
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Yakushimabryum-tonkinense-Broth-Paris-HAkiyama-A-Portion-of-dry-sterile-plant-B_fig1_359132223
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, a tiny yet remarkable moss species stands out: Bryhnia tokubuchii (Broth.) Paris. This unassuming plant, belonging to the Brachytheciaceae family and commonly known as Bryhnia, has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Bryhnia tokubuchii, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play crucial roles in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in diverse environments.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Pseudoparaphysanthus-moutieri-Broth-Paris-SOlsson-Enroth-Huttunen-DQuandt-A_fig8_356611709
Bryhnia tokubuchii is a pleurocarpous moss, meaning its stems and branches grow horizontally along the substrate. Its slender, creeping stems are adorned with delicate, lance-shaped leaves that form a feathery appearance. The leaves are typically 1-2 mm long and have a distinctive midrib that extends nearly to the leaf tip. When viewed under a microscope, the leaf cells reveal a intricate pattern of hexagonal shapes, adding to the moss’s allure.
Global Distribution and Habitat
image from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Fossil-mosses-and-a-beetle-A-Stem-and-leaves-of-the-semiaquatic-moss-Drepanocladus_fig3_23148177
This diminutive moss species has a widespread distribution, found across various regions of the Northern Hemisphere, including North America, Europe, and Asia. Bryhnia tokubuchii thrives in moist, shaded environments, often growing on decaying logs, tree bases, and soil in forests. It prefers acidic substrates and is commonly found in coniferous and mixed forests, where it forms lush, velvety mats.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Bryhnia tokubuchii plays a vital role in forest ecosystems. Its dense mats help retain moisture, creating a microhabitat for other organisms, such as invertebrates and fungi. Additionally, the moss contributes to soil formation and nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients back into the environment.
Bryhnia tokubuchii has developed remarkable adaptations to survive in its preferred habitats. Its ability to withstand desiccation and rapidly rehydrate after periods of drought allows it to thrive in fluctuating moisture conditions. Furthermore, its compact growth form and efficient water transport system enable it to maximize water uptake and minimize water loss.

image from: https://inaturalist.ca/taxa/159496-Bryhnia-graminicolor
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, researchers discovered that

image from: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/30257876
Bryhnia tokubuchii played a crucial role in facilitating the establishment of tree seedlings. The moss’s dense mats provided a suitable microhabitat for germination and early growth, highlighting its importance in forest regeneration processes.
Technical Table

image from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-bryhnia-graminicolor/
image from: https://sciencepress.mnhn.fr/en/periodiques/bryologie/34/1/hygrohypnum-styriacum-limpr-broth-pyrenees-new-record-moss-flora-france
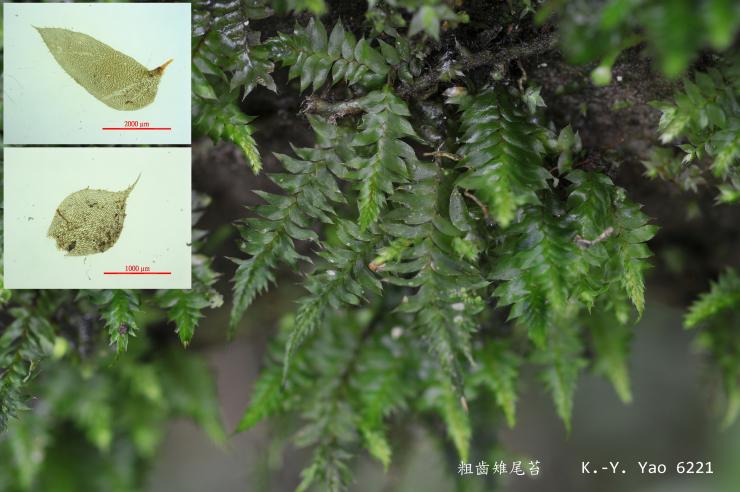

image from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/955167f1c6bb258516cb5ad540356d93

image from: https://ohiomosslichen.org/moss-bryhnia-graminicolor/

image from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/159498-Bryhnia-novae-angliae
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Hypnales |
| Family | Brachytheciaceae |
| Genus | Bryhnia |
| Species | tokubuchii |
| Growth Form | Pleurocarpous moss |
| Leaf Shape | Lance-shaped |
| Leaf Size | 1-2 mm long |
| Habitat | Moist, shaded forests |
| Substrate | Decaying logs, tree bases, soil |