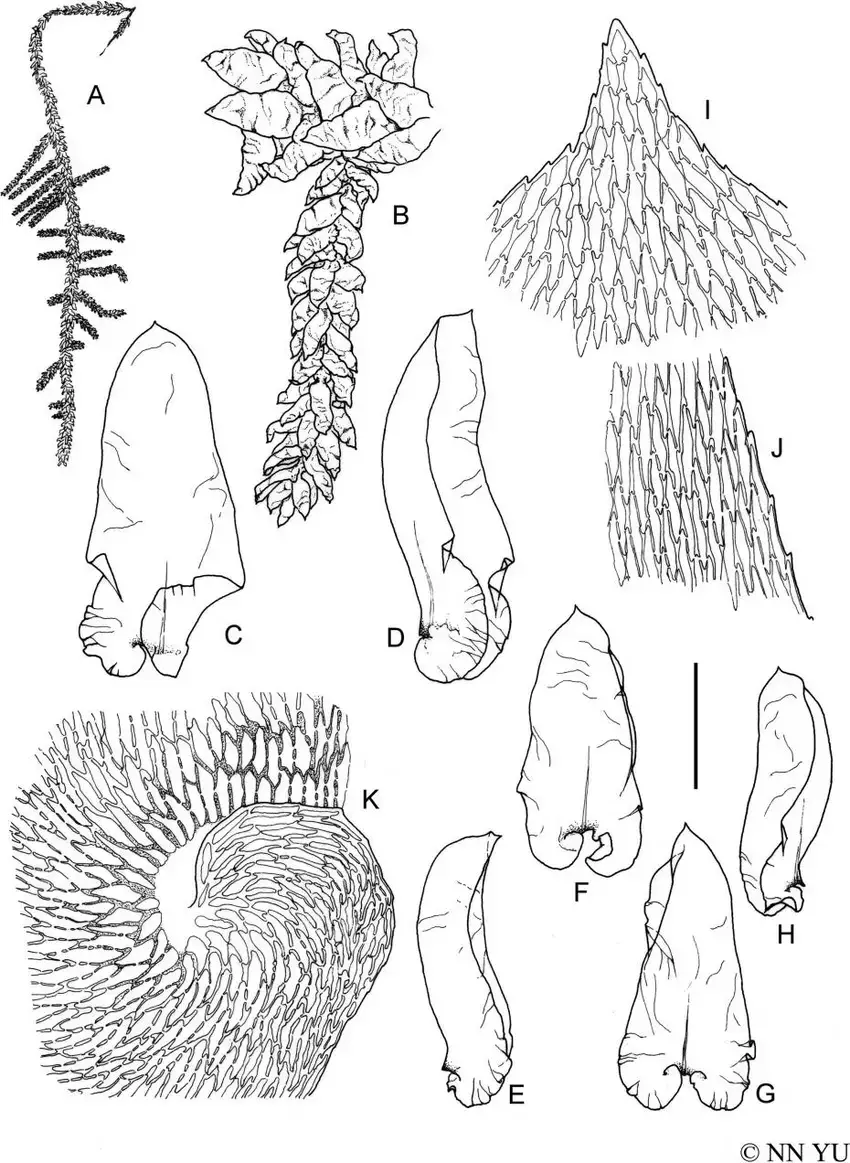
Calyptothecium-recurvulum-Broth-Broth-A-Habit-B-Branch-C-D-Stem-leaves-E-H.png from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Calyptothecium-recurvulum-Broth-Broth-A-Habit-B-Branch-C-D-Stem-leaves-E-H_fig2_293646589
Exploring the Fascinating World of Calyptothecium Wightii Moss

wightii-Zokshyam-Thangsum-4387m-HarryJans.jpg from: https://www.rhododendron.dk/wightii-n.html
Introduction
Mosses are often overlooked, but they play important roles in ecosystems around the world. One particularly interesting species is Calyptothecium wightii (Mitt.) M.Fleisch., also known simply as Calyptothecium. This moss belongs to the Pterobryaceae family. Let’s dive in and learn more about this fascinating little plant!
Background on Mosses
Mosses are small, non-vascular plants in the division Bryophyta. Unlike other plants, they lack true roots, stems, and leaves. Instead, they have leaf-like structures called phyllids. Mosses reproduce via spores rather than seeds and are found in a wide range of habitats worldwide.
Figura-5-Calyptothecium-duplicatulum-a-Aspecto-de-la-planta-b-propagulos-c-d_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Figura-5-Calyptothecium-duplicatulum-a-Aspecto-de-la-planta-b-propagulos-c-d_fig3_259175425
Morphology and Identification
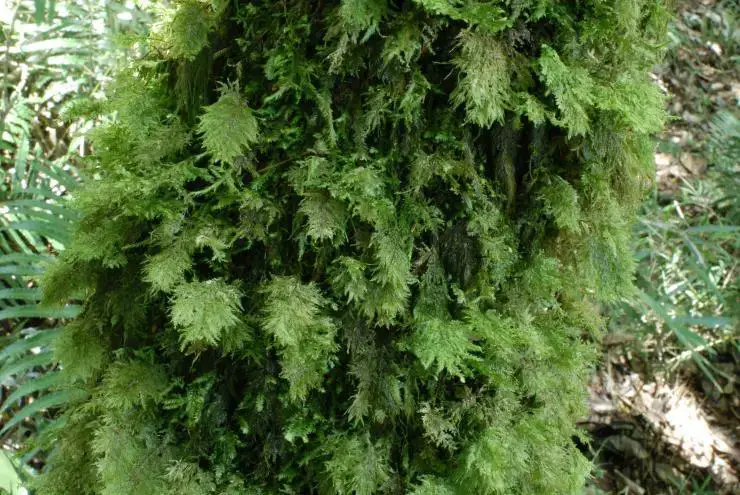
C. wightii forms loose mats. The main stems are creeping with irregular branching. Branches are 1-2 cm long. Leaves are ovate-lanceolate, 1.5-2 mm long, with a short double costa. The leaf margins are entire below and serrulate at the apex.

P1100991_detail.jpg from: https://www.digital-nature.de/baeume/kurios/wurzeln/detail/detail_4.html
The key identification features are:
- Loose mats
- Creeping main stems
- Ovate-lanceolate leaves
- Short double costa
- Serrulate leaf margins at apex
Global Distribution and Habitat
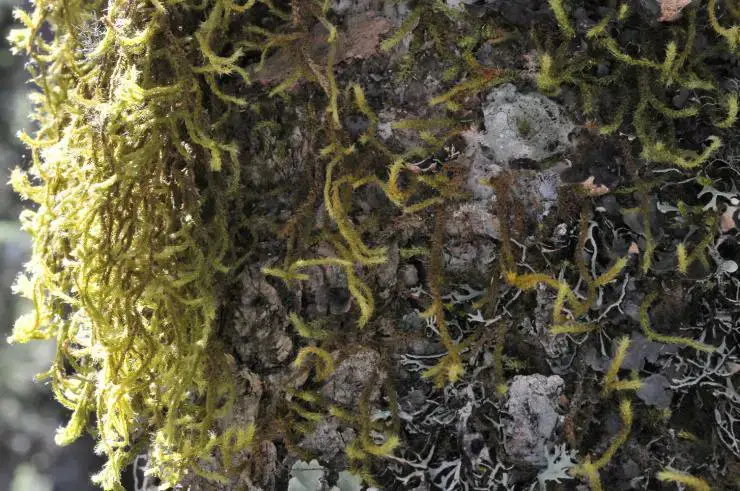
This species is found in tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, Africa, and the Americas. It typically grows on tree trunks and branches in moist forests at low to moderate elevations. The ability to grow as an epiphyte allows it to thrive in various forest habitats.

00ae422930c03355c1279e7d3670b688.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/5c288503a07b98ea98b8f1ea8f885b55
Ecological Roles and Adaptations

61e51ec3c9b940a792bc3f9e0a907a29.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/muse/digi_object/61c0cc1dddb489ae4b135051dc513fdb
Like other mosses, C. wightii plays several important ecological roles:

0f4836145801cfa62535fa6aa82d7b7a.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/35051/articles
- Helps retain moisture in its environment

062fe76a3d99abeabe1f00689b0f6142.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/941620afcf4d576ff03d5d1e1c09f139
- Provides shelter and habitat for small invertebrates
- Contributes to nutrient cycling as it decomposes
- Serves as a pioneer species in ecological succession
It has adapted to epiphytic growth, allowing it to grow on trees where competition from vascular plants is lower. The creeping main stems help it spread across the substrate.
Conclusion
Calyptothecium wightii is a prime example of how even tiny, inconspicuous organisms like mosses can be captivating once you start learning about them. Its unique adaptations and important ecological roles make it a valuable part of the ecosystems where it’s found.

164374263ec8f3936dcedc50f7c0f091.jpg from: https://taieol.tw/pages/8962
Next time you’re in a tropical forest, take a closer look at the mosses – you just might spot some Calyptothecium mats on the trees! What other interesting bryophytes can you find?

5622e6df2ce9f1051a576c6c516b9db2.jpg from: https://openmuseum.tw/muse/digi_object/d3c69fc27fdd03291ec8fc9aa7341fc5