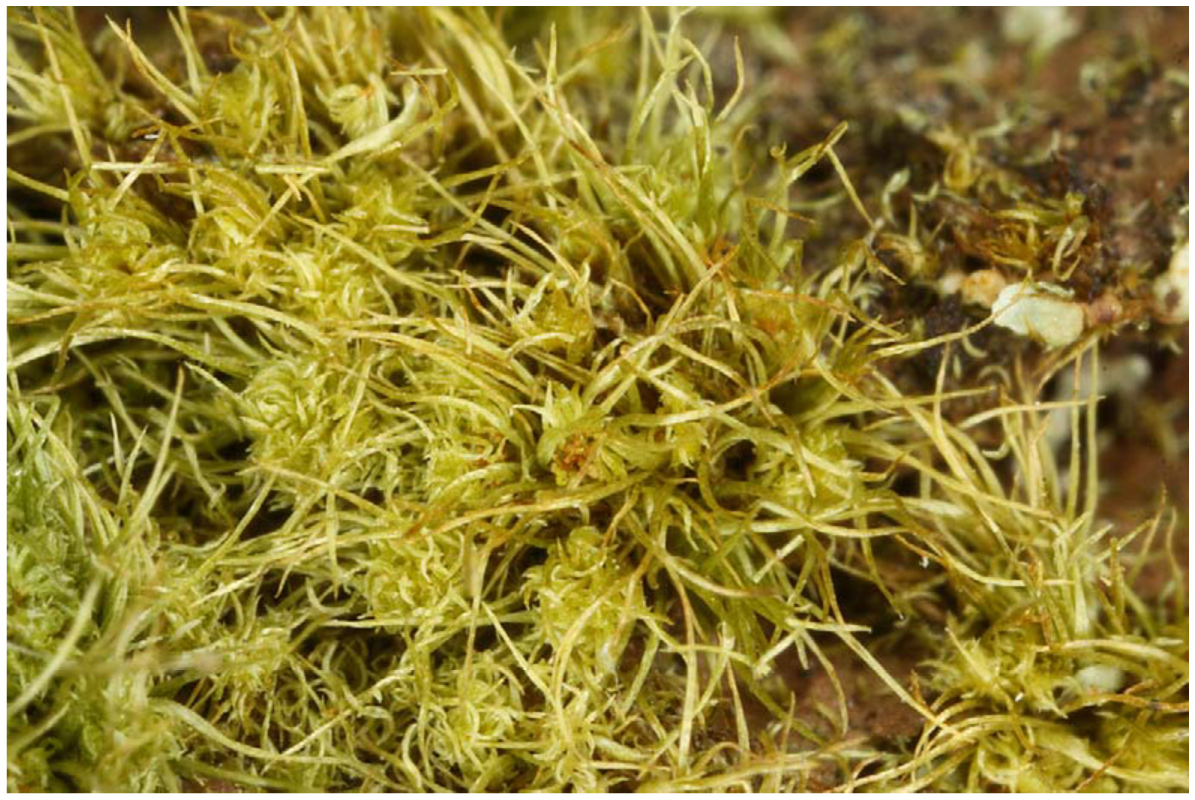

image from: https://bioone.org/journals/Evansia/volume-28/issue-3/079.028.0302/Brothera-leana-Sull-Müll-Hal-Dicranaceae-in-New-Mexico/10.1639/079.028.0302.full
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Campylostelium bruchioides (Müll.Hal.) Broth. moss stands out as a fascinating member of the
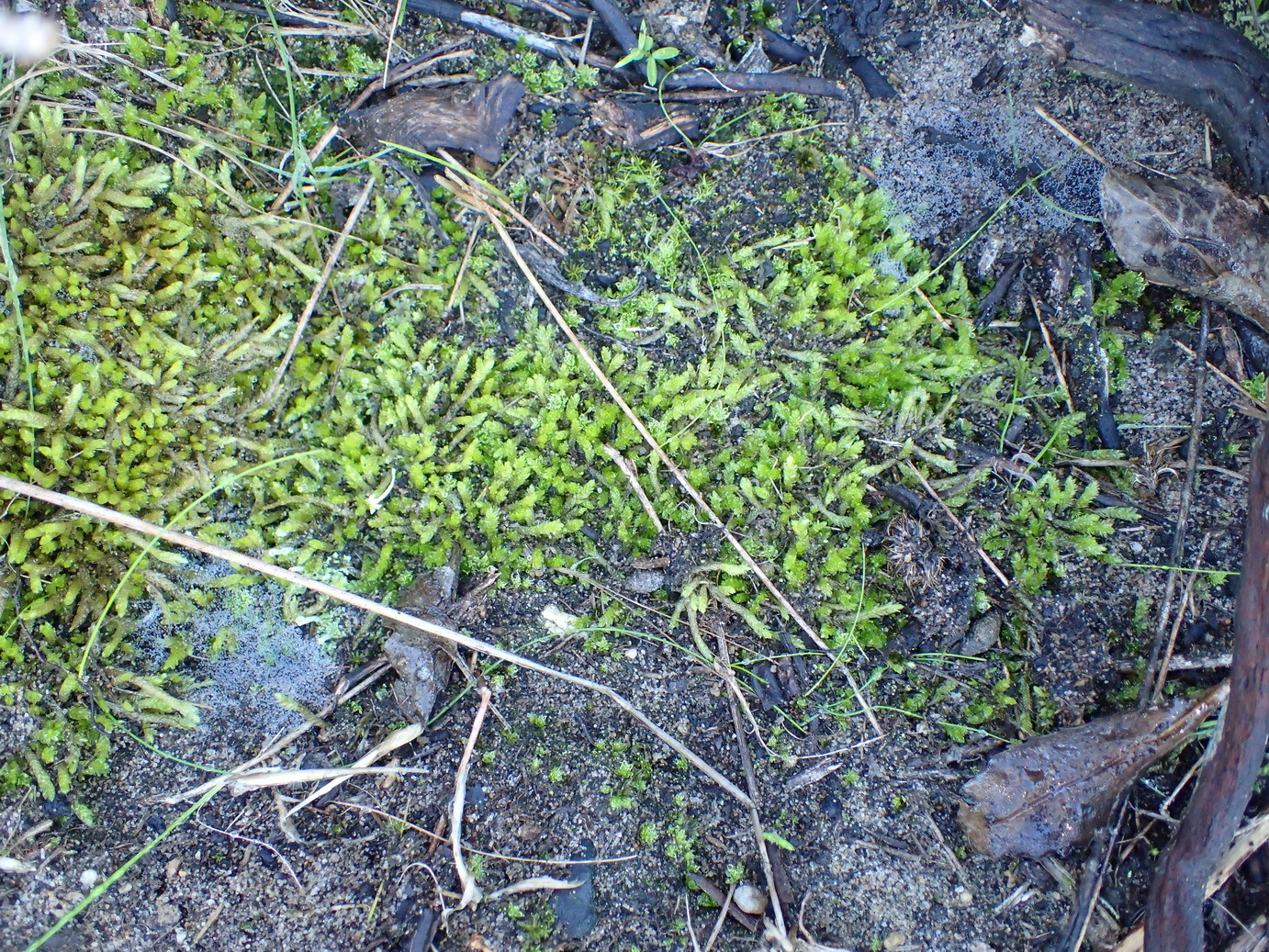

image from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552
Bruchiaceae family. This unassuming yet remarkable plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide, offering a unique glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of this moss species, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of the plant kingdom. Bryophytes, also known as Bryopsida, are a diverse group of non-vascular plants that include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. These ancient organisms have been around for millions of years, predating even the earliest vascular plants.

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Linbergia-sinensis-Muell-Hal-Broth-1-Habit-of-plant-Wet-2-A-portion-of-plant_fig1_341098152
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Campylostelium bruchioides (Müll.Hal.) Broth. is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its slender stems are typically less than 1 cm tall, adorned with delicate, lanceolate leaves that are spirally arranged. The leaves are keeled, meaning they have a distinct ridge or fold along the midrib, giving them a distinctive appearance.
One of the most striking features of this moss is its
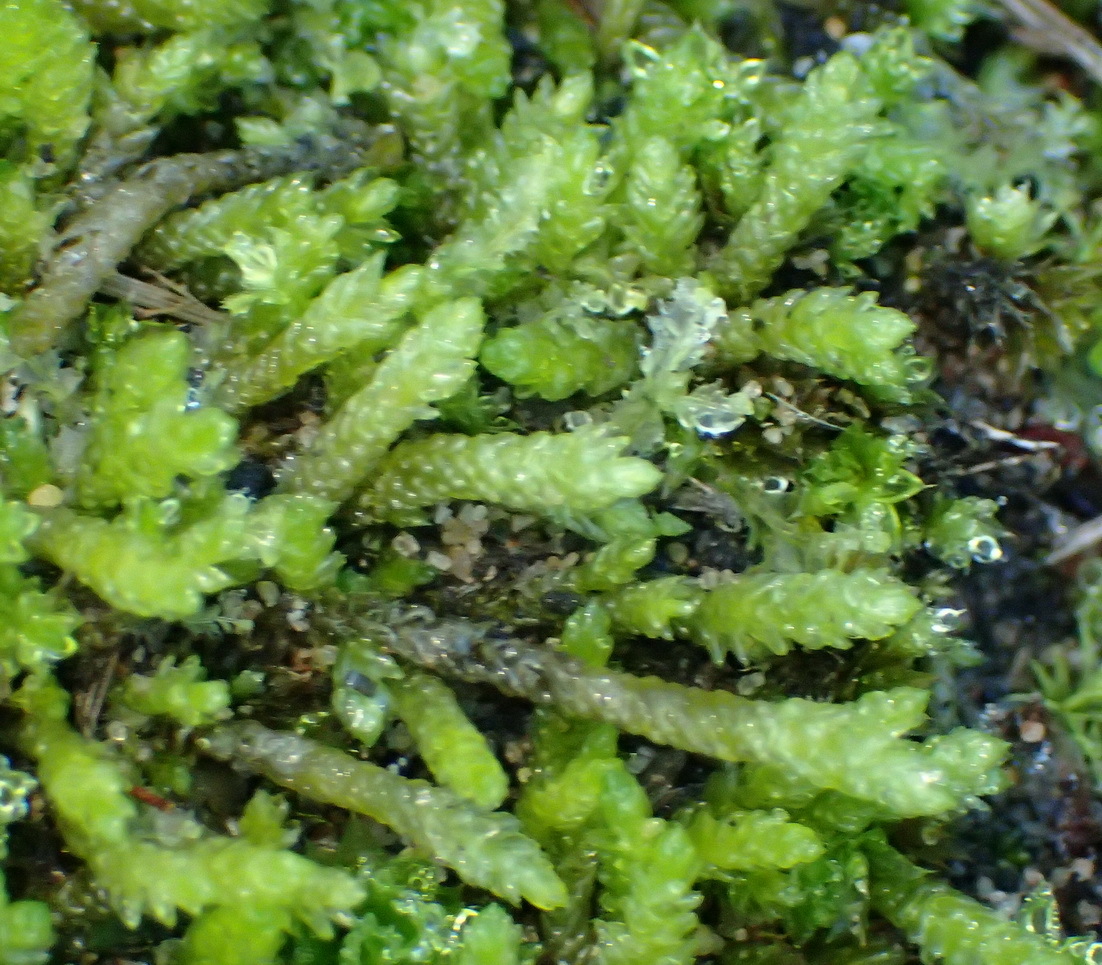

image from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552
capsule, which is curved or campylotropous, hence the genus name “
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-15-Dicranella-ulei-Muell-Hal-Broth-A-Habito-B-Filidios-C-Apices-dos_fig14_343400267
Campylostelium.” This unique shape sets it apart from many other moss species and serves as a key identifying characteristic.
Global Distribution and Habitat
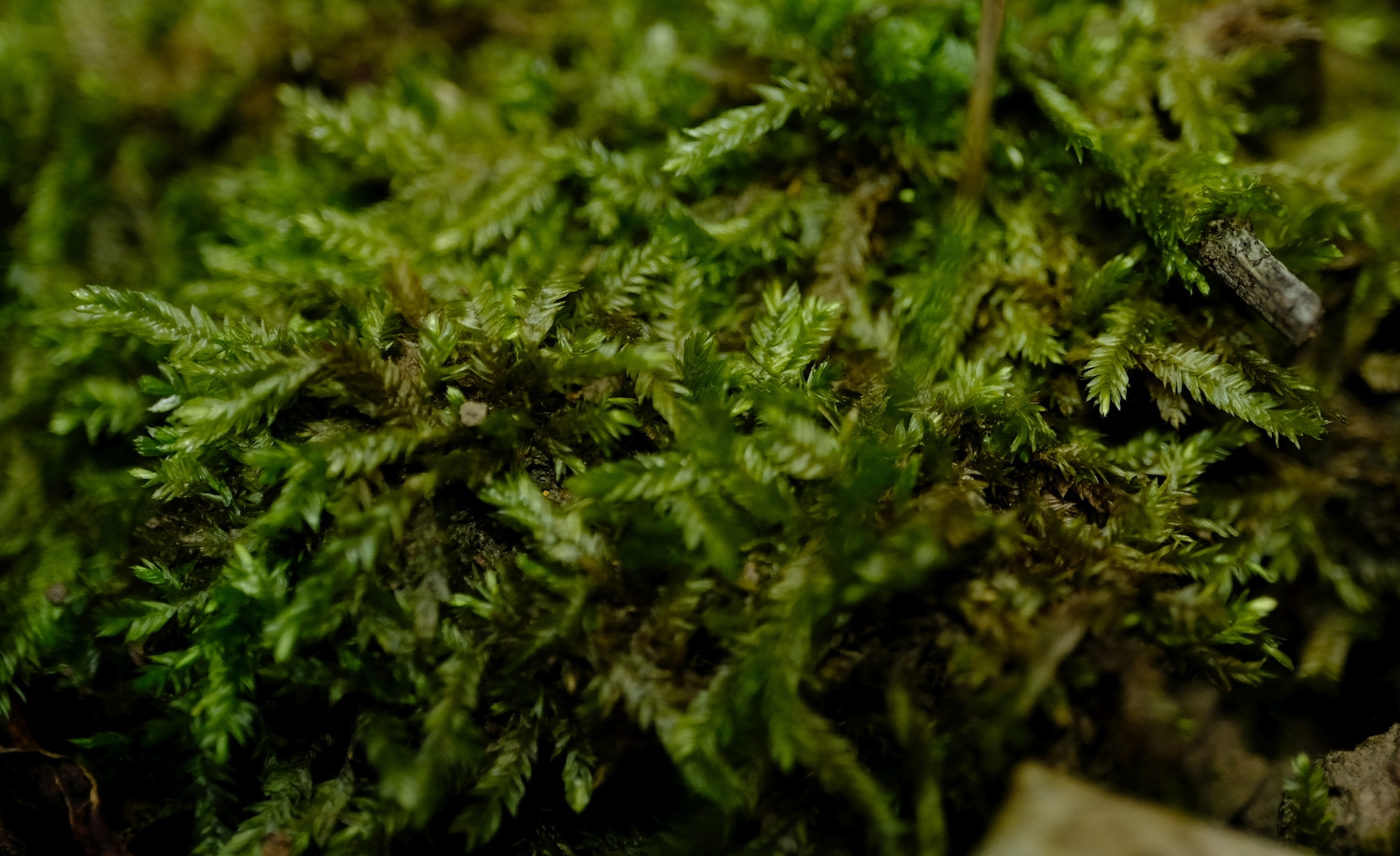

image from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552
Campylostelium bruchioides (Müll.Hal.) Broth. is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, Asia, North America, and parts of South America. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from moist and shaded areas to exposed rock surfaces and even disturbed sites like roadside banks and quarries.
This moss species is particularly well-adapted to acidic and nutrient-poor

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-7-Dicranella-harrisii-Muell-Hal-Broth-A-Habito-B-Filidios-C-Apice-do_fig7_343400267
environments, making it a common sight on decaying logs, tree bark, and rocky outcrops. Its ability to colonize such diverse habitats is a testament to its resilience and adaptability.
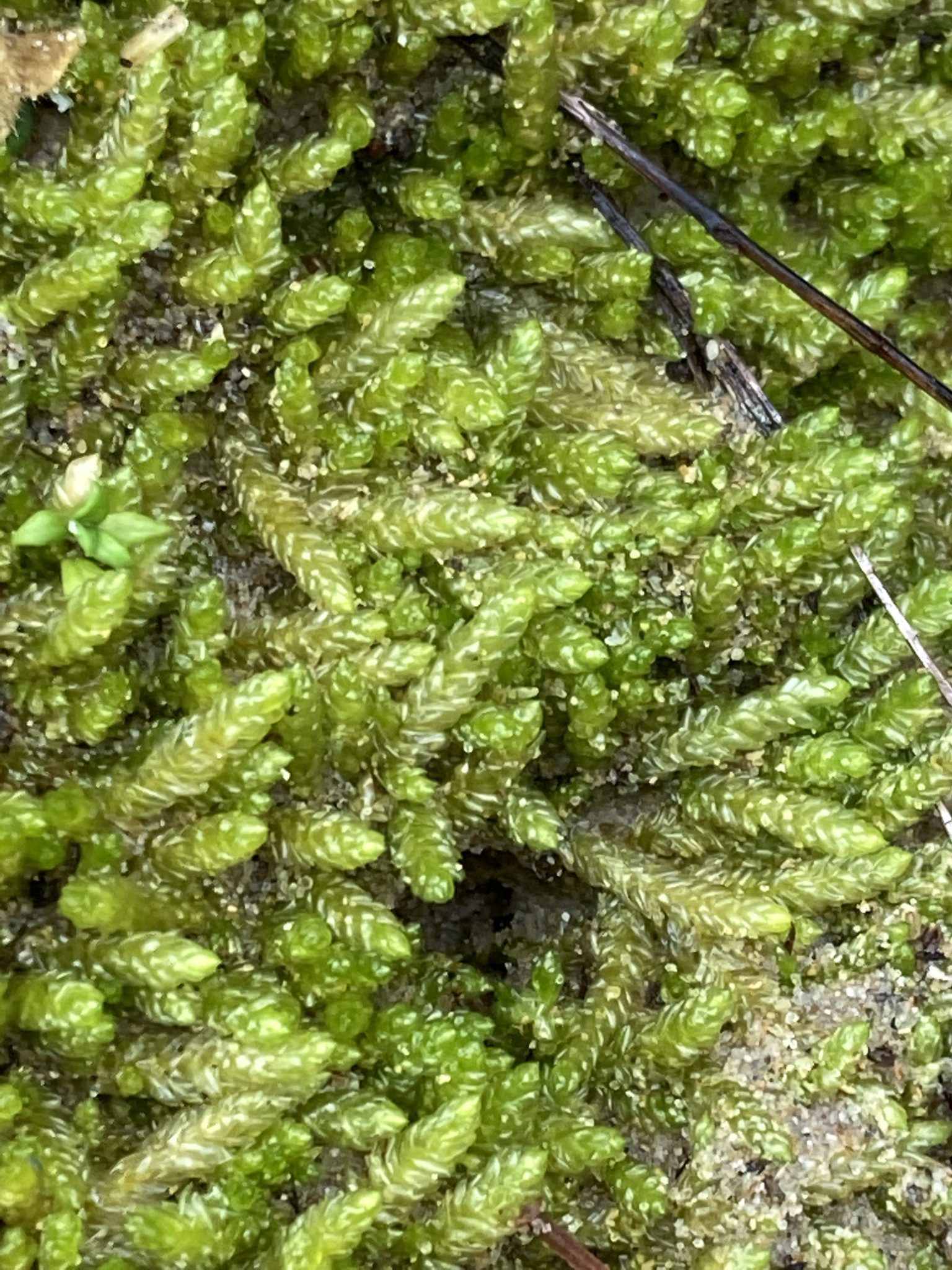

image from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Campylostelium bruchioides (Müll.Hal.) Broth. plays a crucial role in various ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soil, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense mats provide microhabitats for a wide range of invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.
One of the remarkable adaptations of this moss is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During periods of drought, it can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This trait allows it to thrive in environments where water availability is unpredictable.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered a thriving population of Campylostelium bruchioides (Müll.Hal.) Broth. growing on the bark of ancient Douglas fir trees. This finding highlighted the moss’s ability to colonize and persist in unique habitats, contributing to the overall diversity of the forest ecosystem.
Technical Table

image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fissidens-serratus-MuellHal-A-Habit-B-Plant-C-D-Leaves-E-Perichaetial-leaf-F-G_fig8_351104512
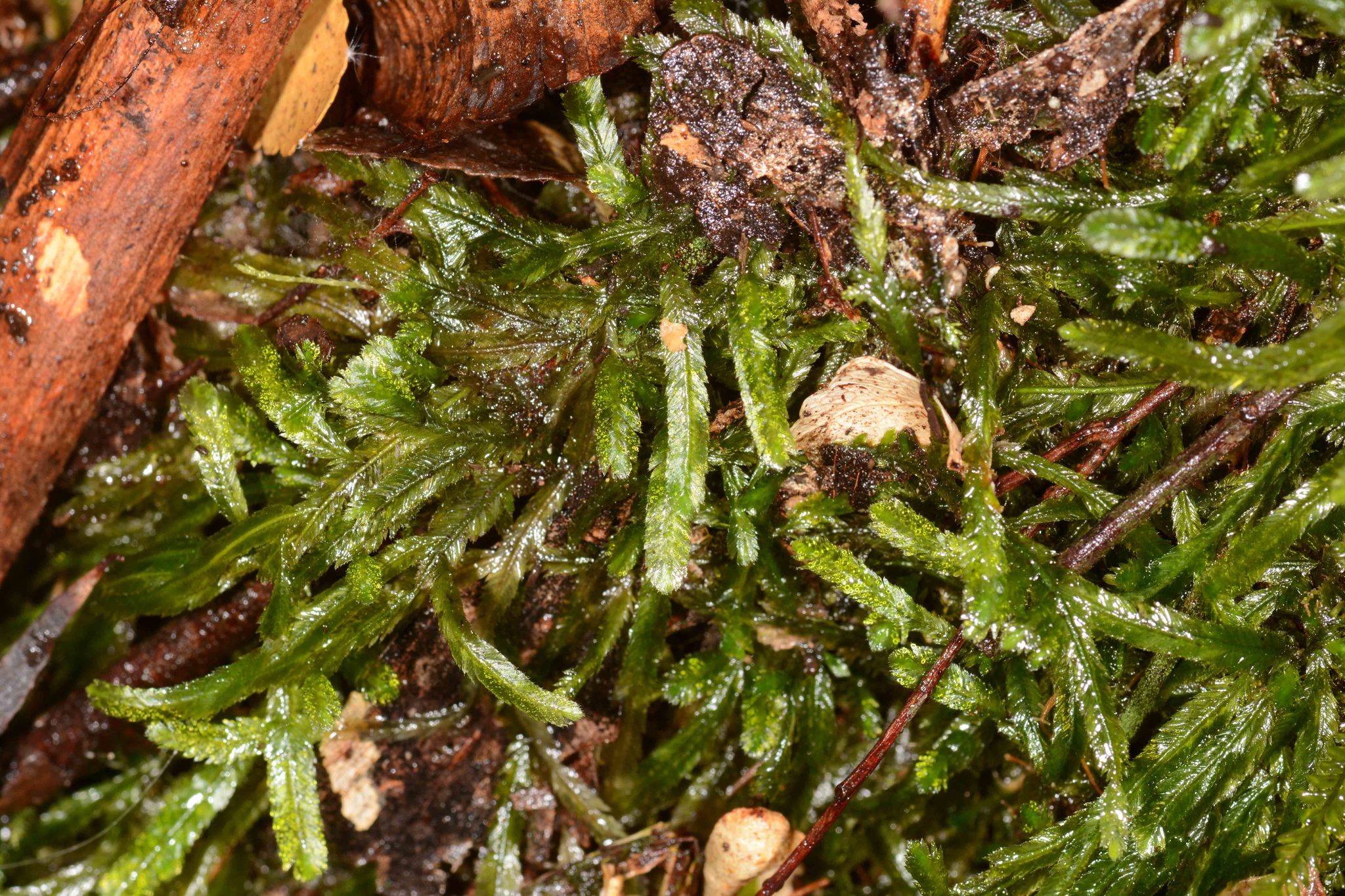

image from: https://www.gbif.org/es/species/2673552
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Dicranales |
| Family | Bruchiaceae |
| Genus | Campylostelium |
| Species | bruchioides |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spirally arranged, lanceolate, keeled |
| Capsule Shape | Curved or campylotropous |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded areas, exposed rock surfaces, disturbed sites |
| Distribution | Europe, Asia, North America, South America |