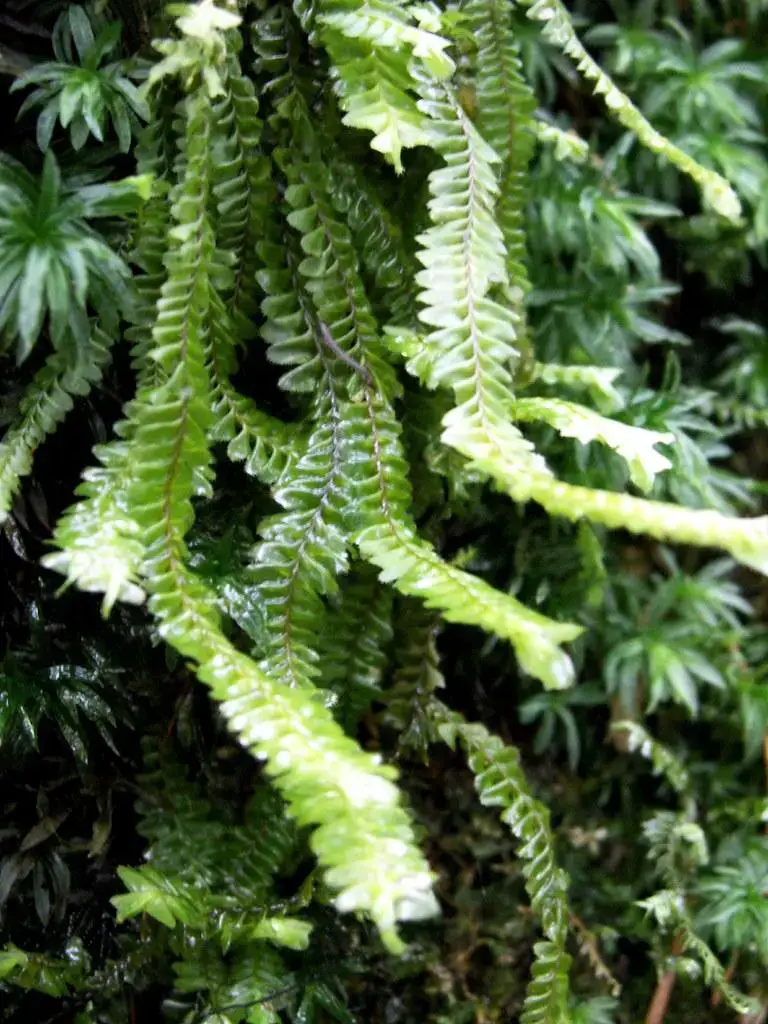

4141241857_842346e043_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/costarica1/4141241857/
Exploring the Fascinating World of Plagiochila radiculosa Mitt. Moss

594a0d5a97c1140d5e15b0b1a9d88172.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/plagiochila-sp-peru–479140847835495633/
Introduction
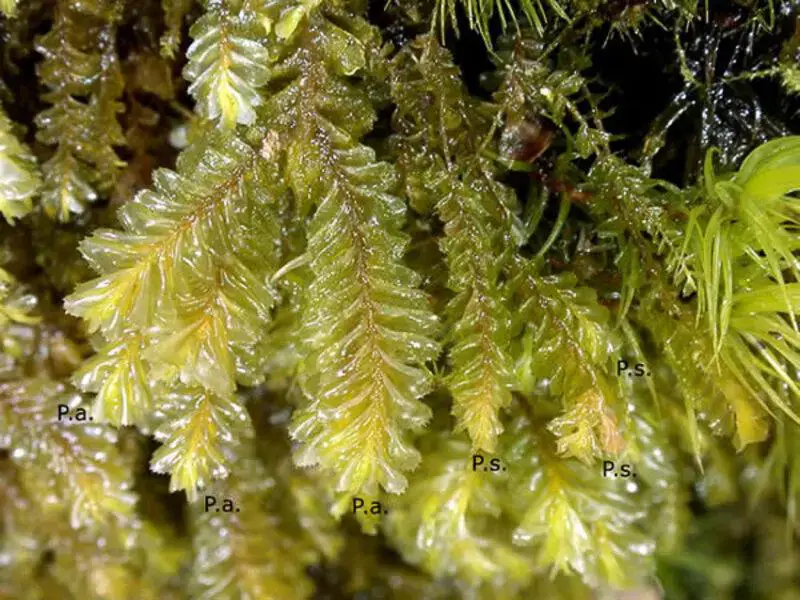

02-10-Plagio_atl_spin-e1645376999999-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/plagiochila-heterophylla/
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play a vital role in many ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Plagiochila radiculosa Mitt., a moss in the Plagiochilaceae family. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the details of this fascinating plant, from its morphology to its ecological roles. Get ready to discover the hidden wonders of Plagiochila!
Background
Plagiochila radiculosa Mitt. is a species of leafy liverwort, which are non-vascular plants in the division Marchantiophyta. Liverworts are similar to mosses but have a unique leaf arrangement. P. radiculosa belongs to the order Jungermanniopsida, which contains over 85% of liverwort species.

plasul_pgd9886web3.jpg from: https://www.southernappalachianbryophytes.org/plagiochilaechinata.html
Morphology and Identification
P. radiculosa has a distinct appearance that sets it apart from other mosses and liverworts. Its leaves are arranged in two rows and are typically oval-shaped with toothed margins. The underside of the stem is covered in rhizoids, root-like structures that help the plant absorb water and nutrients.
The leaves of P. radiculosa also contain oil bodies, which are membrane-bound organelles filled with aromatic oils. These give the plant a unique smell when crushed. Sporophytes (spore-producing structures) are rarely produced.
Global Distribution and Habitat
P. radiculosa has a wide global distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. It typically grows in moist, shaded habitats such as:
- Forests
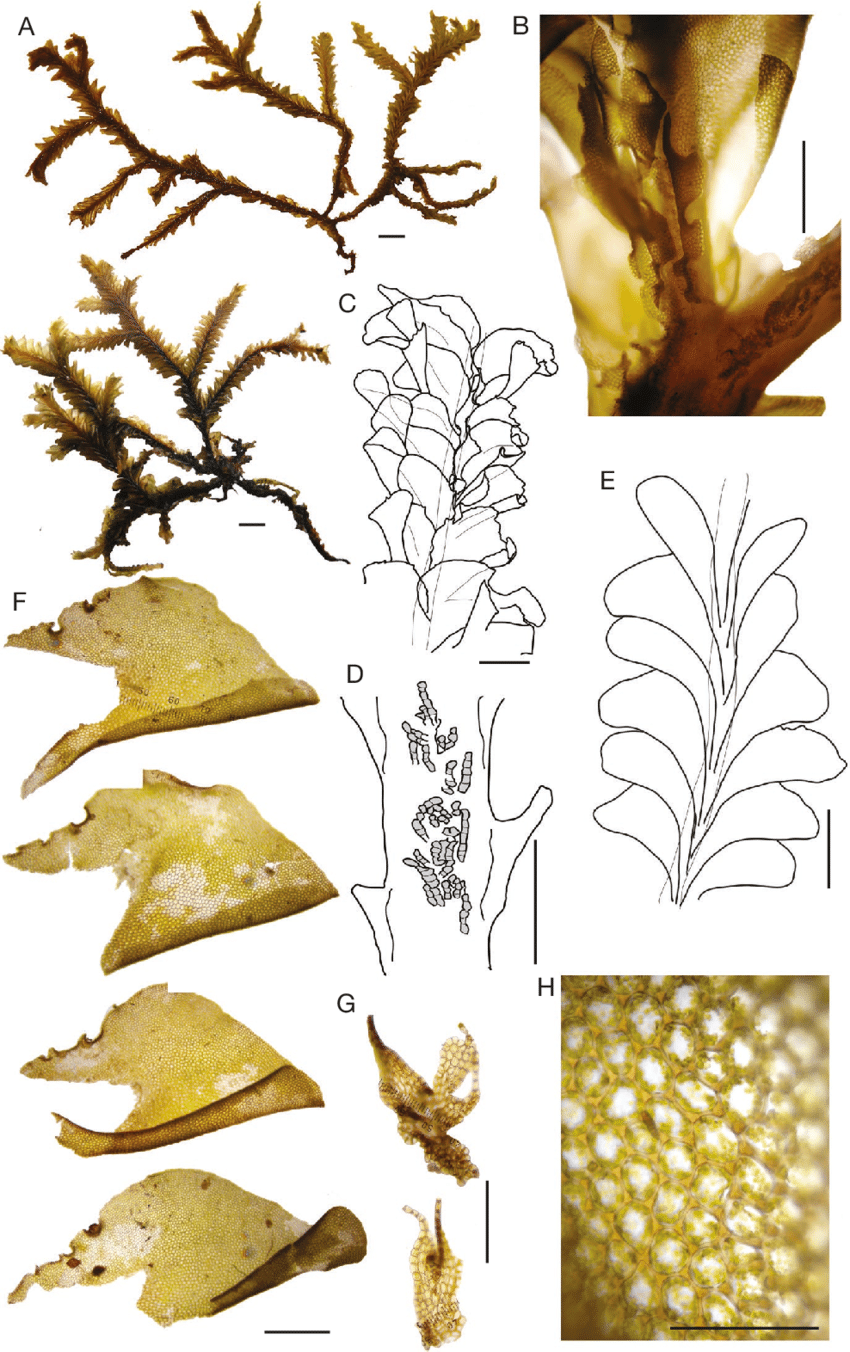
Plagiochila-squamulosa-Mitt-A-habit-B-C-shoot-in-ventral-view-D-shoot-in-ventral.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plagiochila-squamulosa-Mitt-A-habit-B-C-shoot-in-ventral-view-D-shoot-in-ventral_fig15_360631517
- Streambanks
- Rock outcrops
- Rotting logs
This species is especially abundant in tropical and subtropical regions. In some areas, it is considered an indicator of good air quality since it is sensitive to pollution.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Like other mosses and liverworts,

Plag_radicu.jpg from: https://www.utas.edu.au/dicotkey/dicotkey/Lworts/PLAGIOCHILACEAE/sPlagio_radicu.htm
P. radiculosa plays several important ecological roles:

16298.jpg from: https://aquastatus.ru/viewtopic.php?t=9080
Erosion control – Its mat-like growth helps stabilize soil and prevent erosion.
Water retention – The plant acts like a sponge, absorbing and slowly releasing moisture. This helps regulate humidity in its immediate environment.
Habitat for microorganisms – Many tiny invertebrates make their homes among the leaves and stems of P. radiculosa.
Nutrient cycling – As parts of the plant die and decompose, they release nutrients back into the soil.
P. radiculosa has several adaptations that allow it to thrive in its preferred habitats:

Plagiochila-carringtonii-2.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/plagiochila-carringtonii/

41fe9edb6b4feeecd3976279ac633711.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/plagiochila-asplenioides–346988346302434872/
| Adaptation | Function |
|---|---|
| Rhizoids | Absorb water and anchor plant |
| Leaf oil bodies | Deter herbivores, prevent desiccation |
| Spore dispersal | Reproduce and colonize new areas |
Conclusion
Plagiochila radiculosa Mitt. may be small, but it is a remarkably resilient and ecologically important plant. From tropical rainforests to temperate streambanks, this unique moss plays a vital role in its ecosystems.

2b876b43051231be7fb8bceead12d953.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/plagiochila-asplenioides–291045194657579944/
Next time you’re out in nature, take a closer look – you might just spot some Plagiochila hiding in plain sight! What other overlooked organisms in your area play surprisingly important roles?