
3210-l-4.jpg from: https://www.wildflowers.co.il/hebrew/picture.asp?ID=18679
Introduction
In the vast and captivating world of bryophytes, one particular moss species stands out for its unique characteristics and ecological significance – the
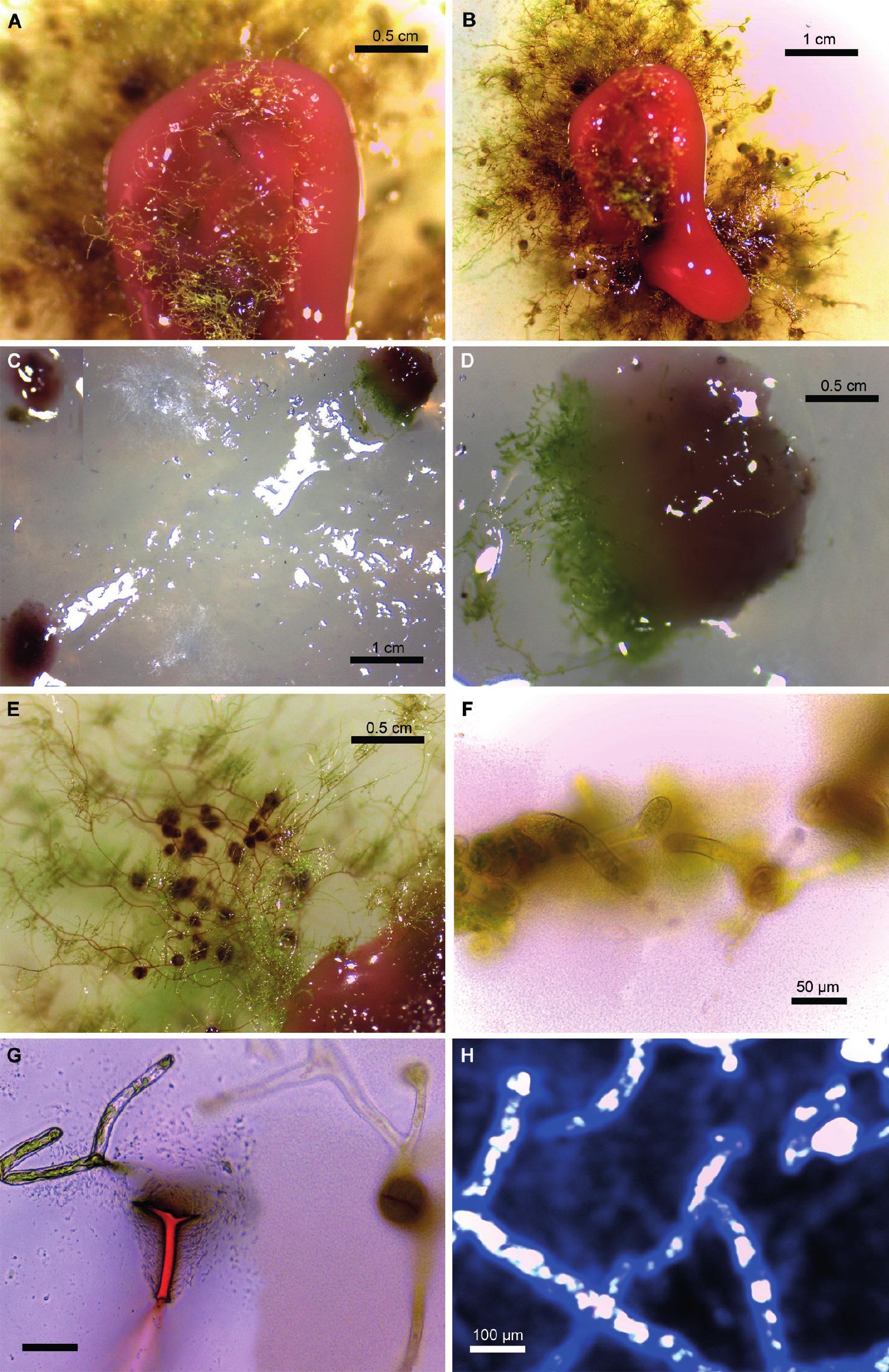
img-z4-1_117.jpg from: https://bioone.org/journals/annales-botanici-fennici/volume-59/issue-1/085.059.0118/Endophytic-Methylobacterium-in-Tissue-Culture-of-the-Moss-Didymodon-tectorum/10.5735/085.059.0118.full
Didymodon montevidensis Broth., commonly known as Didymodon. This unassuming yet remarkable member of the Pottiaceae family has captured the interest of enthusiasts and researchers alike, offering a fascinating glimpse into the intricate tapestry of nature’s diversity.
Background
Before delving into the intricacies of Didymodon montevidensis, it’s essential to understand the broader context in which it thrives. Bryophytes, a group encompassing mosses, liverworts, and hornworts, are among the oldest and most resilient plant lineages on Earth. These diminutive yet mighty organisms have played a crucial role in shaping our planet’s ecosystems, paving the way for the evolution of more complex plant life.
Main Content
Morphology and Identification
Didymodon montevidensis is a small, acrocarpous moss that forms dense, cushion-like tufts or mats. Its slender stems are adorned with delicate, lance-shaped leaves that exhibit a distinctive twist when dry, a characteristic that aids in water retention. The leaves themselves are composed of intricate, elongated cells, lending a unique texture to the plant’s overall appearance.
One of the most striking features of Didymodon montevidensis is its remarkable ability to reproduce both sexually and asexually. During the sexual reproductive cycle, the moss produces distinctive capsules atop slender setae, which facilitate the dispersal of spores. Asexually, it employs a clever strategy known as gemmae – specialized reproductive structures that allow the moss to propagate and colonize new areas with remarkable efficiency.
Global Distribution and Habitat
Didymodon montevidensis is a cosmopolitan species, found across various regions of the world, including North and South America, Europe, Asia, and Africa. Its ability to thrive in a wide range of habitats is a testament to its adaptability and resilience. From rocky outcrops and soil banks to tree bark and even urban environments, this moss has proven its versatility, colonizing diverse substrates and microhabitats.
Ecological Roles and Adaptations
Despite its diminutive stature, Didymodon montevidensis plays a vital role in the ecosystems it inhabits. As a pioneer species, it contributes to soil formation and stabilization, paving the way for the establishment of more complex plant communities. Additionally, its dense mats provide shelter and moisture retention, creating microhabitats for a myriad of microscopic organisms, including tardigrades, rotifers, and nematodes.
One of the most remarkable adaptations of Didymodon montevidensis is its ability to withstand extreme environmental conditions. This moss can enter a state of dormancy, known as desiccation tolerance, during periods of drought or unfavorable conditions. In this state, the moss can effectively “pause” its metabolic processes, only to revive and resume growth when conditions become favorable again – a remarkable feat of resilience.
Case Studies/Examples
Didymodon montevidensis has been the subject of numerous scientific studies, shedding light on its ecological significance and potential applications. For instance, researchers have explored its role in urban environments, where it contributes to the biodiversity of cities and helps mitigate air pollution. Additionally, its ability to colonize disturbed areas has made it a valuable tool in ecological restoration projects, aiding in the recovery of degraded habitats.
Technical Table
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Bryophyta |
| Class | Bryopsida |
| Order | Pottiaceae |
| Genus | Didymodon |
| Species | montevidensis |
| Growth Form | Acrocarpous, cushion-like tufts or mats |
| Leaf Shape | Lance-shaped, twisted when dry |
| Reproduction | Sexual (capsules) and asexual (gemmae) |
| Habitat | Rocky outcrops, soil banks, tree bark, urban environments |
| Distribution | Cosmopolitan (found worldwide) |
Conclusion
The Didymodon montevidensis Broth., or simply Didymodon, is a remarkable moss species that exemplifies the resilience and adaptability of bryophytes. From its intricate morphology and diverse reproductive strategies to its ecological significance and potential applications, this unassuming plant offers a wealth of knowledge and inspiration.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of the natural world, the Didymodon montevidensis serves as a reminder of the intricate tapestry of life that surrounds us, inviting us to ponder: What other hidden gems await discovery in the vast and captivating realm of bryophytes?