
21633043543_ff759c3c87_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/12639178@N07/21633043543/
Introduction
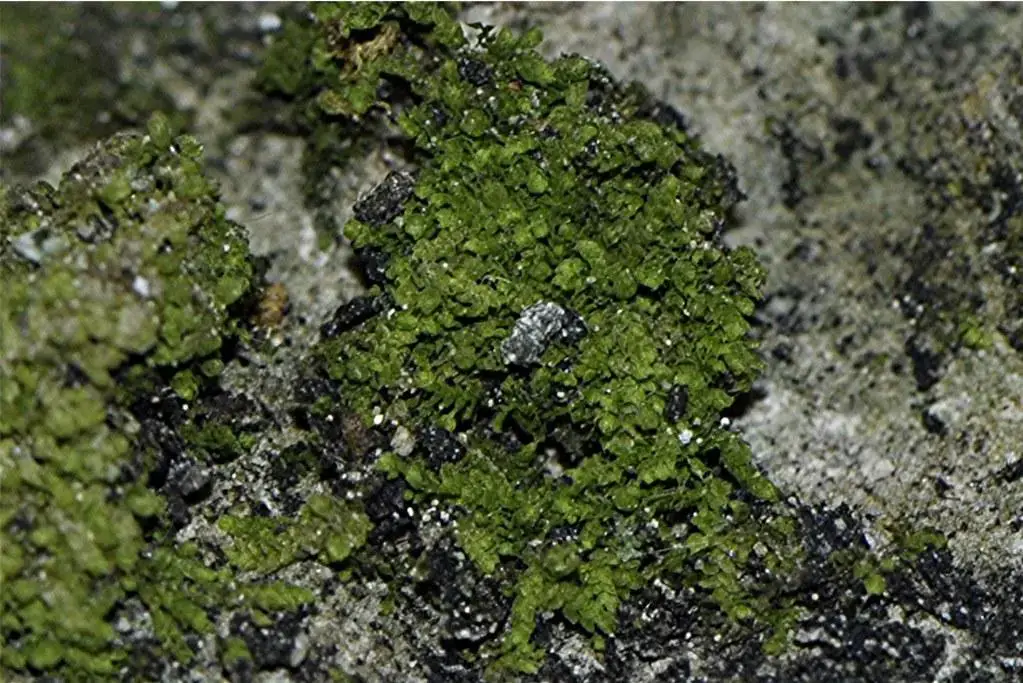
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Cololejeunea calcarea (Lib.) Schiffn. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Lejeuneaceae family. This tiny, unassuming plant has captured the hearts of enthusiasts worldwide with its unique characteristics and ecological significance. Join us as we delve into the fascinating realm of this

22228029736_3846360867_b.jpg from: https://www.flickr.com/photos/12639178@N07/22228029736/
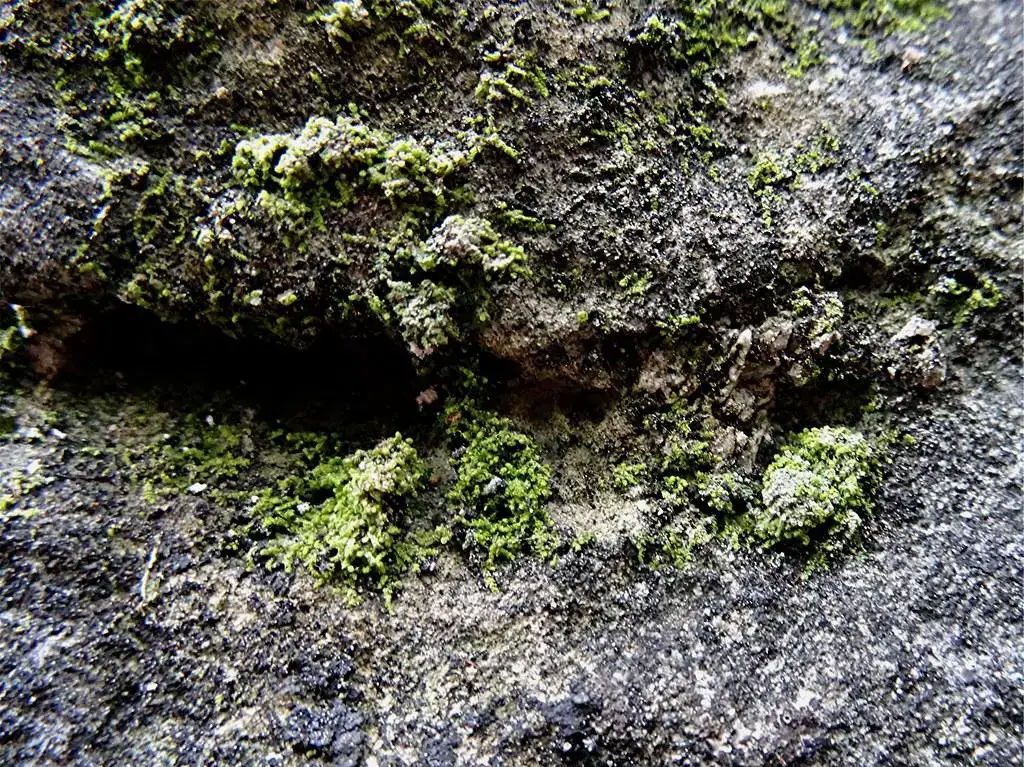
moss, exploring its morphology, global distribution, and the vital roles it plays in nature.
Background
Before we dive into the intricacies of Cololejeunea calcarea, it’s essential to understand its place within the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, dating back to the Paleozoic era, and have adapted to thrive in a wide range of habitats.

302419.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/6696
Main Content
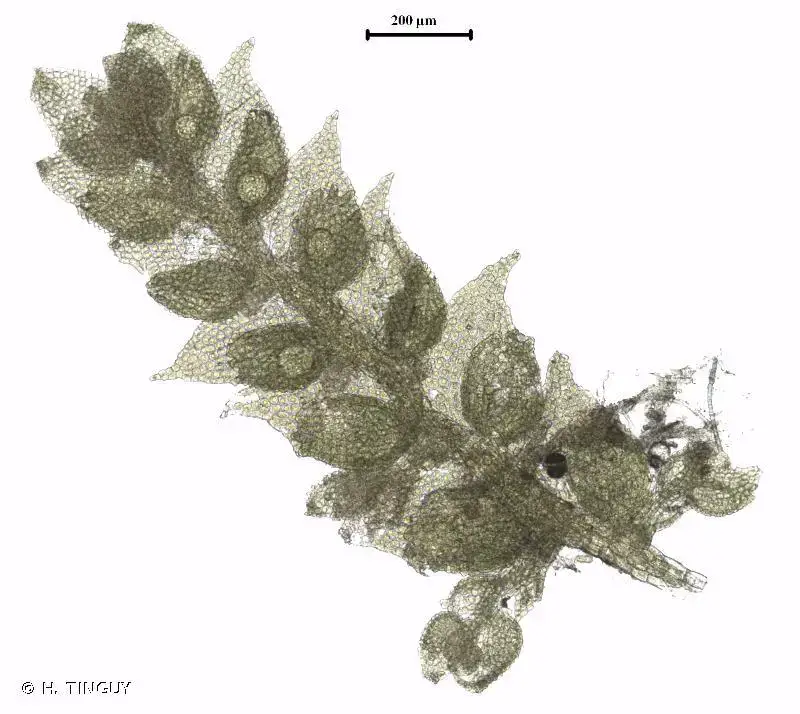
Morphology and Identification
2019-01-14-08-27-06-800×600.jpg from: https://www.britishbryologicalsociety.org.uk/learning/species-finder/cololejeunea-calcarea/
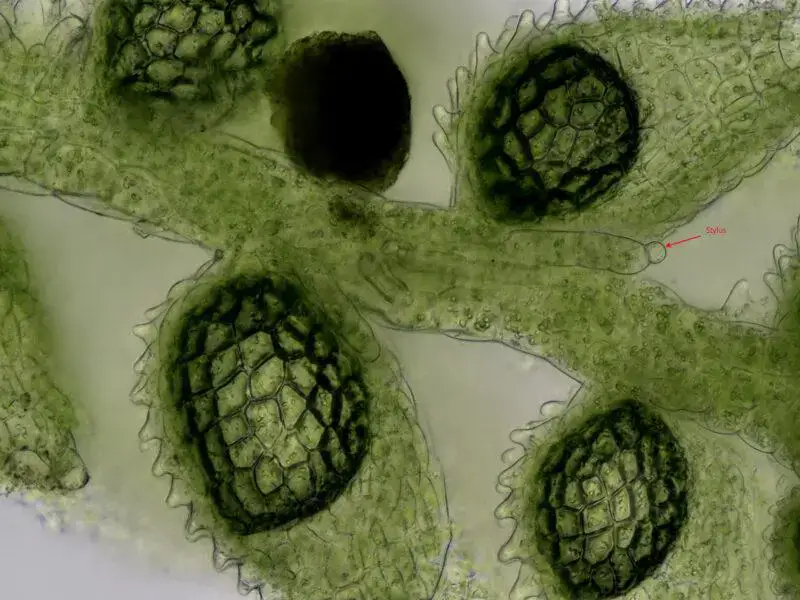
Cololejeunea calcarea is a small, creeping moss that forms dense mats or cushions on calcareous substrates. Its delicate, green to yellowish-green leaves are arranged in two rows, giving it a distinctive feathery appearance. One of the most striking features of this moss is its ability to produce specialized reproductive structures called
![Cololeujeunea+calcarea+(5)+[800x600].JPG](/img/Cololeujeuneacalcarea5800x600.JPG-2.jpg)
Cololeujeunea+calcarea+(5)+[800×600].JPG from: https://fred-mousses.blogspot.com/2010/08/cololejeunea-calcarea.html
gemmae, which aid in its propagation and dispersal.
Global Distribution and Habitat
This remarkable moss has a widespread distribution, found on various continents, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and North America. It thrives in calcareous environments, such as limestone outcrops, cliffs, and rocky areas, where it can obtain the necessary calcium for its growth and development.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive size, Cololejeunea calcarea plays a vital role in its ecosystem. It contributes to soil formation and nutrient cycling, acting as a pioneer species in the colonization of bare rock surfaces. Additionally, this moss serves as a microhabitat for numerous microscopic organisms, including tardigrades, rotifers, and nematodes, further enhancing biodiversity.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Cololejeunea calcarea is its ability to withstand desiccation. During periods of drought, it can enter a state of dormancy, reviving once moisture becomes available again. This resilience allows it to thrive in environments where water availability can be unpredictable.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Appalachian Mountains of North America, researchers discovered a thriving population of
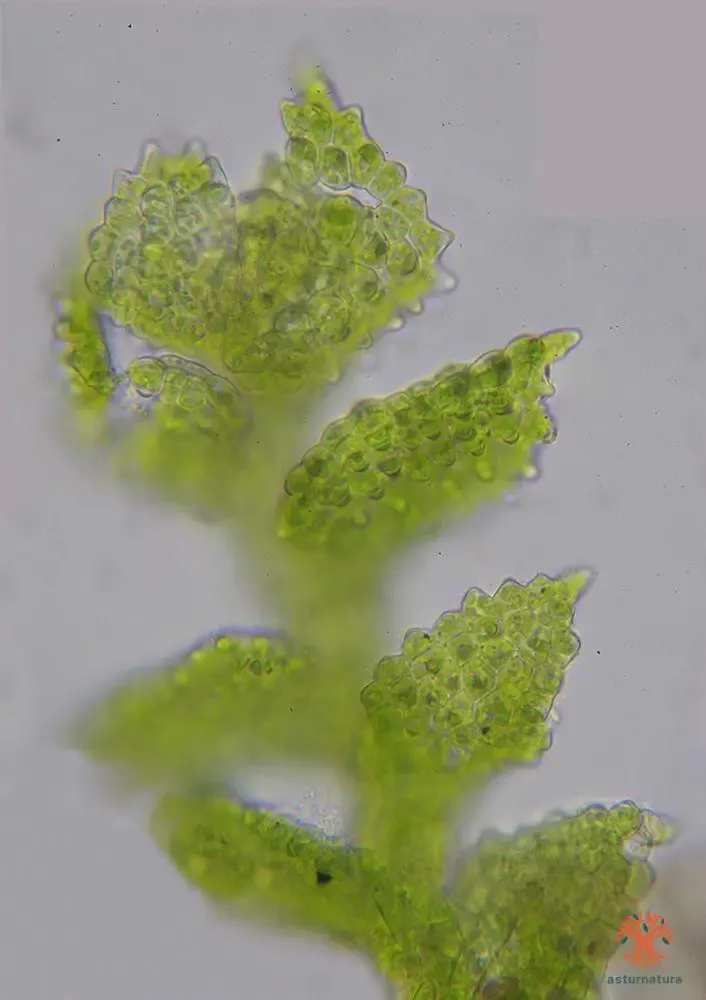

c788b0a7204fba858a9d9fd4838cdb93.jpg from: https://www.asturnatura.com/fotografia/flora/cololejeunea-calcarea-2/31032.html

120px-Cololejeunea_calcarea_(b%2C_144641-474819)_4087.JPG from: https://vi.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cololejeunea_calcarea
Cololejeunea calcarea on a limestone outcrop. This finding not only expanded the known distribution of the species but also highlighted its importance as an indicator of habitat quality and environmental conditions.
Technical Table

120px-Cololejeunea_calcarea_(b%2C_144641-474819)_4082.JPG from: https://vi.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tập_tin:Cololejeunea_calcarea_(b,_144641-474819)_4082.JPG

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/1124111-Campylophyllopsis-calcarea

651134.jpg from: https://waarnemingen.be/species/17715/
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Marchantiophyta |
| Class | Jungermanniopsida |
| Order | Porellales |
| Family | Lejeuneaceae |
| Genus | Cololejeunea |
| Species | Cololejeunea calcarea (Lib.) Schiffn. |
| Common Name | Cololejeunea |
| Growth Form | Creeping, mat-forming |
| Leaf Arrangement | Two rows, feathery appearance |
| Reproductive Structures | Gemmae |
| Habitat | Calcareous substrates, limestone outcrops |
Conclusion
The Cololejeunea calcarea (Lib.) Schiffn. moss, a member of the Lejeuneaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its intricate morphology, global distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject for enthusiasts and researchers alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the diversity of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these often-overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems?