Basidiomata-and-microscopic-structures-of-Sanguinoderma-sinuosum-MEL-2366586-a.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Basidiomata-and-microscopic-structures-of-Sanguinoderma-sinuosum-MEL-2366586-a_fig19_341157329
Exploring the Fascinating World of Holomitrium sinuosum B.H.Allen Moss
Holomitrium sinuosum B.H.Allen is a unique and intriguing species of moss belonging to the Dicranaceae family. Commonly known simply as Holomitrium, this moss has captured the attention of bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike due to its distinct morphology and ecological adaptations. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of Holomitrium sinuosum and explore what makes this moss so special.
Background on Holomitrium Moss
Holomitrium sinuosum is a species of moss classified under the Bryophyta division and Bryopsida class. It was first described by the botanist B.H. Allen and given the specific epithet “sinuosum” which refers to its sinuous or wavy leaf margins. As a member of the Dicranaceae family, Holomitrium shares characteristics with other mosses in this group, such as having single costa (midrib) in the leaves.
Morphology and Identification
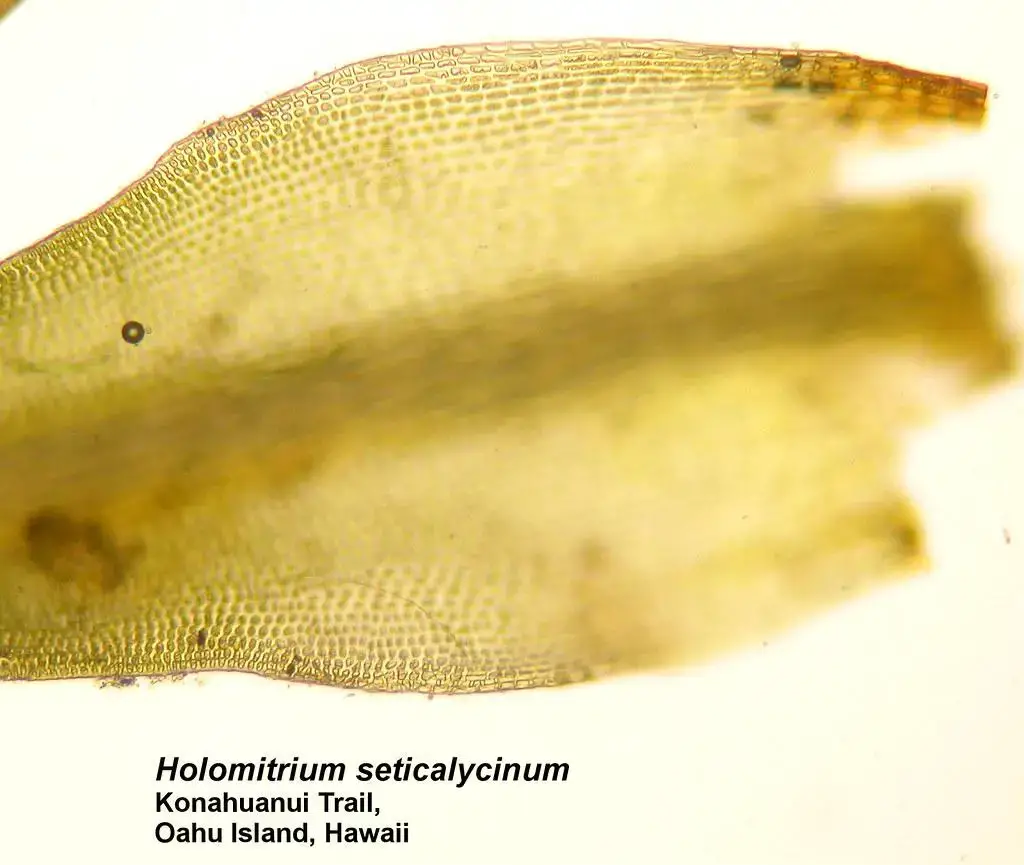
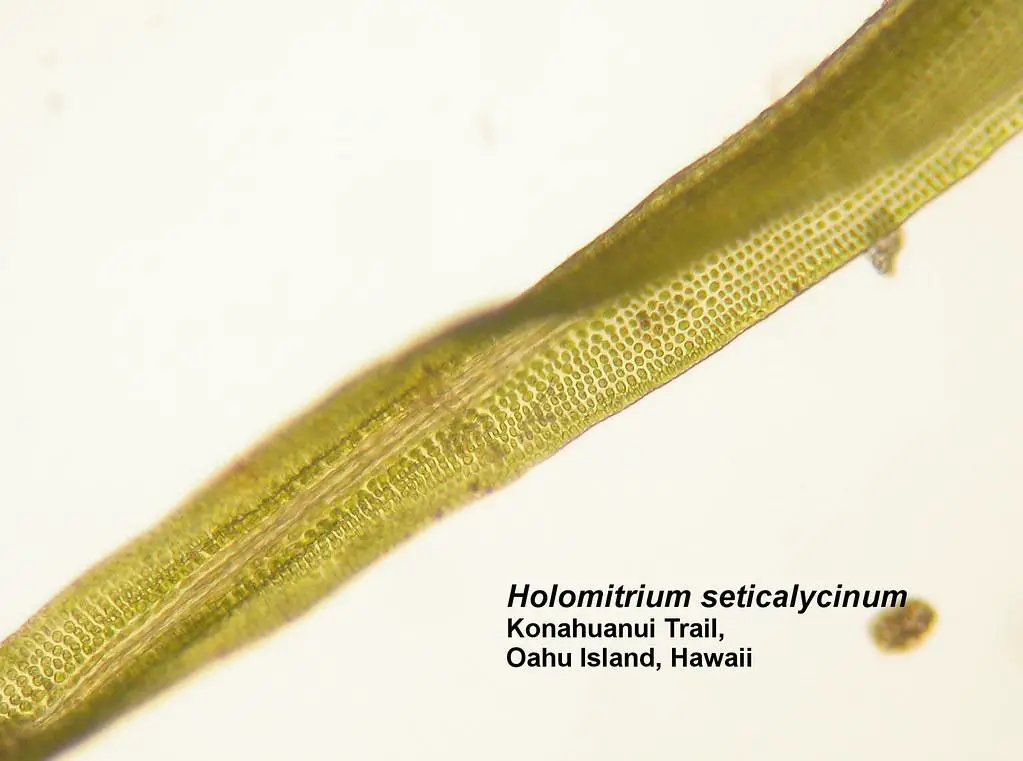
One of the most striking features of Holomitrium sinuosum is its distinctive leaf morphology. The leaves are typically lanceolate (lance-shaped) with wavy or sinuous margins. They are arranged in a spiral pattern around the stem, giving the moss a unique appearance. The leaves also have a single costa (midrib) that extends to the leaf tip.
Holomitrium sinuosum forms dense tufts or cushions, with individual stems reaching heights of 2-5 cm. The stems are erect and often branched, adding to the moss’s bushy appearance. Capsules (spore-bearing structures) are cylindrical and borne on
a-f-Scanning-electron-micrographs-of-Blepharisma-sinuosum-a-Ventral-view-showing-oral.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-f-Scanning-electron-micrographs-of-Blepharisma-sinuosum-a-Ventral-view-showing-oral_fig2_236928833
long setae (stalks).
Global Distribution and Habitat
Holomitrium sinuosum has a wide global distribution, being found in various regions across the world. It is known to occur in Central and South America, Africa, Asia, and Oceania. This moss typically grows on tree trunks, branches, and logs in humid forests and woodland habitats.
The ability of Holomitrium sinuosum to thrive in different geographic locations and habitats showcases its adaptability and resilience. It can tolerate a range of environmental conditions, from lowland tropical forests to

21397851670_d2a277b25e_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/48126735@N03/21397851670/
montane cloud forests.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like many other mosses, Holomitrium sinuosum plays important ecological roles in its habitats. It contributes to nutrient cycling, water retention, and providing micro-habitats for various invertebrates.
One notable adaptation of Holomitrium sinuosum is its ability to capture and retain water. The wavy leaf margins and dense growth form help to trap water droplets and slow down water loss, enabling the moss to maintain hydration in its often humid habitats. This adaptation is crucial for the moss’s survival and allows it to photosynthesize efficiently.

21585941045_43993acb26_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/48126735@N03/21585941045/

21559687656_13c22eaf68_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/48126735@N03/21559687656/
Image2WNMlarge.jpg from: https://www.nzflora.info/factsheet/Taxon/Holomitrium.html
Holomitrium-arboretum-Mitt-A-Dry-habit-B-Wet-habit-C-Stem-in-cross-section-D.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Holomitrium-arboretum-Mitt-A-Dry-habit-B-Wet-habit-C-Stem-in-cross-section-D_fig1_269332851
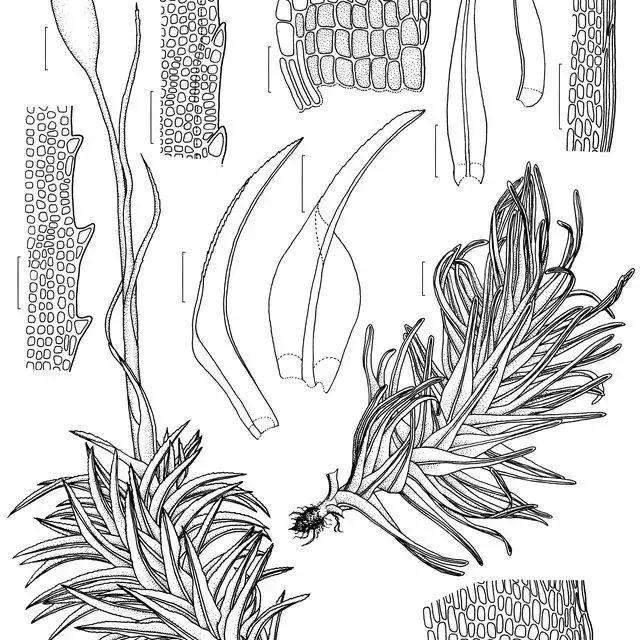
Figura-1-a-f-Holomitrium-arboreum-a-oprculo-b-margem-do-fildio-c-hbito-d_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-1-a-f-Holomitrium-arboreum-a-oprculo-b-margem-do-fildio-c-hbito-d_fig1_327378066
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Leaf shape | Lanceolate with wavy margins |
| Leaf arrangement | Spiral |
| Costa (midrib) | Single, extending to leaf tip |
| Growth form | Dense tufts or cushions |
| Stem height | 2-5 cm |
| Stem branching | Often branched |
| Capsule shape | Cylindrical |
| Seta (stalk) | Long |
Conclusion
Holomitrium sinuosum B.H.Allen is a remarkable moss species that exemplifies the diversity and adaptability of bryophytes. Its distinct morphology, global distribution, and ecological roles make it a fascinating subject of study for bryologists and nature lovers.

a-f-Scanning-electron-micrographs-of-Blepharisma-sinuosum-a-Ventral-view-showing-oral_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/a-g-Photomicrographs-of-Blepharisma-sinuosum-from-live-cells-observed-on-differential_fig1_236928833
As we continue to explore the world of mosses, Holomitrium sinuosum reminds us of the hidden wonders that can be found in even the smallest and most unassuming of organisms. So the next time you come across a patch of moss, take a closer look – you might just be gazing upon the wavy leaves of Holomitrium sinuosum!

sporocarps-fuzzy-clumps-of-rounded-objects-with-stalk.jpg from: https://invam.ku.edu/sinuosum