
153396260257136668.jpeg from: https://www.picturethisai.com/wiki/Anomodon_rostratus.html
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of
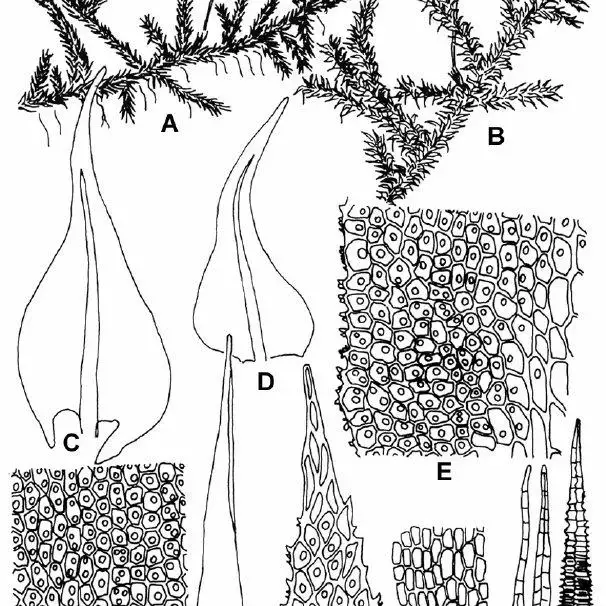
Anomodon-rostratus-Hedw-Schimp-A-dry-plant-6-B-wet-plant-6-C-D-leaves_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Anomodon-rostratus-Hedw-Schimp-A-dry-plant-6-B-wet-plant-6-C-D-leaves_fig1_238738619
bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the Anomodon rostratus (Hedw.) Schimp.
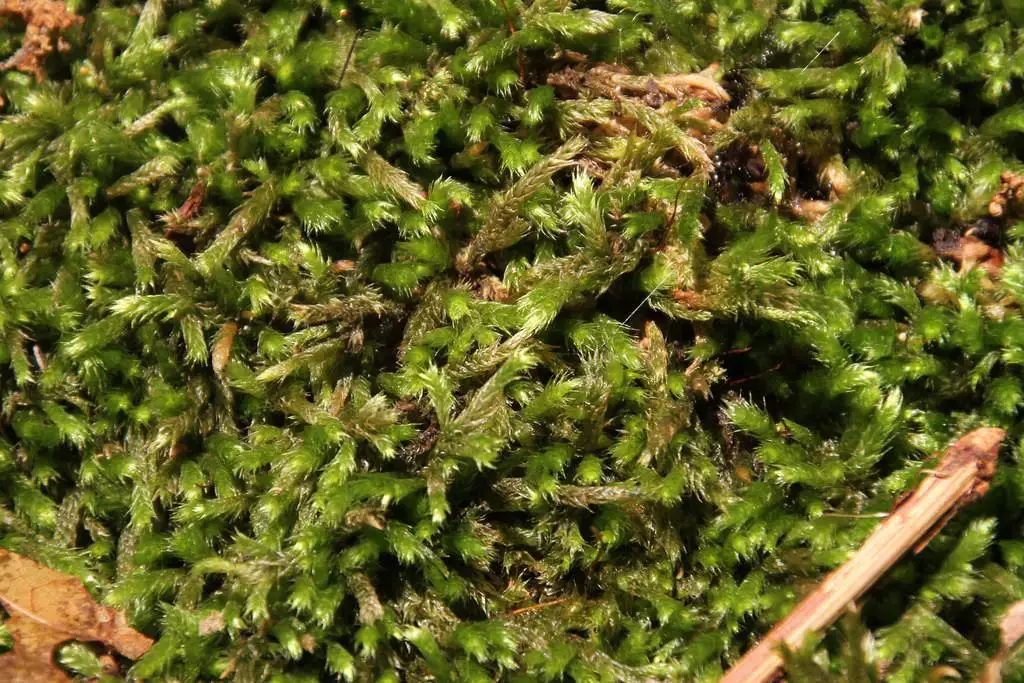

jim__stasz_16148801087_2c0a1b1991_b.jpg from: https://www.marylandbiodiversity.com/view/10703
, commonly known as Anomodon. This unassuming yet fascinating member of the Brachytheciaceae family has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide, offering a delightful glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s smallest wonders.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Anomodon rostratus, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These diminutive yet resilient plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, have been around for millions of years, predating even the earliest vascular plants. Despite their small stature, bryophytes play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and moisture retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
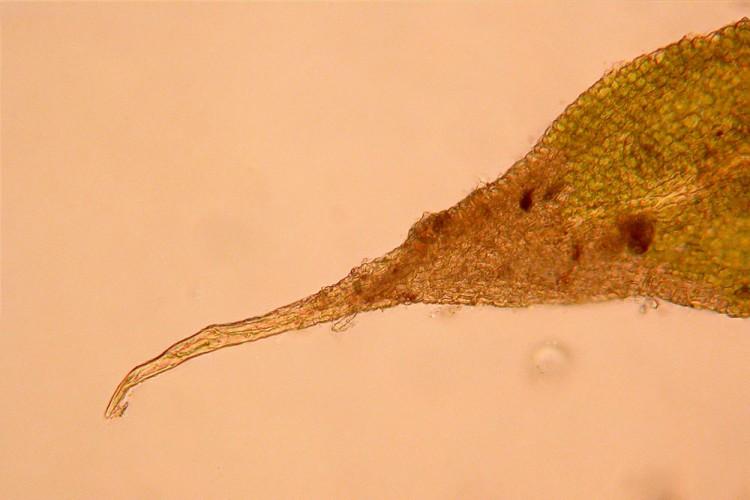
Anomodon rostratus is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems grow horizontally along the substrate. Its vibrant green hue and delicate, feathery appearance make it a true delight to behold. One of its most distinctive features is the rostrate (beaked) appearance of the leaf tips, which gives the moss its specific epithet, “rostratus.”
Global Distribution and Habitat

Anomodon-rostratus-12-750×500.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-Anomodon-rostratus/
This moss species is widely distributed across the Northern Hemisphere, thriving in temperate regions of Europe, Asia, and North America. It favors moist, shaded environments, often found growing on the bark of trees, rotting logs, and rocky outcrops in forests and woodlands.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Anomodon rostratus plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It serves as a microhabitat for various invertebrates, providing shelter and sustenance for these tiny creatures. Additionally, its ability to absorb and retain moisture contributes to the overall health and resilience of the forest floor, creating a nurturing environment for other plant species to thrive.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Anomodon rostratus is its tolerance to desiccation. During periods of drought, the moss can enter a state of dormancy, reviving itself once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to survive in challenging environments and highlights the incredible adaptability of bryophytes.
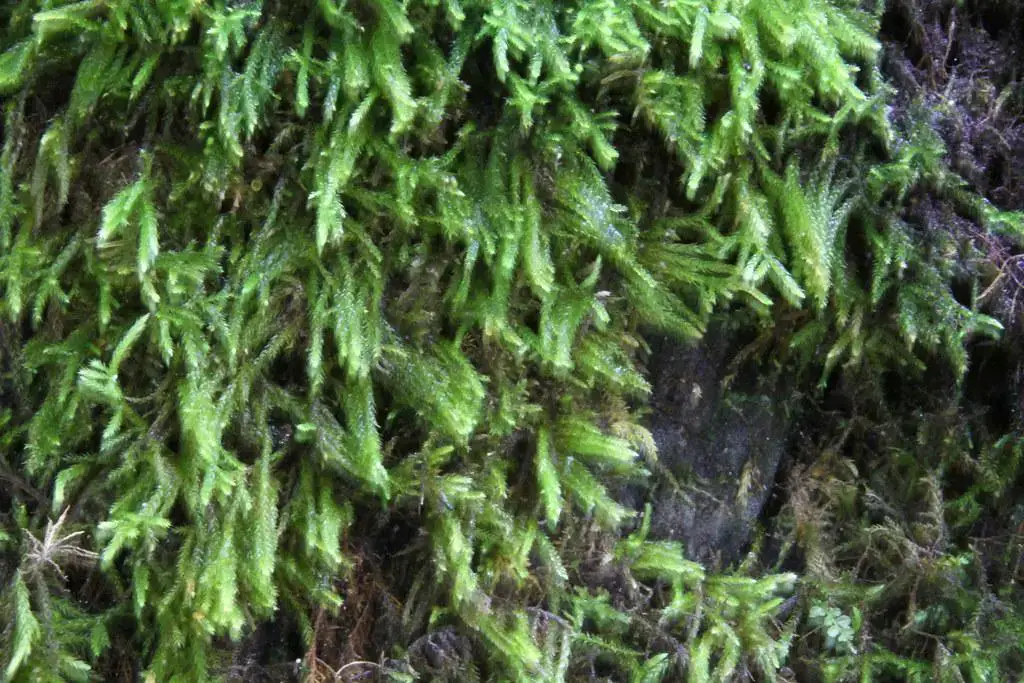

16285682462_0d580cc00e_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/26803925@N05/16285682462/
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Great Smoky Mountains National Park, researchers discovered that Anomodon rostratus played a crucial role in maintaining the biodiversity of the forest floor. The moss provided a suitable microhabitat for various invertebrates, including springtails and mites, which in turn contributed to nutrient cycling and soil formation.
Technical Table

il_fullxfull.4819451174_3rsm.jpg from: https://greenmountainmoss.co/listing/1143726334/yellow-yarn-moss-anomodon-rostratus

Anomodon-minor-sporophytes-750×499.jpg from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-anomodon-minor/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Anomodon rostratus (Hedw.) Schimp. |
| Family | Brachytheciaceae |
| Common Name | Anomodon |
Growth Form
 18869196136_50d33bef97_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/26803925@N05/18869196136/ |
Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Arrangement | Spirally arranged |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, with rostrate (beaked) tips |
| Habitat | Bark of trees, rotting logs, rocky outcrops |
| Distribution | Northern Hemisphere (Europe, Asia, North America) |
Conclusion
Anomodon rostratus, a true gem among mosses, reminds us of the intricate beauty and resilience that can be found in the smallest corners of our natural world. Its unique morphology, ecological significance, and remarkable adaptations make it a fascinating subject of study for bryologists and nature enthusiasts alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the plant kingdom, let us remember the invaluable contributions of these unassuming yet vital organisms, and strive to protect and preserve their delicate habitats for generations to come.