Unveiling Dicranum Spadiceum: A Remarkable Moss with Unique Traits and Global Presence
Affiliate Disclaimer: As an affiliate, we may earn a small commission when you make a purchase from any of the links on this page at no additional cost to you!
330947.jpg from: https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/434128
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, the Dicranum spadiceum J.E.Zetterst. moss stands out as a remarkable member of the Dicranaceae family. Often referred to simply as Dicranum, this unassuming yet fascinating plant has captured the hearts of moss enthusiasts worldwide. Let’s delve into the intriguing realm of this moss, exploring its unique characteristics, global distribution, and ecological significance.
Background
Before we dive into the specifics of Dicranum spadiceum, it’s essential to understand the broader context of bryophytes. These non-vascular plants, which include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are often overlooked but play a crucial role in various ecosystems. They are among the oldest land plants on Earth, with a rich evolutionary history dating back millions of years.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Dicranum spadiceum is a moss that belongs to the Bryopsida class, commonly known as the true mosses. It is characterized by its distinctive reddish-brown color, which can range from deep chestnut to a rich mahogany hue. The leaves of this moss are lanceolate (lance-shaped) and strongly curved, giving it a unique and easily recognizable appearance.
One of the most striking features of Dicranum spadiceum is its seta, the slender stalk that supports the sporophyte (spore-bearing structure). This seta is often reddish-brown in color, adding to the overall aesthetic appeal of the moss. The sporophyte itself is a capsule

medium.jpeg from: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/161870-Dicranum-spadiceum
that contains the spores, which are essential for the reproduction and dispersal of the species.
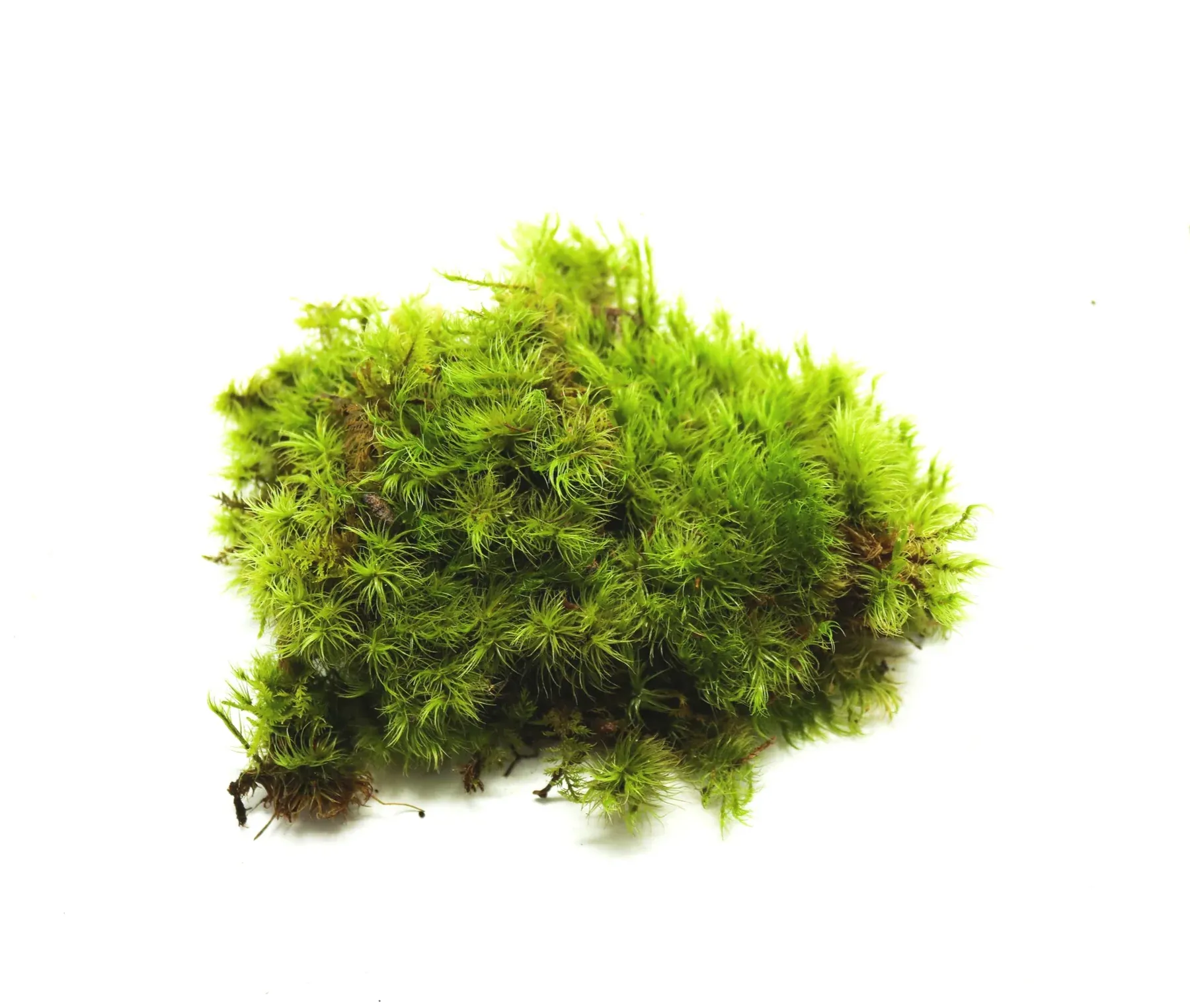
Global Distribution and Habitat
Dicranum spadiceum is widely distributed across various regions of the world, including Europe, North America, and parts of Asia. It thrives in a variety of habitats, from

IMG_2996_1800x1525.jpg from: https://frogdaddy.net/products/feather-moss-hypnum-sp
coniferous and deciduous forests to rocky outcrops and shaded areas. This moss is particularly fond of acidic and nutrient-poor soils, making it a common sight in areas with these conditions.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its small size, Dicranum spadiceum plays a significant role in its ecosystem. As a pioneer species, it is often one of the first plants to colonize disturbed or newly exposed areas, helping to stabilize the soil and pave the way for other plant species to establish themselves.
This moss is also an important contributor to the

a5e02bf36e7b8ceb316ea68c50ba0f0b.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/dicranum-scoparium–777152479423469749/
nutrient cycle

DSC_0017_34bc112e-c36f-49cd-8765-31d0f4fb6b76.JPG from: https://www.mountainmoss.com/products/dicranum
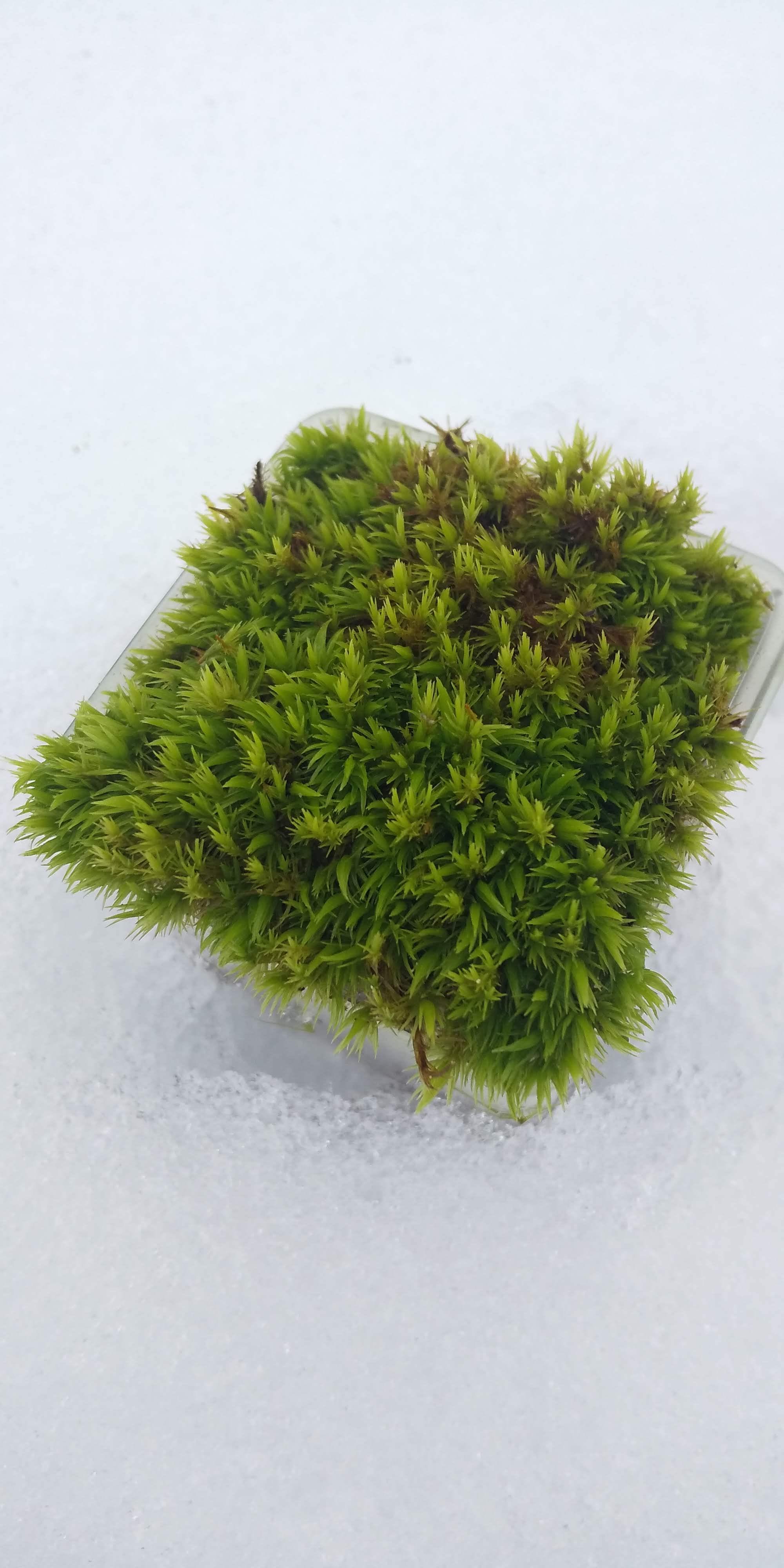

541520613cd1e926834636e074271eb3.jpg from: https://mossymossyjp.thebase.in/items/38315411
, as it helps to break down organic matter and release essential nutrients back into the soil. Additionally, Dicranum spadiceum provides a microhabitat for various invertebrates, such as mites and springtails, further enhancing the biodiversity of its environment.
One of the remarkable adaptations of Dicranum spadiceum is its ability to tolerate desiccation. During periods of drought, the
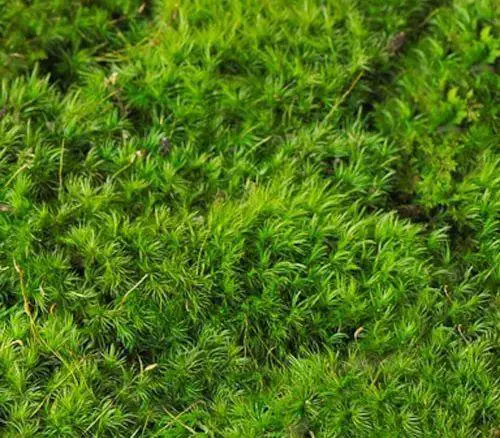

fefe6b2f81085fe0cbab5bdc41b037db.jpg from: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/262123640797969421/
moss can enter a state of dormancy, effectively shutting down its metabolic processes until favorable conditions return. This remarkable resilience allows it to thrive in environments where water availability can be unpredictable.
Case Studies/Examples
In a recent study conducted in the Białowieża Forest in Poland, researchers found that Dicranum spadiceum played a crucial role in the regeneration of oak and pine forests after disturbances. The moss acted as a nursery for tree seedlings, providing them with a suitable microclimate and protecting them from desiccation and extreme temperatures.
Another interesting example comes from the Pacific Northwest region of North America, where Dicranum spadiceum is commonly found in old-growth forests. Here, the moss forms a thick and lush carpet, contributing to the overall biodiversity and moisture retention of these ecosystems.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Dicranum spadiceum J.E.Zetterst. |
| Family | Dicranaceae |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Color | Reddish-brown |
| Leaf Shape | Lanceolate (lance-shaped) |
| Seta Color | Reddish-brown |
| Sporophyte | Capsule |
| Habitat | Coniferous and deciduous forests, rocky outcrops, shaded areas |
| Soil Preference | Acidic and nutrient-poor |
| Ecological Roles | Pioneer species, nutrient cycling, microhabitat provision |
| Adaptations | Desiccation tolerance, dormancy |
Conclusion
The Dicranum spadiceum J.E.Zetterst. moss, a member of the Dicranaceae family, is a true marvel of nature. Its striking appearance, global distribution, and ecological significance make it a fascinating subject for moss enthusiasts and naturalists alike. As we continue to explore and appreciate the intricate world of bryophytes, let us ponder this thought-provoking question: How can we better protect and conserve these often-overlooked yet vital components of our ecosystems?
