Lepelbladveenmos-Sphagnum-platyphyllum-Braithw-Warnst-in-het-Drents-Friese-Wold.ppm from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Lepelbladveenmos-Sphagnum-platyphyllum-Braithw-Warnst-in-het-Drents-Friese-Wold_fig1_291676401

Sphagnum-platyphyllum-DC-scaled.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/sphagnum-platyphyllum/
Introduction
Welcome, fellow enthusiasts, to the captivating world of Sphagnum platyphyllum (Lindb. ex Braithw.) Sull. ex Warnst., a remarkable moss species that belongs to the Sphagnaceae family, commonly known as Sphagnum. This unassuming yet extraordinary plant has captured the hearts and minds of bryologists and nature lovers alike, offering a fascinating glimpse into the intricate tapestry of life that thrives in the most unexpected places.
Background
Before we delve into the intricacies of Sphagnum platyphyllum, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which this moss resides. The Bryophyta division, encompassing mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, represents one of the earliest lineages of land plants, dating back over 400 million years. These ancient organisms played a pivotal role in the colonization of terrestrial environments, paving the way for the evolution of more complex plant life.
Main Content
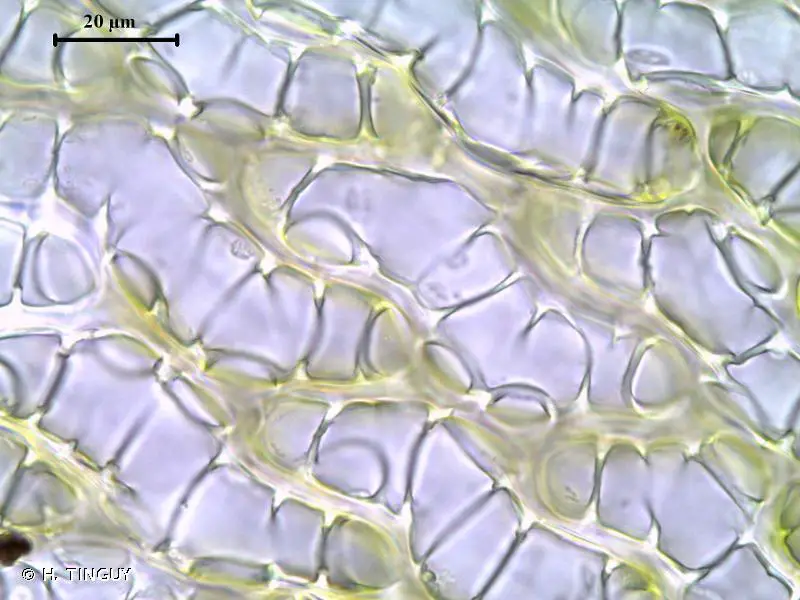
Morphology and Identification
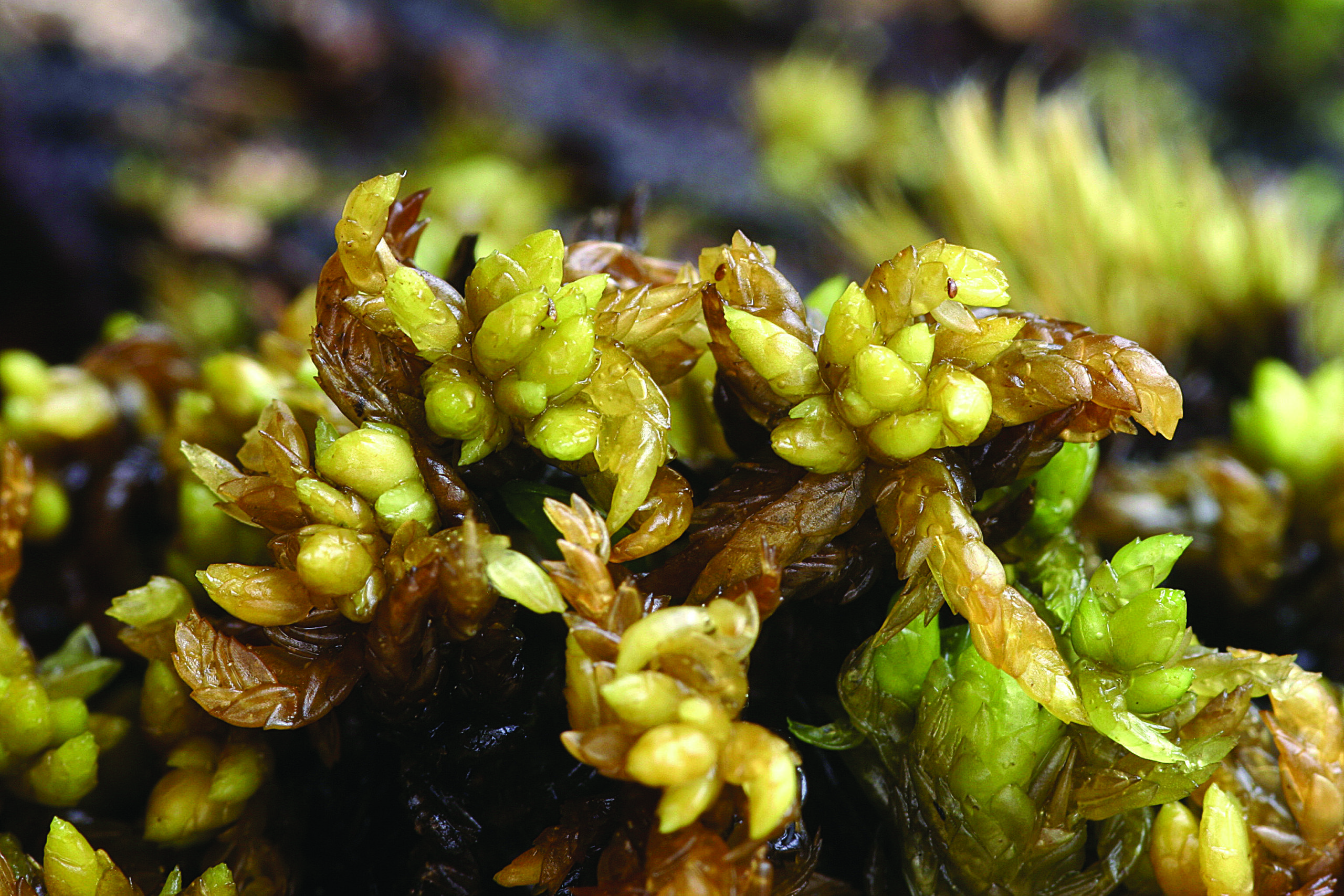
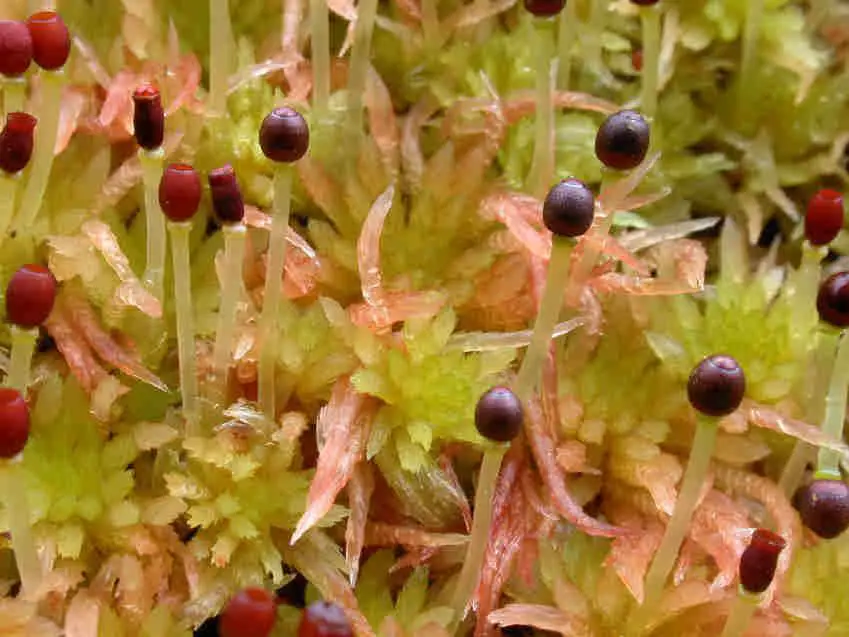
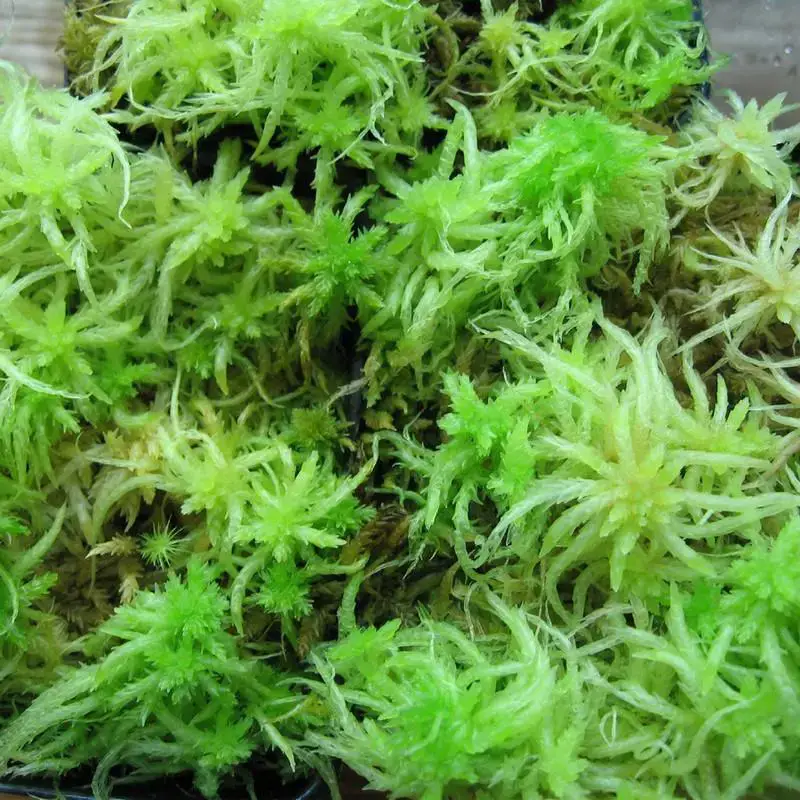
Sphagnum platyphyllum is a striking moss species, characterized by its dense, cushion-like growth habit and vibrant green to yellowish-green hues. Its stems are slender and delicate, adorned with closely overlapping leaves that form a compact, feathery appearance. One of the most distinctive features of this moss is its flattened, tongue-shaped branch leaves, which give it a unique and easily recognizable silhouette.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss species can be found across various regions of the world, thriving in cool, moist environments such as bogs, fens, and wetlands. It is particularly abundant in the northern hemisphere, where it plays a crucial role in the formation and maintenance of peatlands. These ecosystems are not only vital for preserving biodiversity but also serve as important carbon sinks, helping to mitigate the effects of climate change.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Sphagnum platyphyllum is a true marvel of adaptation, possessing a remarkable ability to absorb and retain vast quantities of water

Sphagnum-pulchrum-Lindberg-1880-25-Warnstorf-1900-42-Alaska-Photo-Blanka-Shaw_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Sphagnum-pulchrum-Lindberg-1880-25-Warnstorf-1900-42-Alaska-Photo-Blanka-Shaw_fig3_270711021
. This trait is facilitated by its unique cellular structure, which allows it to act like a sponge, soaking up moisture from its surroundings. This incredible water-holding capacity has earned Sphagnum mosses the nickname “nature’s water reservoirs.”
Moreover, Sphagnum platyphyllum plays a vital role in regulating the pH levels of its environment, creating acidic conditions that are essential for the survival of many specialized plant and animal species. This moss also contributes to the formation of

46846712962_5f8328a634_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/155873633@N07/albums/72157702840888292
peat, a valuable natural resource with numerous applications, ranging from horticulture to energy production.
Case Studies/Examples
One fascinating example of the ecological significance of Sphagnum platyphyllum

509.50293129.jpg from: https://eol.org/pages/928409/media?page=2
can be found in the Mer Bleue Bog near Ottawa, Canada. This remarkable peatland is home to a diverse array of plant and animal species, including several rare and endangered species. Sphagnum platyphyllum is a key component of this ecosystem, forming dense carpets that provide a unique habitat for various organisms, including carnivorous plants like the sundew and pitcher plant.
Technical Table

Sphagnum_subnitens_003.JPG from: https://cisfbr.org.uk/Bryo/Cornish_Bryophytes_Sphagnum_subnitens_var_subnitens.html

ssp__22320.1511407161.jpg from: https://www.nativewildflowers.net/sphagnum-moss/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Sphagnum platyphyllum (Lindb. ex Braithw.) Sull. ex Warnst.
 206153.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6780 |
| Family | Sphagnaceae |
| Division | Bryophyta
rs=w:1200,h:1200 from: https://fromtheforestidaho.com/shop/ols/products/sphagnum-moss-s-mendocinum-s-platyphyllum-monograph |
| Class | Sphagnopsida |
| Growth Habit | Dense, cushion-like |
| Leaf Shape | Flattened, tongue-shaped |
| Color | Green to yellowish-green |
| Habitat | Bogs, fens, wetlands |
| Distribution | Northern hemisphere |
| Ecological Role | Water retention, pH regulation, peat formation |
Conclusion
As we bid farewell to the enchanting world of Sphagnum platyphyllum, we are left with a profound appreciation for the intricate tapestry of life that surrounds us. This unassuming moss species serves as a powerful reminder of the interconnectedness of all living beings and the vital roles they play in maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystems.
Sphagnum-lindbergii-Cairn-of-Claise_v1.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/sphagnum-lindbergii/
Ponder this: What other hidden wonders lie waiting to be discovered in the vast expanse of nature, and how can we, as enthusiasts and stewards of the natural world, contribute to their preservation for generations to come?