F6.png from: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/84609
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes

pixie-cup-lichen-cladonia-asahinae-in-amongst-moss-community-essex-H2MEN2.jpg from: https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/asahinae-pixie-cup-lichen.html
, one particular moss species stands out for its unique charm and ecological significance – the Chorisodontium fulvastrum (Besch.) Broth. moss, commonly known as Chorisodontium. This unassuming yet fascinating member of the Dicranaceae family has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide, offering a glimpse into the intricate beauty and resilience of these ancient plant forms.
Background
Before delving into the specifics of Chorisodontium fulvastrum

Mosses_rs.jpg from: https://today.ttu.edu/posts/2019/01/Stories/antarctica-van_gestel
, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, have been around for over 400 million years, predating even the earliest vascular plants. They play a crucial role in various ecosystems, acting as pioneers in colonizing new environments and contributing to soil formation and water retention.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
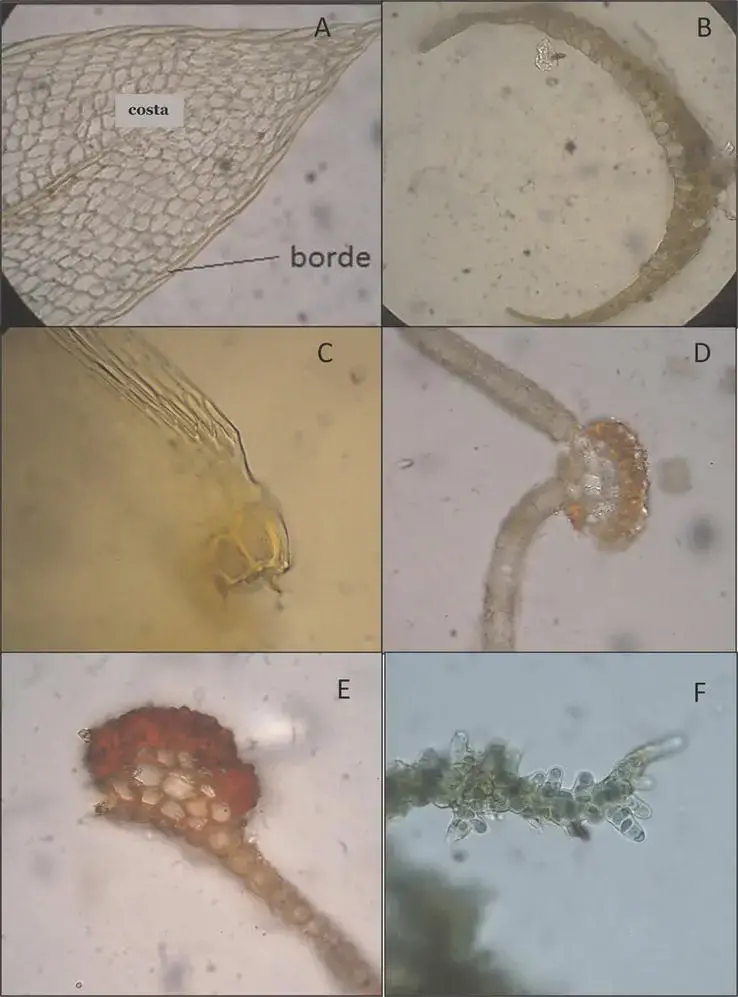
Chorisodontium fulvastrum is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, golden-green tufts or cushions. Its leaves are lanceolate in shape, with a distinctive costa (midrib) that extends beyond the leaf apex, forming a hair-like awn. This characteristic feature, along with the falcate (sickle-shaped) leaves when dry, makes Chorisodontium easily recognizable to the trained eye.
Global Distribution and Habitat
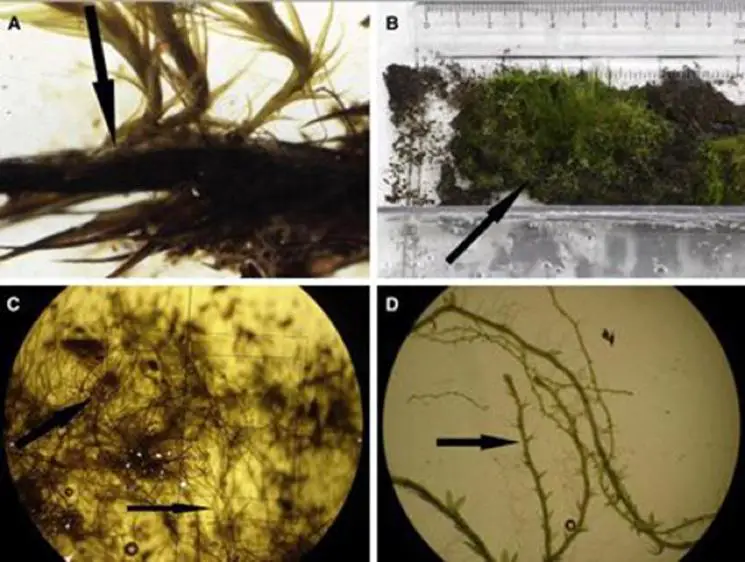
This moss species has a widespread distribution, occurring in various regions across the globe, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and North America. It thrives in a range of habitats, from acidic soils in forests and heathlands to rock crevices and even disturbed areas like roadside banks and quarries. Its ability to colonize diverse environments is a testament to its remarkable adaptability.

Syrrhopodon-japonicus-Besch-Broth-A-Plants-B-Cross-section-of-leaf-B-1-median_Q320.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Syrrhopodon-japonicus-Besch-Broth-A-Plants-B-Cross-section-of-leaf-B-1-median_fig1_283888063
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Chorisodontium fulvastrum plays a vital role in its ecosystems. As a pioneer species, it helps stabilize and enrich soils, creating favorable conditions for other plants to establish themselves. Additionally, its dense cushions provide microhabitats for various invertebrates, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area.
One of the key adaptations that allow

048305086607b6c79356f84b0eb4ef49.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/25403185367658950/
Chorisodontium to thrive in harsh environments is its ability to desiccate and revive upon rehydration. This remarkable trait, known as poikilohydry, enables the moss to survive prolonged periods of drought, making it a true survivor in challenging conditions.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Scottish Highlands, researchers discovered a thriving population of

018-Choristodontium-prymes-1-768×576.jpg from: http://expedicia.org/roslinniy-svit-ta-grunti-rayonu-argen/
Chorisodontium fulvastrum on an abandoned quarry site. This finding highlights the moss’s ability to colonize disturbed areas and contribute to the restoration of degraded landscapes.
Technical Table
mhi-2.jpg from: https://www.sciencedebate2008.com/moss-times-of-king-arthur/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Dicranales |
| Family | Dicranaceae
 b23327.jpg from: https://www.srf.ch/wissen/natur-tiere/natur-tiere-moos-spriesst-wieder-nach-1500-jahren-dauerfrost |
| Genus | Chorisodontium |
| Species | Chorisodontium fulvastrum (Besch.) Broth. |
| Common Name | Chorisodontium moss |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-forming |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate, falcate when dry |
| Distinctive Feature | Hair-like awn extending from leaf apex |
Conclusion
The Chorisodontium fulvastrum (Besch.) Broth.

Diversidad-de-hepaticas-en-las-turberas-de-Sphagnum-de-Aysen-A-Adelanthus_Q640.jpg from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Diversidad-de-musgos-en-las-turberas-de-Sphagnum-de-Aysen-A-Polytrichum-strictum-B_fig3_353450263
moss, or Chorisodontium, is a true marvel of nature, showcasing the incredible diversity and resilience of bryophytes. From its golden-green tufts to its ability to thrive in challenging environments, this moss species serves as a reminder of the intricate web of life that surrounds us. As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, perhaps we can find inspiration in the tenacity and adaptability of these unassuming yet remarkable plants. Who knows what other secrets and lessons await us in the realm of bryophytes?

3625506f3a30936eacf15c0ffad212dd–garden.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/cheriechisgarden-mossgardenbycheriechi-moss-sematophyllum-robustulumcardbroth–557390891371707469/