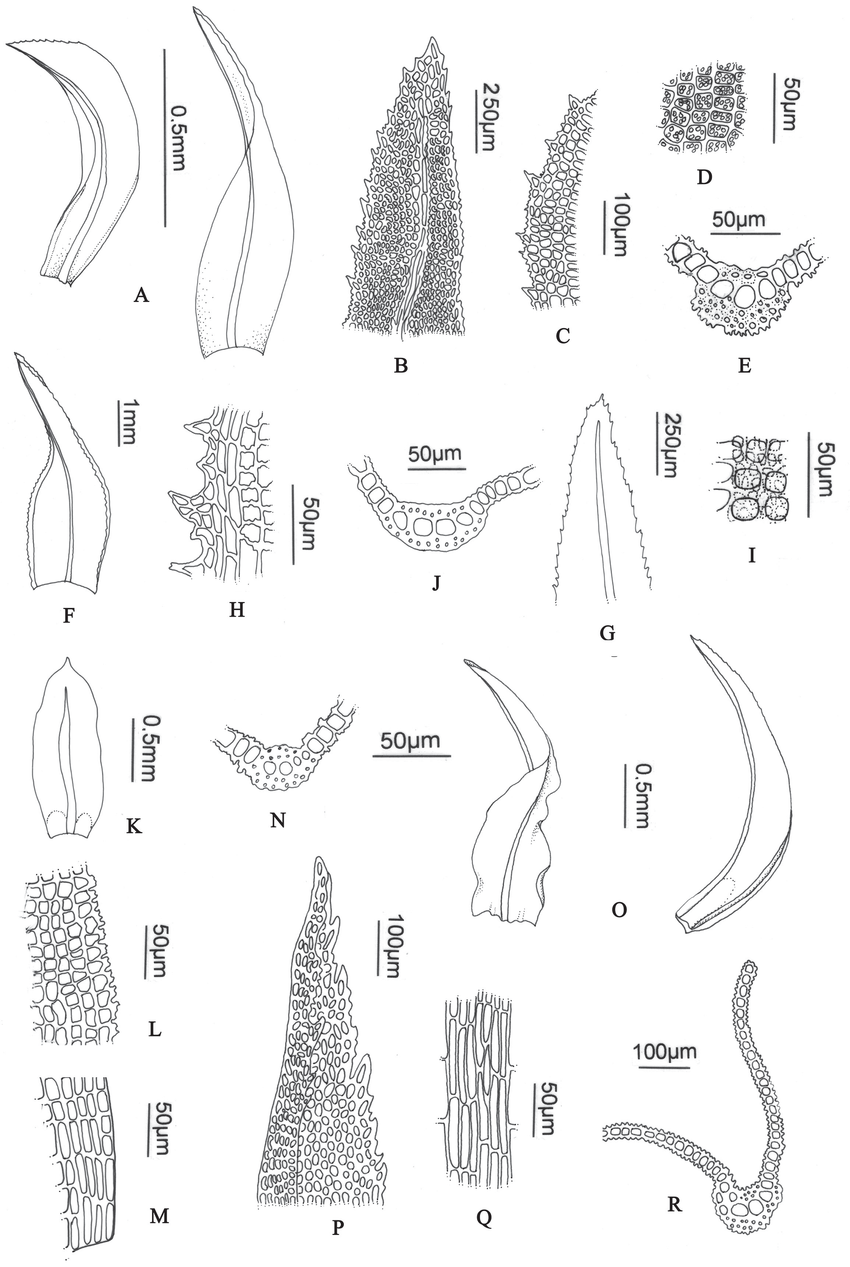
A-E-Leptodontium-flexifolium-A-Leaves-B-Leaf-apex-C-Marginal-cells-D-Papillae.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/A-E-Leptodontium-flexifolium-A-Leaves-B-Leaf-apex-C-Marginal-cells-D-Papillae_fig4_281820899
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

29fc5a3bf7eec09b7a1a2d3b31d65408.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/494692340290372782/
Despite its diminutive size, Leptodontium excelsum plays a vital role in its ecosystems. It contributes to soil formation and stabilization, helps retain moisture, and provides a microhabitat for numerous other organisms, such as insects, fungi, and other bryophytes.
One of the key adaptations that allow Leptodontium excelsum to thrive in challenging environments is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This remarkable trait is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of this species.
Case Studies/Examples
Leptodontium excelsum has been the subject of numerous scientific studies, shedding light on its unique characteristics and ecological significance. For instance, researchers have investigated the role of this moss in stabilizing soil and preventing erosion in alpine regions, where its dense mats help anchor the substrate and retain moisture.

medium.jpg from: https://enciclovida.mx/especies/136928-leptodontium
Technical Table

2021-10-14-10-23-10.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/leptodontium-flexifolium/

Leptodontium_gemmascens_005C.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Leptodontium_gemmascens.html
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Leptodontium excelsum (Sull.) E.Britton |
| Family | Pottiaceae |
| Growth Form | Cushion-like tufts or mats |
Stem Height
 169143.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/5311 |
Up to several centimeters |
| Leaf Shape | Narrow, lance-shaped, often curved or twisted |
| Reproduction | Gemmae (specialized propagules) |
| Distribution | North America, Europe, Asia, Africa |
| Habitat | Rocky outcrops, cliffs, soil banks, tree bark |
| Ecological Roles | Soil formation, moisture retention, microhabitat provision |
| Adaptations | Desiccation tolerance, dormancy |
Conclusion

leptodontium_longicaule01.jpg from: https://www.musgosdechile.cl/leptodontium.html
Leptodontium excelsum is a true marvel of the bryophyte world, showcasing the incredible diversity and resilience of these often-overlooked plants. From its striking morphology and unique reproductive strategies to its vital ecological roles and remarkable adaptations, this moss species deserves our admiration and appreciation.
As we bid farewell to this captivating journey, a thought-provoking question lingers: How can we better protect and conserve the habitats of species like Leptodontium excelsum, ensuring their continued existence and contribution to our planet’s delicate ecosystems?